Yiyu Zhuang
IDOL: Instant Photorealistic 3D Human Creation from a Single Image
Dec 19, 2024



Abstract:Creating a high-fidelity, animatable 3D full-body avatar from a single image is a challenging task due to the diverse appearance and poses of humans and the limited availability of high-quality training data. To achieve fast and high-quality human reconstruction, this work rethinks the task from the perspectives of dataset, model, and representation. First, we introduce a large-scale HUman-centric GEnerated dataset, HuGe100K, consisting of 100K diverse, photorealistic sets of human images. Each set contains 24-view frames in specific human poses, generated using a pose-controllable image-to-multi-view model. Next, leveraging the diversity in views, poses, and appearances within HuGe100K, we develop a scalable feed-forward transformer model to predict a 3D human Gaussian representation in a uniform space from a given human image. This model is trained to disentangle human pose, body shape, clothing geometry, and texture. The estimated Gaussians can be animated without post-processing. We conduct comprehensive experiments to validate the effectiveness of the proposed dataset and method. Our model demonstrates the ability to efficiently reconstruct photorealistic humans at 1K resolution from a single input image using a single GPU instantly. Additionally, it seamlessly supports various applications, as well as shape and texture editing tasks.
Towards Native Generative Model for 3D Head Avatar
Oct 02, 2024



Abstract:Creating 3D head avatars is a significant yet challenging task for many applicated scenarios. Previous studies have set out to learn 3D human head generative models using massive 2D image data. Although these models are highly generalizable for human appearance, their result models are not 360$^\circ$-renderable, and the predicted 3D geometry is unreliable. Therefore, such results cannot be used in VR, game modeling, and other scenarios that require 360$^\circ$-renderable 3D head models. An intuitive idea is that 3D head models with limited amount but high 3D accuracy are more reliable training data for a high-quality 3D generative model. In this vein, we delve into how to learn a native generative model for 360$^\circ$ full head from a limited 3D head dataset. Specifically, three major problems are studied: 1) how to effectively utilize various representations for generating the 360$^\circ$-renderable human head; 2) how to disentangle the appearance, shape, and motion of human faces to generate a 3D head model that can be edited by appearance and driven by motion; 3) and how to extend the generalization capability of the generative model to support downstream tasks. Comprehensive experiments are conducted to verify the effectiveness of the proposed model. We hope the proposed models and artist-designed dataset can inspire future research on learning native generative 3D head models from limited 3D datasets.
Head360: Learning a Parametric 3D Full-Head for Free-View Synthesis in 360°
Aug 01, 2024



Abstract:Creating a 360{\deg} parametric model of a human head is a very challenging task. While recent advancements have demonstrated the efficacy of leveraging synthetic data for building such parametric head models, their performance remains inadequate in crucial areas such as expression-driven animation, hairstyle editing, and text-based modifications. In this paper, we build a dataset of artist-designed high-fidelity human heads and propose to create a novel parametric 360{\deg} renderable parametric head model from it. Our scheme decouples the facial motion/shape and facial appearance, which are represented by a classic parametric 3D mesh model and an attached neural texture, respectively. We further propose a training method for decompositing hairstyle and facial appearance, allowing free-swapping of the hairstyle. A novel inversion fitting method is presented based on single image input with high generalization and fidelity. To the best of our knowledge, our model is the first parametric 3D full-head that achieves 360{\deg} free-view synthesis, image-based fitting, appearance editing, and animation within a single model. Experiments show that facial motions and appearances are well disentangled in the parametric space, leading to SOTA performance in rendering and animating quality. The code and SynHead100 dataset are released at https://nju-3dv.github.io/projects/Head360.
Mani-GS: Gaussian Splatting Manipulation with Triangular Mesh
May 28, 2024Abstract:Neural 3D representations such as Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF), excel at producing photo-realistic rendering results but lack the flexibility for manipulation and editing which is crucial for content creation. Previous works have attempted to address this issue by deforming a NeRF in canonical space or manipulating the radiance field based on an explicit mesh. However, manipulating NeRF is not highly controllable and requires a long training and inference time. With the emergence of 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), extremely high-fidelity novel view synthesis can be achieved using an explicit point-based 3D representation with much faster training and rendering speed. However, there is still a lack of effective means to manipulate 3DGS freely while maintaining rendering quality. In this work, we aim to tackle the challenge of achieving manipulable photo-realistic rendering. We propose to utilize a triangular mesh to manipulate 3DGS directly with self-adaptation. This approach reduces the need to design various algorithms for different types of Gaussian manipulation. By utilizing a triangle shape-aware Gaussian binding and adapting method, we can achieve 3DGS manipulation and preserve high-fidelity rendering after manipulation. Our approach is capable of handling large deformations, local manipulations, and soft body simulations while keeping high-quality rendering. Furthermore, we demonstrate that our method is also effective with inaccurate meshes extracted from 3DGS. Experiments conducted demonstrate the effectiveness of our method and its superiority over baseline approaches.
Anti-Aliased Neural Implicit Surfaces with Encoding Level of Detail
Sep 19, 2023Abstract:We present LoD-NeuS, an efficient neural representation for high-frequency geometry detail recovery and anti-aliased novel view rendering. Drawing inspiration from voxel-based representations with the level of detail (LoD), we introduce a multi-scale tri-plane-based scene representation that is capable of capturing the LoD of the signed distance function (SDF) and the space radiance. Our representation aggregates space features from a multi-convolved featurization within a conical frustum along a ray and optimizes the LoD feature volume through differentiable rendering. Additionally, we propose an error-guided sampling strategy to guide the growth of the SDF during the optimization. Both qualitative and quantitative evaluations demonstrate that our method achieves superior surface reconstruction and photorealistic view synthesis compared to state-of-the-art approaches.
High-Fidelity 3D Face Generation from Natural Language Descriptions
May 05, 2023

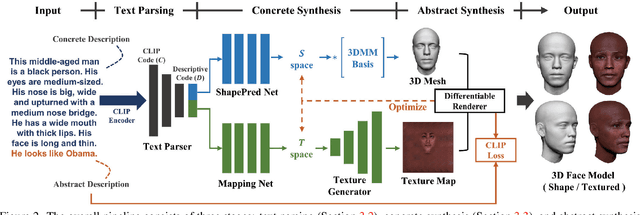

Abstract:Synthesizing high-quality 3D face models from natural language descriptions is very valuable for many applications, including avatar creation, virtual reality, and telepresence. However, little research ever tapped into this task. We argue the major obstacle lies in 1) the lack of high-quality 3D face data with descriptive text annotation, and 2) the complex mapping relationship between descriptive language space and shape/appearance space. To solve these problems, we build Describe3D dataset, the first large-scale dataset with fine-grained text descriptions for text-to-3D face generation task. Then we propose a two-stage framework to first generate a 3D face that matches the concrete descriptions, then optimize the parameters in the 3D shape and texture space with abstract description to refine the 3D face model. Extensive experimental results show that our method can produce a faithful 3D face that conforms to the input descriptions with higher accuracy and quality than previous methods. The code and Describe3D dataset are released at https://github.com/zhuhao-nju/describe3d .
NeAI: A Pre-convoluted Representation for Plug-and-Play Neural Ambient Illumination
Apr 18, 2023



Abstract:Recent advances in implicit neural representation have demonstrated the ability to recover detailed geometry and material from multi-view images. However, the use of simplified lighting models such as environment maps to represent non-distant illumination, or using a network to fit indirect light modeling without a solid basis, can lead to an undesirable decomposition between lighting and material. To address this, we propose a fully differentiable framework named neural ambient illumination (NeAI) that uses Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) as a lighting model to handle complex lighting in a physically based way. Together with integral lobe encoding for roughness-adaptive specular lobe and leveraging the pre-convoluted background for accurate decomposition, the proposed method represents a significant step towards integrating physically based rendering into the NeRF representation. The experiments demonstrate the superior performance of novel-view rendering compared to previous works, and the capability to re-render objects under arbitrary NeRF-style environments opens up exciting possibilities for bridging the gap between virtual and real-world scenes. The project and supplementary materials are available at https://yiyuzhuang.github.io/NeAI/.
MoFaNeRF: Morphable Facial Neural Radiance Field
Dec 04, 2021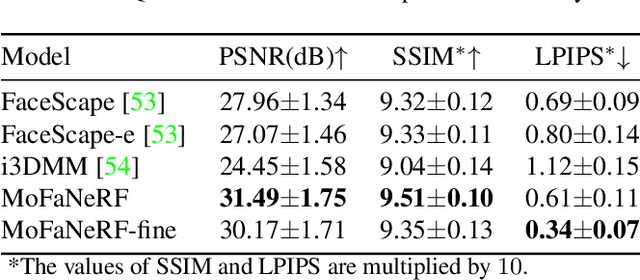
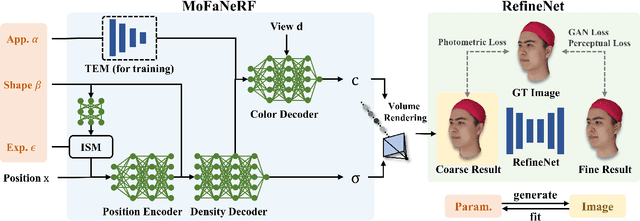


Abstract:We propose a parametric model that maps free-view images into a vector space of coded facial shape, expression and appearance using a neural radiance field, namely Morphable Facial NeRF. Specifically, MoFaNeRF takes the coded facial shape, expression and appearance along with space coordinate and view direction as input to an MLP, and outputs the radiance of the space point for photo-realistic image synthesis. Compared with conventional 3D morphable models (3DMM), MoFaNeRF shows superiority in directly synthesizing photo-realistic facial details even for eyes, mouths, and beards. Also, continuous face morphing can be easily achieved by interpolating the input shape, expression and appearance codes. By introducing identity-specific modulation and texture encoder, our model synthesizes accurate photometric details and shows strong representation ability. Our model shows strong ability on multiple applications including image-based fitting, random generation, face rigging, face editing, and novel view synthesis. Experiments show that our method achieves higher representation ability than previous parametric models, and achieves competitive performance in several applications. To the best of our knowledge, our work is the first facial parametric model built upon a neural radiance field that can be used in fitting, generation and manipulation. Our code and model are released in https://github.com/zhuhao-nju/mofanerf.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge