Yibin Wang
Unified Personalized Reward Model for Vision Generation
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Recent advancements in multimodal reward models (RMs) have significantly propelled the development of visual generation. Existing frameworks typically adopt Bradley-Terry-style preference modeling or leverage generative VLMs as judges, and subsequently optimize visual generation models via reinforcement learning. However, current RMs suffer from inherent limitations: they often follow a one-size-fits-all paradigm that assumes a monolithic preference distribution or relies on fixed evaluation rubrics. As a result, they are insensitive to content-specific visual cues, leading to systematic misalignment with subjective and context-dependent human preferences. To this end, inspired by human assessment, we propose UnifiedReward-Flex, a unified personalized reward model for vision generation that couples reward modeling with flexible and context-adaptive reasoning. Specifically, given a prompt and the generated visual content, it first interprets the semantic intent and grounds on visual evidence, then dynamically constructs a hierarchical assessment by instantiating fine-grained criteria under both predefined and self-generated high-level dimensions. Our training pipeline follows a two-stage process: (1) we first distill structured, high-quality reasoning traces from advanced closed-source VLMs to bootstrap SFT, equipping the model with flexible and context-adaptive reasoning behaviors; (2) we then perform direct preference optimization (DPO) on carefully curated preference pairs to further strengthen reasoning fidelity and discriminative alignment. To validate the effectiveness, we integrate UnifiedReward-Flex into the GRPO framework for image and video synthesis, and extensive results demonstrate its superiority.
UniReason 1.0: A Unified Reasoning Framework for World Knowledge Aligned Image Generation and Editing
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Unified multimodal models often struggle with complex synthesis tasks that demand deep reasoning, and typically treat text-to-image generation and image editing as isolated capabilities rather than interconnected reasoning steps. To address this, we propose UniReason, a unified framework that harmonizes these two tasks through a dual reasoning paradigm. We formulate generation as world knowledge-enhanced planning to inject implicit constraints, and leverage editing capabilities for fine-grained visual refinement to further correct visual errors via self-reflection. This approach unifies generation and editing within a shared representation, mirroring the human cognitive process of planning followed by refinement. We support this framework by systematically constructing a large-scale reasoning-centric dataset (~300k samples) covering five major knowledge domains (e.g., cultural commonsense, physics, etc.) for planning, alongside an agent-generated corpus for visual self-correction. Extensive experiments demonstrate that UniReason achieves advanced performance on reasoning-intensive benchmarks such as WISE, KrisBench and UniREditBench, while maintaining superior general synthesis capabilities.
FairExpand: Individual Fairness on Graphs with Partial Similarity Information
Dec 20, 2025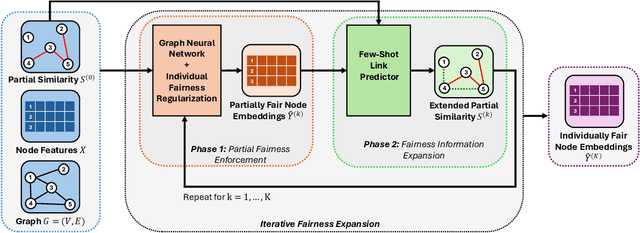
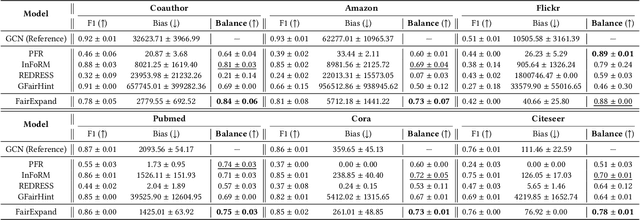
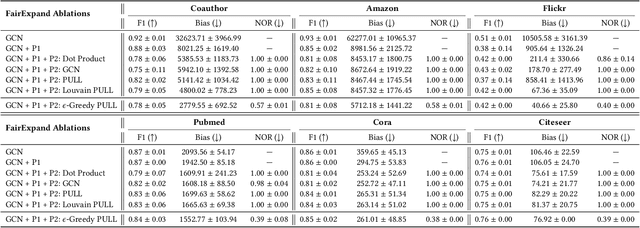
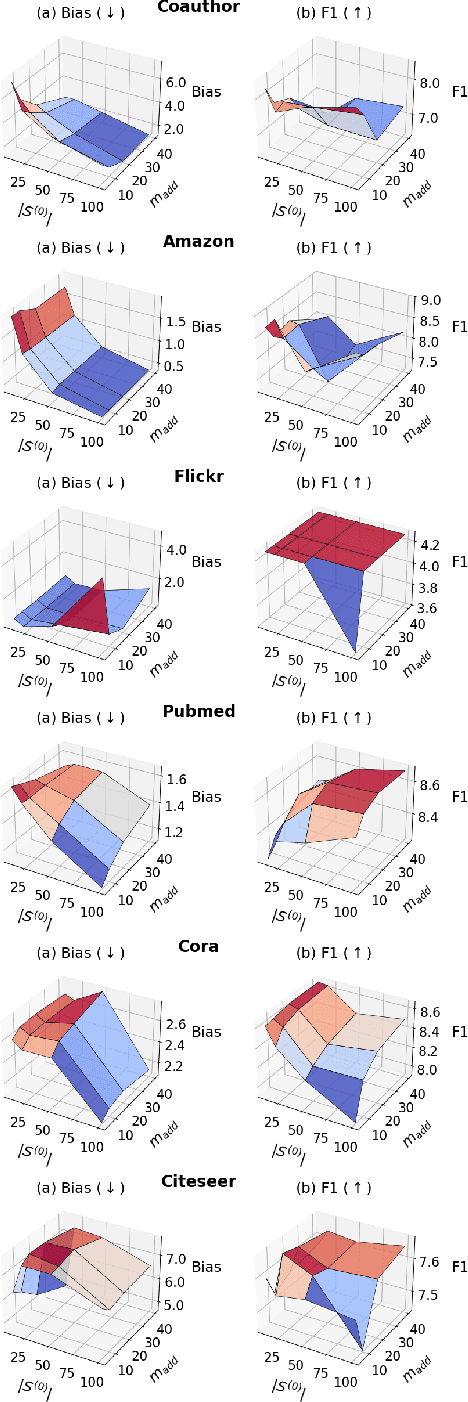
Abstract:Individual fairness, which requires that similar individuals should be treated similarly by algorithmic systems, has become a central principle in fair machine learning. Individual fairness has garnered traction in graph representation learning due to its practical importance in high-stakes Web areas such as user modeling, recommender systems, and search. However, existing methods assume the existence of predefined similarity information over all node pairs, an often unrealistic requirement that prevents their operationalization in practice. In this paper, we assume the similarity information is only available for a limited subset of node pairs and introduce FairExpand, a flexible framework that promotes individual fairness in this more realistic partial information scenario. FairExpand follows a two-step pipeline that alternates between refining node representations using a backbone model (e.g., a graph neural network) and gradually propagating similarity information, which allows fairness enforcement to effectively expand to the entire graph. Extensive experiments show that FairExpand consistently enhances individual fairness while preserving performance, making it a practical solution for enabling graph-based individual fairness in real-world applications with partial similarity information.
$\text{G}^2$RPO: Granular GRPO for Precise Reward in Flow Models
Oct 02, 2025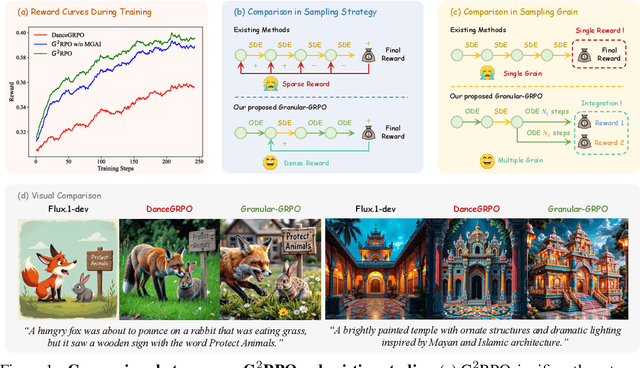
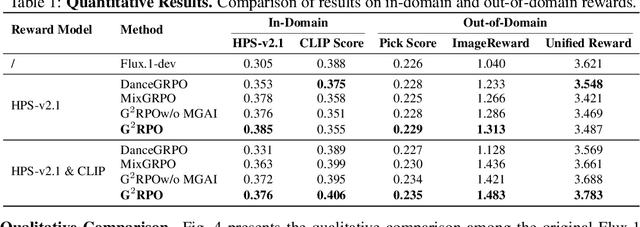
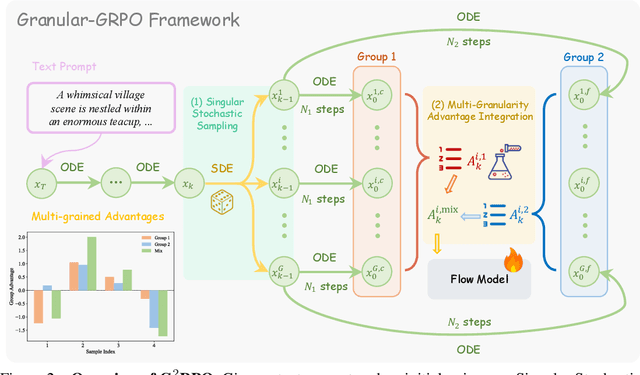
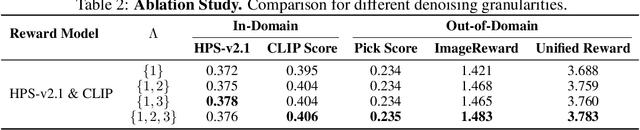
Abstract:The integration of online reinforcement learning (RL) into diffusion and flow models has recently emerged as a promising approach for aligning generative models with human preferences. Stochastic sampling via Stochastic Differential Equations (SDE) is employed during the denoising process to generate diverse denoising directions for RL exploration. While existing methods effectively explore potential high-value samples, they suffer from sub-optimal preference alignment due to sparse and narrow reward signals. To address these challenges, we propose a novel Granular-GRPO ($\text{G}^2$RPO ) framework that achieves precise and comprehensive reward assessments of sampling directions in reinforcement learning of flow models. Specifically, a Singular Stochastic Sampling strategy is introduced to support step-wise stochastic exploration while enforcing a high correlation between the reward and the injected noise, thereby facilitating a faithful reward for each SDE perturbation. Concurrently, to eliminate the bias inherent in fixed-granularity denoising, we introduce a Multi-Granularity Advantage Integration module that aggregates advantages computed at multiple diffusion scales, producing a more comprehensive and robust evaluation of the sampling directions. Experiments conducted on various reward models, including both in-domain and out-of-domain evaluations, demonstrate that our $\text{G}^2$RPO significantly outperforms existing flow-based GRPO baselines,highlighting its effectiveness and robustness.
Towards Confidential and Efficient LLM Inference with Dual Privacy Protection
Sep 11, 2025Abstract:CPU-based trusted execution environments (TEEs) and differential privacy (DP) have gained wide applications for private inference. Due to high inference latency in TEEs, researchers use partition-based approaches that offload linear model components to GPUs. However, dense nonlinear layers of large language models (LLMs) result in significant communication overhead between TEEs and GPUs. DP-based approaches apply random noise to protect data privacy, but this compromises LLM performance and semantic understanding. To overcome the above drawbacks, this paper proposes CMIF, a Confidential and efficient Model Inference Framework. CMIF confidentially deploys the embedding layer in the client-side TEE and subsequent layers on GPU servers. Meanwhile, it optimizes the Report-Noisy-Max mechanism to protect sensitive inputs with a slight decrease in model performance. Extensive experiments on Llama-series models demonstrate that CMIF reduces additional inference overhead in TEEs while preserving user data privacy.
An U-Net-Based Deep Neural Network for Cloud Shadow and Sun-Glint Correction of Unmanned Aerial System (UAS) Imagery
Sep 10, 2025Abstract:The use of unmanned aerial systems (UASs) has increased tremendously in the current decade. They have significantly advanced remote sensing with the capability to deploy and image the terrain as per required spatial, spectral, temporal, and radiometric resolutions for various remote sensing applications. One of the major advantages of UAS imagery is that images can be acquired in cloudy conditions by flying the UAS under the clouds. The limitation to the technology is that the imagery is often sullied by cloud shadows. Images taken over water are additionally affected by sun glint. These are two pose serious issues for estimating water quality parameters from the UAS images. This study proposes a novel machine learning approach first to identify and extract regions with cloud shadows and sun glint and separate such regions from non-obstructed clear sky regions and sun-glint unaffected regions. The data was extracted from the images at pixel level to train an U-Net based deep learning model and best settings for model training was identified based on the various evaluation metrics from test cases. Using this evaluation, a high-quality image correction model was determined, which was used to recover the cloud shadow and sun glint areas in the images.
Pref-GRPO: Pairwise Preference Reward-based GRPO for Stable Text-to-Image Reinforcement Learning
Aug 28, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements highlight the importance of GRPO-based reinforcement learning methods and benchmarking in enhancing text-to-image (T2I) generation. However, current methods using pointwise reward models (RM) for scoring generated images are susceptible to reward hacking. We reveal that this happens when minimal score differences between images are amplified after normalization, creating illusory advantages that drive the model to over-optimize for trivial gains, ultimately destabilizing the image generation process. To address this, we propose Pref-GRPO, a pairwise preference reward-based GRPO method that shifts the optimization objective from score maximization to preference fitting, ensuring more stable training. In Pref-GRPO, images are pairwise compared within each group using preference RM, and the win rate is used as the reward signal. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PREF-GRPO differentiates subtle image quality differences, providing more stable advantages and mitigating reward hacking. Additionally, existing T2I benchmarks are limited by coarse evaluation criteria, hindering comprehensive model assessment. To solve this, we introduce UniGenBench, a unified T2I benchmark comprising 600 prompts across 5 main themes and 20 subthemes. It evaluates semantic consistency through 10 primary and 27 sub-criteria, leveraging MLLM for benchmark construction and evaluation. Our benchmarks uncover the strengths and weaknesses of both open and closed-source T2I models and validate the effectiveness of Pref-GRPO.
DiCache: Let Diffusion Model Determine Its Own Cache
Aug 24, 2025

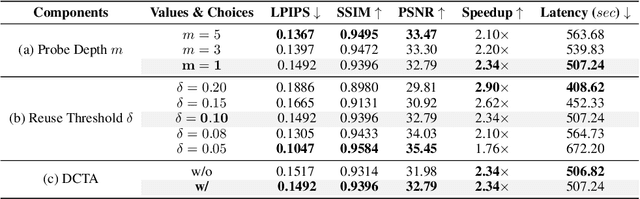
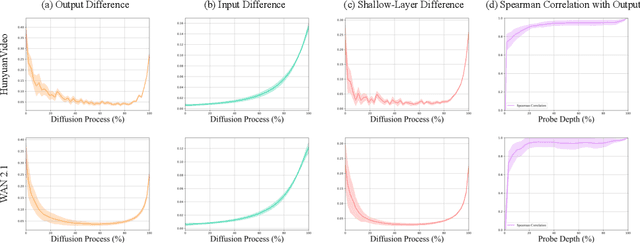
Abstract:Recent years have witnessed the rapid development of acceleration techniques for diffusion models, especially caching-based acceleration methods. These studies seek to answer two fundamental questions: "When to cache" and "How to use cache", typically relying on predefined empirical laws or dataset-level priors to determine the timing of caching and utilizing handcrafted rules for leveraging multi-step caches. However, given the highly dynamic nature of the diffusion process, they often exhibit limited generalizability and fail on outlier samples. In this paper, a strong correlation is revealed between the variation patterns of the shallow-layer feature differences in the diffusion model and those of final model outputs. Moreover, we have observed that the features from different model layers form similar trajectories. Based on these observations, we present DiCache, a novel training-free adaptive caching strategy for accelerating diffusion models at runtime, answering both when and how to cache within a unified framework. Specifically, DiCache is composed of two principal components: (1) Online Probe Profiling Scheme leverages a shallow-layer online probe to obtain a stable prior for the caching error in real time, enabling the model to autonomously determine caching schedules. (2) Dynamic Cache Trajectory Alignment combines multi-step caches based on shallow-layer probe feature trajectory to better approximate the current feature, facilitating higher visual quality. Extensive experiments validate DiCache's capability in achieving higher efficiency and improved visual fidelity over state-of-the-art methods on various leading diffusion models including WAN 2.1, HunyuanVideo for video generation, and Flux for image generation.
GeometryZero: Improving Geometry Solving for LLM with Group Contrastive Policy Optimization
Jun 08, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities across diverse domains, particularly in mathematical reasoning, amid which geometry problem solving remains a challenging area where auxiliary construction plays a enssential role. Existing approaches either achieve suboptimal performance or rely on massive LLMs (e.g., GPT-4o), incurring massive computational costs. We posit that reinforcement learning with verifiable reward (e.g., GRPO) offers a promising direction for training smaller models that effectively combine auxiliary construction with robust geometric reasoning. However, directly applying GRPO to geometric reasoning presents fundamental limitations due to its dependence on unconditional rewards, which leads to indiscriminate and counterproductive auxiliary constructions. To address these challenges, we propose Group Contrastive Policy Optimization (GCPO), a novel reinforcement learning framework featuring two key innovations: (1) Group Contrastive Masking, which adaptively provides positive or negative reward signals for auxiliary construction based on contextual utility, and a (2) length reward that promotes longer reasoning chains. Building on GCPO, we develop GeometryZero, a family of affordable-size geometric reasoning models that judiciously determine when to employ auxiliary construction. Our extensive empirical evaluation across popular geometric benchmarks (Geometry3K, MathVista) demonstrates that GeometryZero models consistently outperform baselines (e.g. GRPO), achieving an average improvement of 4.29% across all benchmarks.
Improving Data Efficiency for LLM Reinforcement Fine-tuning Through Difficulty-targeted Online Data Selection and Rollout Replay
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has become an effective approach for fine-tuning large language models (LLMs), particularly to enhance their reasoning capabilities. However, RL fine-tuning remains highly resource-intensive, and existing work has largely overlooked the problem of data efficiency. In this paper, we propose two techniques to improve data efficiency in LLM RL fine-tuning: difficulty-targeted online data selection and rollout replay. We introduce the notion of adaptive difficulty to guide online data selection, prioritizing questions of moderate difficulty that are more likely to yield informative learning signals. To estimate adaptive difficulty efficiently, we develop an attention-based framework that requires rollouts for only a small reference set of questions. The adaptive difficulty of the remaining questions is then estimated based on their similarity to this set. To further reduce rollout cost, we introduce a rollout replay mechanism that reuses recent rollouts, lowering per-step computation while maintaining stable updates. Extensive experiments across 6 LLM-dataset combinations show that our method reduces RL fine-tuning time by 25% to 65% to reach the same level of performance as the original GRPO algorithm.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge