Yufei Feng
OneTrans: Unified Feature Interaction and Sequence Modeling with One Transformer in Industrial Recommender
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:In recommendation systems, scaling up feature-interaction modules (e.g., Wukong, RankMixer) or user-behavior sequence modules (e.g., LONGER) has achieved notable success. However, these efforts typically proceed on separate tracks, which not only hinders bidirectional information exchange but also prevents unified optimization and scaling. In this paper, we propose OneTrans, a unified Transformer backbone that simultaneously performs user-behavior sequence modeling and feature interaction. OneTrans employs a unified tokenizer to convert both sequential and non-sequential attributes into a single token sequence. The stacked OneTrans blocks share parameters across similar sequential tokens while assigning token-specific parameters to non-sequential tokens. Through causal attention and cross-request KV caching, OneTrans enables precomputation and caching of intermediate representations, significantly reducing computational costs during both training and inference. Experimental results on industrial-scale datasets demonstrate that OneTrans scales efficiently with increasing parameters, consistently outperforms strong baselines, and yields a 5.68% lift in per-user GMV in online A/B tests.
Graph Disentangle Causal Model: Enhancing Causal Inference in Networked Observational Data
Dec 05, 2024



Abstract:Estimating individual treatment effects (ITE) from observational data is a critical task across various domains. However, many existing works on ITE estimation overlook the influence of hidden confounders, which remain unobserved at the individual unit level. To address this limitation, researchers have utilized graph neural networks to aggregate neighbors' features to capture the hidden confounders and mitigate confounding bias by minimizing the discrepancy of confounder representations between the treated and control groups. Despite the success of these approaches, practical scenarios often treat all features as confounders and involve substantial differences in feature distributions between the treated and control groups. Confusing the adjustment and confounder and enforcing strict balance on the confounder representations could potentially undermine the effectiveness of outcome prediction. To mitigate this issue, we propose a novel framework called the \textit{Graph Disentangle Causal model} (GDC) to conduct ITE estimation in the network setting. GDC utilizes a causal disentangle module to separate unit features into adjustment and confounder representations. Then we design a graph aggregation module consisting of three distinct graph aggregators to obtain adjustment, confounder, and counterfactual confounder representations. Finally, a causal constraint module is employed to enforce the disentangled representations as true causal factors. The effectiveness of our proposed method is demonstrated by conducting comprehensive experiments on two networked datasets.
Neuro-symbolic Natural Logic with Introspective Revision for Natural Language Inference
Mar 09, 2022
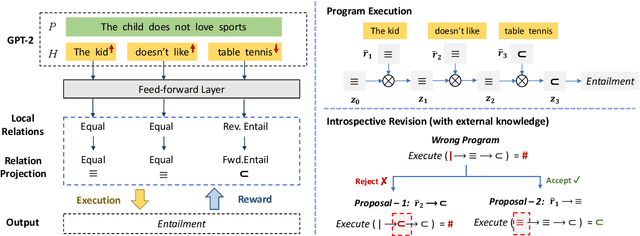

Abstract:We introduce a neuro-symbolic natural logic framework based on reinforcement learning with introspective revision. The model samples and rewards specific reasoning paths through policy gradient, in which the introspective revision algorithm modifies intermediate symbolic reasoning steps to discover reward-earning operations as well as leverages external knowledge to alleviate spurious reasoning and training inefficiency. The framework is supported by properly designed local relation models to avoid input entangling, which helps ensure the interpretability of the proof paths. The proposed model has built-in interpretability and shows superior capability in monotonicity inference, systematic generalization, and interpretability, compared to previous models on the existing datasets.
GRN: Generative Rerank Network for Context-wise Recommendation
Apr 07, 2021



Abstract:Reranking is attracting incremental attention in the recommender systems, which rearranges the input ranking list into the final rank-ing list to better meet user demands. Most existing methods greedily rerank candidates through the rating scores from point-wise or list-wise models. Despite effectiveness, neglecting the mutual influence between each item and its contexts in the final ranking list often makes the greedy strategy based reranking methods sub-optimal. In this work, we propose a new context-wise reranking framework named Generative Rerank Network (GRN). Specifically, we first design the evaluator, which applies Bi-LSTM and self-attention mechanism to model the contextual information in the labeled final ranking list and predict the interaction probability of each item more precisely. Afterwards, we elaborate on the generator, equipped with GRU, attention mechanism and pointer network to select the item from the input ranking list step by step. Finally, we apply cross-entropy loss to train the evaluator and, subsequently, policy gradient to optimize the generator under the guidance of the evaluator. Empirical results show that GRN consistently and significantly outperforms state-of-the-art point-wise and list-wise methods. Moreover, GRN has achieved a performance improvement of 5.2% on PV and 6.1% on IPV metric after the successful deployment in one popular recommendation scenario of Taobao application.
Complementary Evidence Identification in Open-Domain Question Answering
Apr 05, 2021


Abstract:This paper proposes a new problem of complementary evidence identification for open-domain question answering (QA). The problem aims to efficiently find a small set of passages that covers full evidence from multiple aspects as to answer a complex question. To this end, we proposes a method that learns vector representations of passages and models the sufficiency and diversity within the selected set, in addition to the relevance between the question and passages. Our experiments demonstrate that our method considers the dependence within the supporting evidence and significantly improves the accuracy of complementary evidence selection in QA domain.
Revisit Recommender System in the Permutation Prospective
Feb 24, 2021



Abstract:Recommender systems (RS) work effective at alleviating information overload and matching user interests in various web-scale applications. Most RS retrieve the user's favorite candidates and then rank them by the rating scores in the greedy manner. In the permutation prospective, however, current RS come to reveal the following two limitations: 1) They neglect addressing the permutation-variant influence within the recommended results; 2) Permutation consideration extends the latent solution space exponentially, and current RS lack the ability to evaluate the permutations. Both drive RS away from the permutation-optimal recommended results and better user experience. To approximate the permutation-optimal recommended results effectively and efficiently, we propose a novel permutation-wise framework PRS in the re-ranking stage of RS, which consists of Permutation-Matching (PMatch) and Permutation-Ranking (PRank) stages successively. Specifically, the PMatch stage is designed to obtain the candidate list set, where we propose the FPSA algorithm to generate multiple candidate lists via the permutation-wise and goal-oriented beam search algorithm. Afterwards, for the candidate list set, the PRank stage provides a unified permutation-wise ranking criterion named LR metric, which is calculated by the rating scores of elaborately designed permutation-wise model DPWN. Finally, the list with the highest LR score is recommended to the user. Empirical results show that PRS consistently and significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods. Moreover, PRS has achieved a performance improvement of 11.0% on PV metric and 8.7% on IPV metric after the successful deployment in one popular recommendation scenario of Taobao application.
Learning to Retrieve Entity-Aware Knowledge and Generate Responses with Copy Mechanism for Task-Oriented Dialogue Systems
Dec 22, 2020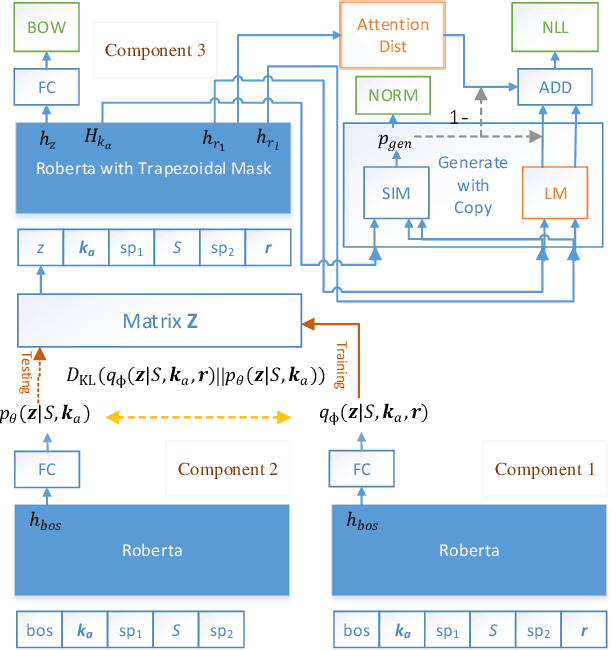
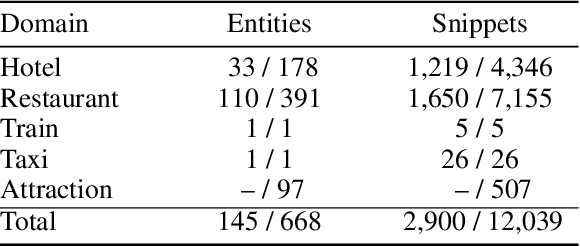

Abstract:Task-oriented conversational modeling with unstructured knowledge access, as track 1 of the 9th Dialogue System Technology Challenges (DSTC 9), requests to build a system to generate response given dialogue history and knowledge access. This challenge can be separated into three subtasks, (1) knowledge-seeking turn detection, (2) knowledge selection, and (3) knowledge-grounded response generation. We use pre-trained language models, ELECTRA and RoBERTa, as our base encoder for different subtasks. For subtask 1 and 2, the coarse-grained information like domain and entity are used to enhance knowledge usage. For subtask 3, we use a latent variable to encode dialog history and selected knowledge better and generate responses combined with copy mechanism. Meanwhile, some useful post-processing strategies are performed on the model's final output to make further knowledge usage in the generation task. As shown in released evaluation results, our proposed system ranks second under objective metrics and ranks fourth under human metrics.
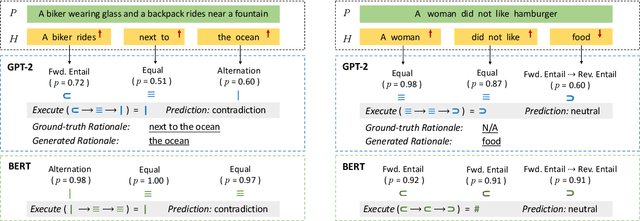
Exploring End-to-End Differentiable Natural Logic Modeling
Nov 08, 2020
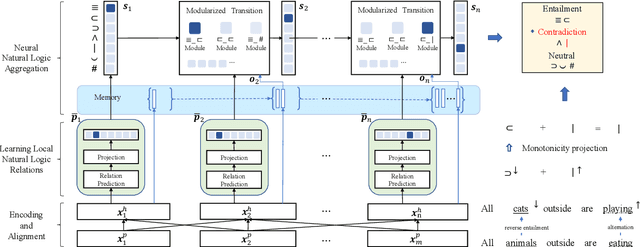
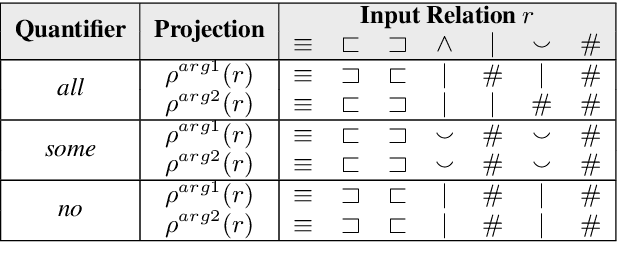
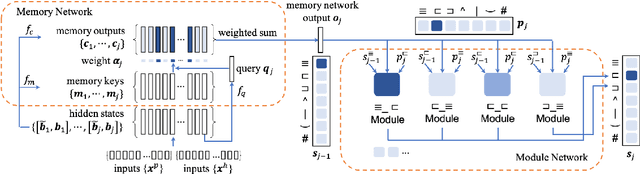
Abstract:We explore end-to-end trained differentiable models that integrate natural logic with neural networks, aiming to keep the backbone of natural language reasoning based on the natural logic formalism while introducing subsymbolic vector representations and neural components. The proposed model adapts module networks to model natural logic operations, which is enhanced with a memory component to model contextual information. Experiments show that the proposed framework can effectively model monotonicity-based reasoning, compared to the baseline neural network models without built-in inductive bias for monotonicity-based reasoning. Our proposed model shows to be robust when transferred from upward to downward inference. We perform further analyses on the performance of the proposed model on aggregation, showing the effectiveness of the proposed subcomponents on helping achieve better intermediate aggregation performance.
* 10 pages
Deriving Commonsense Inference Tasks from Interactive Fictions
Oct 19, 2020


Abstract:Commonsense reasoning simulates the human ability to make presumptions about our physical world, and it is an indispensable cornerstone in building general AI systems. We propose a new commonsense reasoning dataset based on human's interactive fiction game playings as human players demonstrate plentiful and diverse commonsense reasoning. The new dataset mitigates several limitations of the prior art. Experiments show that our task is solvable to human experts with sufficient commonsense knowledge but poses challenges to existing machine reading models, with a big performance gap of more than 30%.
Program Enhanced Fact Verification with Verbalization and Graph Attention Network
Oct 14, 2020



Abstract:Performing fact verification based on structured data is important for many real-life applications and is a challenging research problem, particularly when it involves both symbolic operations and informal inference based on language understanding. In this paper, we present a Program-enhanced Verbalization and Graph Attention Network (ProgVGAT) to integrate programs and execution into textual inference models. Specifically, a verbalization with program execution model is proposed to accumulate evidences that are embedded in operations over the tables. Built on that, we construct the graph attention verification networks, which are designed to fuse different sources of evidences from verbalized program execution, program structures, and the original statements and tables, to make the final verification decision. To support the above framework, we propose a program selection module optimized with a new training strategy based on margin loss, to produce more accurate programs, which is shown to be effective in enhancing the final verification results. Experimental results show that the proposed framework achieves the new state-of-the-art performance, a 74.4% accuracy, on the benchmark dataset TABFACT.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge