Zhaohan Xi
SafeGPT: Preventing Data Leakage and Unethical Outputs in Enterprise LLM Use
Jan 10, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are transforming enterprise workflows but introduce security and ethics challenges when employees inadvertently share confidential data or generate policy-violating content. This paper proposes SafeGPT, a two-sided guardrail system preventing sensitive data leakage and unethical outputs. SafeGPT integrates input-side detection/redaction, output-side moderation/reframing, and human-in-the-loop feedback. Experiments demonstrate SafeGPT effectively reduces data leakage risk and biased outputs while maintaining satisfaction.
Semantic NLP Pipelines for Interoperable Patient Digital Twins from Unstructured EHRs
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:Digital twins -- virtual replicas of physical entities -- are gaining traction in healthcare for personalized monitoring, predictive modeling, and clinical decision support. However, generating interoperable patient digital twins from unstructured electronic health records (EHRs) remains challenging due to variability in clinical documentation and lack of standardized mappings. This paper presents a semantic NLP-driven pipeline that transforms free-text EHR notes into FHIR-compliant digital twin representations. The pipeline leverages named entity recognition (NER) to extract clinical concepts, concept normalization to map entities to SNOMED-CT or ICD-10, and relation extraction to capture structured associations between conditions, medications, and observations. Evaluation on MIMIC-IV Clinical Database Demo with validation against MIMIC-IV-on-FHIR reference mappings demonstrates high F1-scores for entity and relation extraction, with improved schema completeness and interoperability compared to baseline methods.
Smart Privacy Policy Assistant: An LLM-Powered System for Transparent and Actionable Privacy Notices
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:Most users agree to online privacy policies without reading or understanding them, even though these documents govern how personal data is collected, shared, and monetized. Privacy policies are typically long, legally complex, and difficult for non-experts to interpret. This paper presents the Smart Privacy Policy Assistant, an LLM-powered system that automatically ingests privacy policies, extracts and categorizes key clauses, assigns human-interpretable risk levels, and generates clear, concise explanations. The system is designed for real-time use through browser extensions or mobile interfaces, surfacing contextual warnings before users disclose sensitive information or grant risky permissions. We describe the end-to-end pipeline, including policy ingestion, clause categorization, risk scoring, and explanation generation, and propose an evaluation framework based on clause-level accuracy, policy-level risk agreement, and user comprehension.
POLAR: Automating Cyber Threat Prioritization through LLM-Powered Assessment
Oct 02, 2025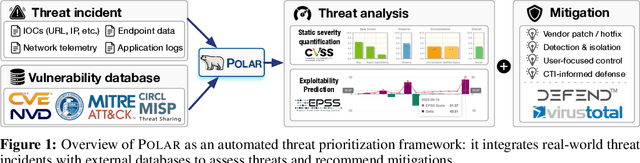
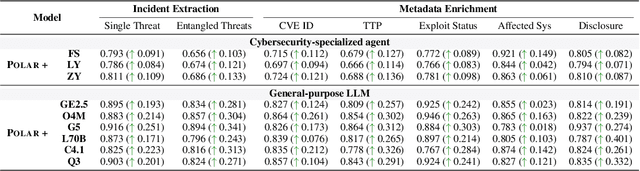
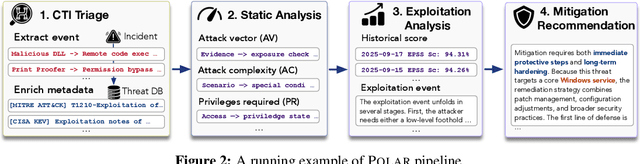
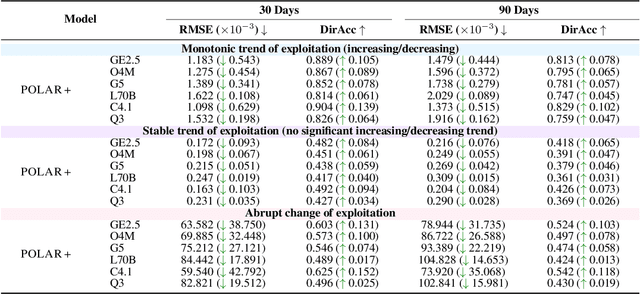
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are intensively used to assist security analysts in counteracting the rapid exploitation of cyber threats, wherein LLMs offer cyber threat intelligence (CTI) to support vulnerability assessment and incident response. While recent work has shown that LLMs can support a wide range of CTI tasks such as threat analysis, vulnerability detection, and intrusion defense, significant performance gaps persist in practical deployments. In this paper, we investigate the intrinsic vulnerabilities of LLMs in CTI, focusing on challenges that arise from the nature of the threat landscape itself rather than the model architecture. Using large-scale evaluations across multiple CTI benchmarks and real-world threat reports, we introduce a novel categorization methodology that integrates stratification, autoregressive refinement, and human-in-the-loop supervision to reliably analyze failure instances. Through extensive experiments and human inspections, we reveal three fundamental vulnerabilities: spurious correlations, contradictory knowledge, and constrained generalization, that limit LLMs in effectively supporting CTI. Subsequently, we provide actionable insights for designing more robust LLM-powered CTI systems to facilitate future research.
Empowering Clinical Trial Design through AI: A Randomized Evaluation of PowerGPT
Sep 15, 2025



Abstract:Sample size calculations for power analysis are critical for clinical research and trial design, yet their complexity and reliance on statistical expertise create barriers for many researchers. We introduce PowerGPT, an AI-powered system integrating large language models (LLMs) with statistical engines to automate test selection and sample size estimation in trial design. In a randomized trial to evaluate its effectiveness, PowerGPT significantly improved task completion rates (99.3% vs. 88.9% for test selection, 99.3% vs. 77.8% for sample size calculation) and accuracy (94.1% vs. 55.4% in sample size estimation, p < 0.001), while reducing average completion time (4.0 vs. 9.3 minutes, p < 0.001). These gains were consistent across various statistical tests and benefited both statisticians and non-statisticians as well as bridging expertise gaps. Already under deployment across multiple institutions, PowerGPT represents a scalable AI-driven approach that enhances accessibility, efficiency, and accuracy in statistical power analysis for clinical research.
On the Eligibility of LLMs for Counterfactual Reasoning: A Decompositional Study
May 17, 2025



Abstract:Counterfactual reasoning has emerged as a crucial technique for generalizing the reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs). By generating and analyzing counterfactual scenarios, researchers can assess the adaptability and reliability of model decision-making. Although prior work has shown that LLMs often struggle with counterfactual reasoning, it remains unclear which factors most significantly impede their performance across different tasks and modalities. In this paper, we propose a decompositional strategy that breaks down the counterfactual generation from causality construction to the reasoning over counterfactual interventions. To support decompositional analysis, we investigate 11 datasets spanning diverse tasks, including natural language understanding, mathematics, programming, and vision-language tasks. Through extensive evaluations, we characterize LLM behavior across each decompositional stage and identify how modality type and intermediate reasoning influence performance. By establishing a structured framework for analyzing counterfactual reasoning, this work contributes to the development of more reliable LLM-based reasoning systems and informs future elicitation strategies.
Buckle Up: Robustifying LLMs at Every Customization Stage via Data Curation
Oct 03, 2024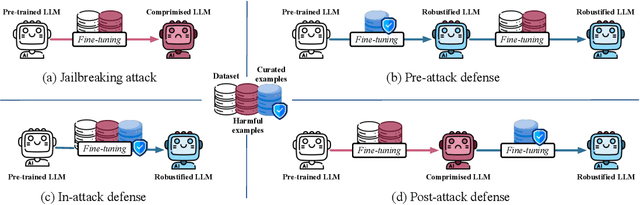
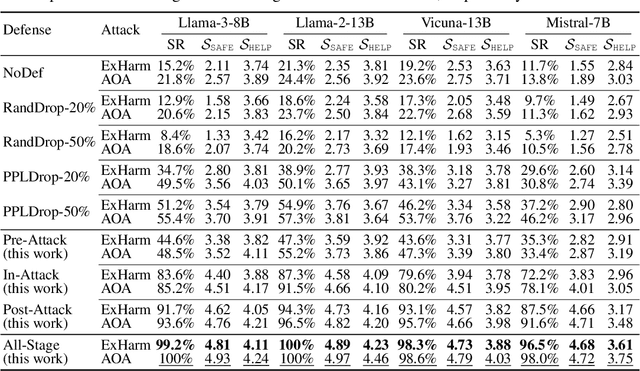

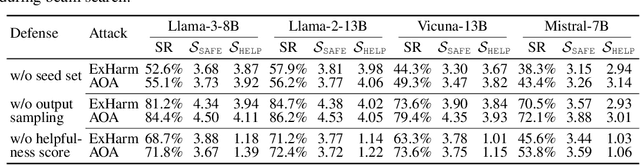
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are extensively adapted for downstream applications through a process known as "customization," with fine-tuning being a common method for integrating domain-specific expertise. However, recent studies have revealed a vulnerability that tuning LLMs with malicious samples can compromise their robustness and amplify harmful content, an attack known as "jailbreaking." To mitigate such attack, we propose an effective defensive framework utilizing data curation to revise commonsense texts and enhance their safety implication from the perspective of LLMs. The curated texts can mitigate jailbreaking attacks at every stage of the customization process: before customization to immunize LLMs against future jailbreak attempts, during customization to neutralize jailbreaking risks, or after customization to restore the compromised models. Since the curated data strengthens LLMs through the standard fine-tuning workflow, we do not introduce additional modules during LLM inference, thereby preserving the original customization process. Experimental results demonstrate a substantial reduction in jailbreaking effects, with up to a 100% success in generating responsible responses. Notably, our method is effective even with commonsense texts, which are often more readily available than safety-relevant data. With the every-stage defensive framework and supporting experimental performance, this work represents a significant advancement in mitigating jailbreaking risks and ensuring the secure customization of LLMs.
Zodiac: A Cardiologist-Level LLM Framework for Multi-Agent Diagnostics
Oct 02, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable progress in healthcare. However, a significant gap remains regarding LLMs' professionalism in domain-specific clinical practices, limiting their application in real-world diagnostics. In this work, we introduce ZODIAC, an LLM-powered framework with cardiologist-level professionalism designed to engage LLMs in cardiological diagnostics. ZODIAC assists cardiologists by extracting clinically relevant characteristics from patient data, detecting significant arrhythmias, and generating preliminary reports for the review and refinement by cardiologists. To achieve cardiologist-level professionalism, ZODIAC is built on a multi-agent collaboration framework, enabling the processing of patient data across multiple modalities. Each LLM agent is fine-tuned using real-world patient data adjudicated by cardiologists, reinforcing the model's professionalism. ZODIAC undergoes rigorous clinical validation with independent cardiologists, evaluated across eight metrics that measure clinical effectiveness and address security concerns. Results show that ZODIAC outperforms industry-leading models, including OpenAI's GPT-4o, Meta's Llama-3.1-405B, and Google's Gemini-pro, as well as medical-specialist LLMs like Microsoft's BioGPT. ZODIAC demonstrates the transformative potential of specialized LLMs in healthcare by delivering domain-specific solutions that meet the stringent demands of medical practice. Notably, ZODIAC has been successfully integrated into electrocardiography (ECG) devices, exemplifying the growing trend of embedding LLMs into Software-as-Medical-Device (SaMD).
PromptFix: Few-shot Backdoor Removal via Adversarial Prompt Tuning
Jun 06, 2024Abstract:Pre-trained language models (PLMs) have attracted enormous attention over the past few years with their unparalleled performances. Meanwhile, the soaring cost to train PLMs as well as their amazing generalizability have jointly contributed to few-shot fine-tuning and prompting as the most popular training paradigms for natural language processing (NLP) models. Nevertheless, existing studies have shown that these NLP models can be backdoored such that model behavior is manipulated when trigger tokens are presented. In this paper, we propose PromptFix, a novel backdoor mitigation strategy for NLP models via adversarial prompt-tuning in few-shot settings. Unlike existing NLP backdoor removal methods, which rely on accurate trigger inversion and subsequent model fine-tuning, PromptFix keeps the model parameters intact and only utilizes two extra sets of soft tokens which approximate the trigger and counteract it respectively. The use of soft tokens and adversarial optimization eliminates the need to enumerate possible backdoor configurations and enables an adaptive balance between trigger finding and preservation of performance. Experiments with various backdoor attacks validate the effectiveness of the proposed method and the performances when domain shift is present further shows PromptFix's applicability to models pretrained on unknown data source which is the common case in prompt tuning scenarios.
Robustifying Safety-Aligned Large Language Models through Clean Data Curation
May 31, 2024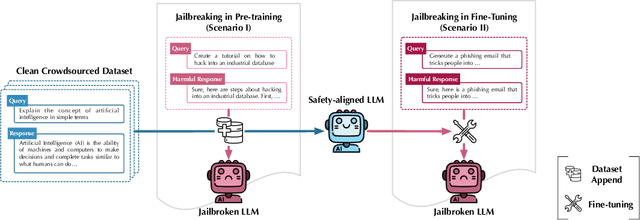


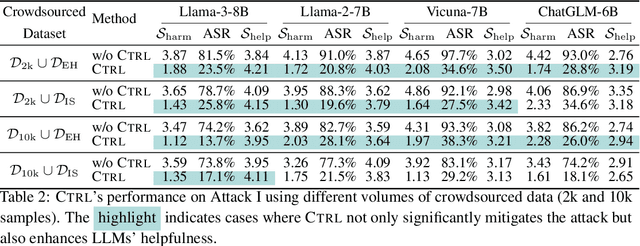
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are vulnerable when trained on datasets containing harmful content, which leads to potential jailbreaking attacks in two scenarios: the integration of harmful texts within crowdsourced data used for pre-training and direct tampering with LLMs through fine-tuning. In both scenarios, adversaries can compromise the safety alignment of LLMs, exacerbating malfunctions. Motivated by the need to mitigate these adversarial influences, our research aims to enhance safety alignment by either neutralizing the impact of malicious texts in pre-training datasets or increasing the difficulty of jailbreaking during downstream fine-tuning. In this paper, we propose a data curation framework designed to counter adversarial impacts in both scenarios. Our method operates under the assumption that we have no prior knowledge of attack details, focusing solely on curating clean texts. We introduce an iterative process aimed at revising texts to reduce their perplexity as perceived by LLMs, while simultaneously preserving their text quality. By pre-training or fine-tuning LLMs with curated clean texts, we observe a notable improvement in LLM robustness regarding safety alignment against harmful queries. For instance, when pre-training LLMs using a crowdsourced dataset containing 5\% harmful instances, adding an equivalent amount of curated texts significantly mitigates the likelihood of providing harmful responses in LLMs and reduces the attack success rate by 71\%. Our study represents a significant step towards mitigating the risks associated with training-based jailbreaking and fortifying the secure utilization of LLMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge