Yueming Wang
Human-like Cognitive Generalization for Large Models via Brain-in-the-loop Supervision
May 14, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in deep neural networks (DNNs), particularly large-scale language models, have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in image and natural language understanding. Although scaling up model parameters with increasing volume of training data has progressively improved DNN capabilities, achieving complex cognitive abilities - such as understanding abstract concepts, reasoning, and adapting to novel scenarios, which are intrinsic to human cognition - remains a major challenge. In this study, we show that brain-in-the-loop supervised learning, utilizing a small set of brain signals, can effectively transfer human conceptual structures to DNNs, significantly enhancing their comprehension of abstract and even unseen concepts. Experimental results further indicate that the enhanced cognitive capabilities lead to substantial performance gains in challenging tasks, including few-shot/zero-shot learning and out-of-distribution recognition, while also yielding highly interpretable concept representations. These findings highlight that human-in-the-loop supervision can effectively augment the complex cognitive abilities of large models, offering a promising pathway toward developing more human-like cognitive abilities in artificial systems.
Improving Unsupervised Task-driven Models of Ventral Visual Stream via Relative Position Predictivity
May 13, 2025Abstract:Based on the concept that ventral visual stream (VVS) mainly functions for object recognition, current unsupervised task-driven methods model VVS by contrastive learning, and have achieved good brain similarity. However, we believe functions of VVS extend beyond just object recognition. In this paper, we introduce an additional function involving VVS, named relative position (RP) prediction. We first theoretically explain contrastive learning may be unable to yield the model capability of RP prediction. Motivated by this, we subsequently integrate RP learning with contrastive learning, and propose a new unsupervised task-driven method to model VVS, which is more inline with biological reality. We conduct extensive experiments, demonstrating that: (i) our method significantly improves downstream performance of object recognition while enhancing RP predictivity; (ii) RP predictivity generally improves the model brain similarity. Our results provide strong evidence for the involvement of VVS in location perception (especially RP prediction) from a computational perspective.
A Simple Review of EEG Foundation Models: Datasets, Advancements and Future Perspectives
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:Electroencephalogram (EEG) signals play a crucial role in understanding brain activity and diagnosing neurological disorders. This review focuses on the recent development of EEG foundation models(EEG-FMs), which have shown great potential in processing and analyzing EEG data. We discuss various EEG-FMs, including their architectures, pre-training strategies, their pre-training and downstream datasets and other details. The review also highlights the challenges and future directions in this field, aiming to provide a comprehensive overview for researchers and practitioners interested in EEG analysis and related EEG-FMs.
Self-Attentive Spatio-Temporal Calibration for Precise Intermediate Layer Matching in ANN-to-SNN Distillation
Jan 14, 2025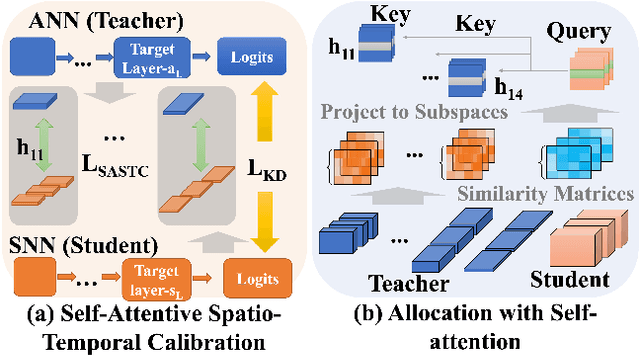

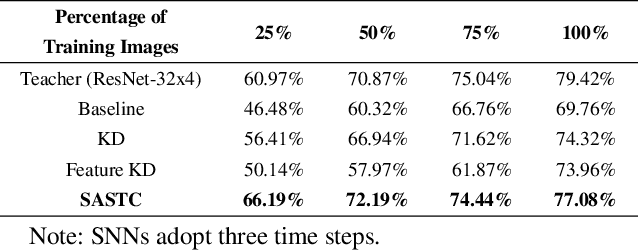
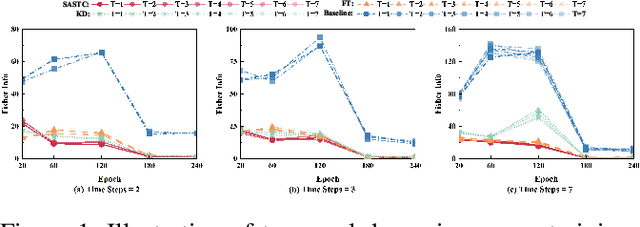
Abstract:Spiking Neural Networks (SNNs) are promising for low-power computation due to their event-driven mechanism but often suffer from lower accuracy compared to Artificial Neural Networks (ANNs). ANN-to-SNN knowledge distillation can improve SNN performance, but previous methods either focus solely on label information, missing valuable intermediate layer features, or use a layer-wise approach that neglects spatial and temporal semantic inconsistencies, leading to performance degradation.To address these limitations, we propose a novel method called self-attentive spatio-temporal calibration (SASTC). SASTC uses self-attention to identify semantically aligned layer pairs between ANN and SNN, both spatially and temporally. This enables the autonomous transfer of relevant semantic information. Extensive experiments show that SASTC outperforms existing methods, effectively solving the mismatching problem. Superior accuracy results include 95.12% on CIFAR-10, 79.40% on CIFAR-100 with 2 time steps, and 68.69% on ImageNet with 4 time steps for static datasets, and 97.92% on DVS-Gesture and 83.60% on DVS-CIFAR10 for neuromorphic datasets. This marks the first time SNNs have outperformed ANNs on both CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100, shedding the new light on the potential applications of SNNs.
Copiloting Diagnosis of Autism in Real Clinical Scenarios via LLMs
Oct 10, 2024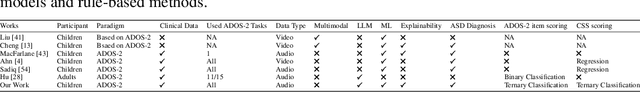
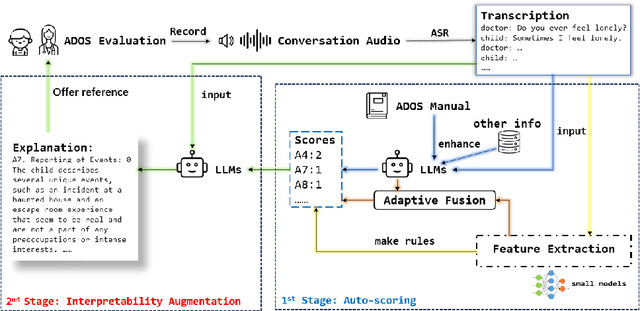
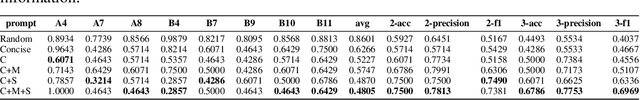

Abstract:Autism spectrum disorder(ASD) is a pervasive developmental disorder that significantly impacts the daily functioning and social participation of individuals. Despite the abundance of research focused on supporting the clinical diagnosis of ASD, there is still a lack of systematic and comprehensive exploration in the field of methods based on Large Language Models (LLMs), particularly regarding the real-world clinical diagnostic scenarios based on Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule, Second Edition (ADOS-2). Therefore, we have proposed a framework called ADOS-Copilot, which strikes a balance between scoring and explanation and explored the factors that influence the performance of LLMs in this task. The experimental results indicate that our proposed framework is competitive with the diagnostic results of clinicians, with a minimum MAE of 0.4643, binary classification F1-score of 81.79\%, and ternary classification F1-score of 78.37\%. Furthermore, we have systematically elucidated the strengths and limitations of current LLMs in this task from the perspectives of ADOS-2, LLMs' capabilities, language, and model scale aiming to inspire and guide the future application of LLMs in a broader fields of mental health disorders. We hope for more research to be transferred into real clinical practice, opening a window of kindness to the world for eccentric children.
Speed-enhanced Subdomain Adaptation Regression for Long-term Stable Neural Decoding in Brain-computer Interfaces
Jul 25, 2024



Abstract:Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) offer a means to convert neural signals into control signals, providing a potential restoration of movement for people with paralysis. Despite their promise, BCIs face a significant challenge in maintaining decoding accuracy over time due to neural nonstationarities. However, the decoding accuracy of BCI drops severely across days due to the neural data drift. While current recalibration techniques address this issue to a degree, they often fail to leverage the limited labeled data, to consider the signal correlation between two days, or to perform conditional alignment in regression tasks. This paper introduces a novel approach to enhance recalibration performance. We begin with preliminary experiments that reveal the temporal patterns of neural signal changes and identify three critical elements for effective recalibration: global alignment, conditional speed alignment, and feature-label consistency. Building on these insights, we propose the Speed-enhanced Subdomain Adaptation Regression (SSAR) framework, integrating semi-supervised learning with domain adaptation techniques in regression neural decoding. SSAR employs Speed-enhanced Subdomain Alignment (SeSA) for global and speed conditional alignment of similarly labeled data, with Contrastive Consistency Constraint (CCC) to enhance the alignment of SeSA by reinforcing feature-label consistency through contrastive learning. Our comprehensive set of experiments, both qualitative and quantitative, substantiate the superior recalibration performance and robustness of SSAR.
Actions Speak Louder than Words: Trillion-Parameter Sequential Transducers for Generative Recommendations
Feb 27, 2024



Abstract:Large-scale recommendation systems are characterized by their reliance on high cardinality, heterogeneous features and the need to handle tens of billions of user actions on a daily basis. Despite being trained on huge volume of data with thousands of features, most Deep Learning Recommendation Models (DLRMs) in industry fail to scale with compute. Inspired by success achieved by Transformers in language and vision domains, we revisit fundamental design choices in recommendation systems. We reformulate recommendation problems as sequential transduction tasks within a generative modeling framework (``Generative Recommenders''), and propose a new architecture, HSTU, designed for high cardinality, non-stationary streaming recommendation data. HSTU outperforms baselines over synthetic and public datasets by up to 65.8\% in NDCG, and is 5.3x to 15.2x faster than FlashAttention2-based Transformers on 8192 length sequences. HSTU-based Generative Recommenders, with 1.5 trillion parameters, improve metrics in online A/B tests by 12.4\% and have been deployed on multiple surfaces of a large internet platform with billions of users. More importantly, the model quality of Generative Recommenders empirically scales as a power-law of training compute across three orders of magnitude, up to GPT-3/LLaMa-2 scale, which reduces carbon footprint needed for future model developments, and further paves the way for the first foundational models in recommendations.
MindGPT: Interpreting What You See with Non-invasive Brain Recordings
Sep 27, 2023Abstract:Decoding of seen visual contents with non-invasive brain recordings has important scientific and practical values. Efforts have been made to recover the seen images from brain signals. However, most existing approaches cannot faithfully reflect the visual contents due to insufficient image quality or semantic mismatches. Compared with reconstructing pixel-level visual images, speaking is a more efficient and effective way to explain visual information. Here we introduce a non-invasive neural decoder, termed as MindGPT, which interprets perceived visual stimuli into natural languages from fMRI signals. Specifically, our model builds upon a visually guided neural encoder with a cross-attention mechanism, which permits us to guide latent neural representations towards a desired language semantic direction in an end-to-end manner by the collaborative use of the large language model GPT. By doing so, we found that the neural representations of the MindGPT are explainable, which can be used to evaluate the contributions of visual properties to language semantics. Our experiments show that the generated word sequences truthfully represented the visual information (with essential details) conveyed in the seen stimuli. The results also suggested that with respect to language decoding tasks, the higher visual cortex (HVC) is more semantically informative than the lower visual cortex (LVC), and using only the HVC can recover most of the semantic information. The code of the MindGPT model will be publicly available at https://github.com/JxuanC/MindGPT.
A Human-Machine Joint Learning Framework to Boost Endogenous BCI Training
Aug 25, 2023



Abstract:Brain-computer interfaces (BCIs) provide a direct pathway from the brain to external devices and have demonstrated great potential for assistive and rehabilitation technologies. Endogenous BCIs based on electroencephalogram (EEG) signals, such as motor imagery (MI) BCIs, can provide some level of control. However, mastering spontaneous BCI control requires the users to generate discriminative and stable brain signal patterns by imagery, which is challenging and is usually achieved over a very long training time (weeks/months). Here, we propose a human-machine joint learning framework to boost the learning process in endogenous BCIs, by guiding the user to generate brain signals towards an optimal distribution estimated by the decoder, given the historical brain signals of the user. To this end, we firstly model the human-machine joint learning process in a uniform formulation. Then a human-machine joint learning framework is proposed: 1) for the human side, we model the learning process in a sequential trial-and-error scenario and propose a novel ``copy/new'' feedback paradigm to help shape the signal generation of the subject toward the optimal distribution; 2) for the machine side, we propose a novel adaptive learning algorithm to learn an optimal signal distribution along with the subject's learning process. Specifically, the decoder reweighs the brain signals generated by the subject to focus more on ``good'' samples to cope with the learning process of the subject. Online and psuedo-online BCI experiments with 18 healthy subjects demonstrated the advantages of the proposed joint learning process over co-adaptive approaches in both learning efficiency and effectiveness.
Revisiting Neural Retrieval on Accelerators
Jun 06, 2023



Abstract:Retrieval finds a small number of relevant candidates from a large corpus for information retrieval and recommendation applications. A key component of retrieval is to model (user, item) similarity, which is commonly represented as the dot product of two learned embeddings. This formulation permits efficient inference, commonly known as Maximum Inner Product Search (MIPS). Despite its popularity, dot products cannot capture complex user-item interactions, which are multifaceted and likely high rank. We hence examine non-dot-product retrieval settings on accelerators, and propose \textit{mixture of logits} (MoL), which models (user, item) similarity as an adaptive composition of elementary similarity functions. This new formulation is expressive, capable of modeling high rank (user, item) interactions, and further generalizes to the long tail. When combined with a hierarchical retrieval strategy, \textit{h-indexer}, we are able to scale up MoL to 100M corpus on a single GPU with latency comparable to MIPS baselines. On public datasets, our approach leads to uplifts of up to 77.3\% in hit rate (HR). Experiments on a large recommendation surface at Meta showed strong metric gains and reduced popularity bias, validating the proposed approach's performance and improved generalization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge