Lakshminarayanan Subramanian
Self-Regulating Cars: Automating Traffic Control in Free Flow Road Networks
Jun 13, 2025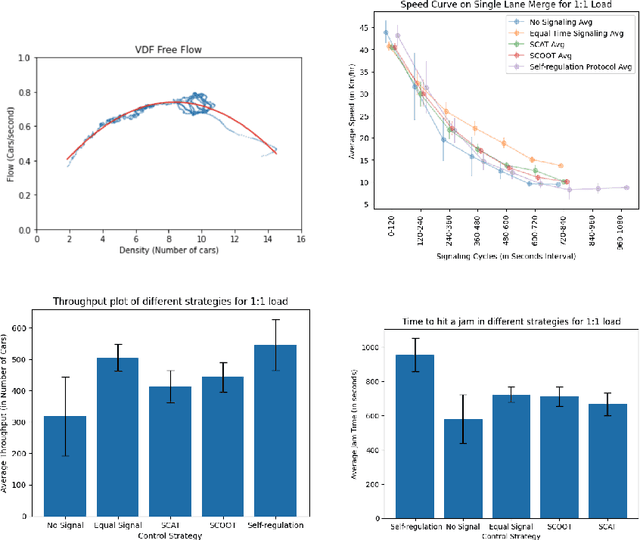
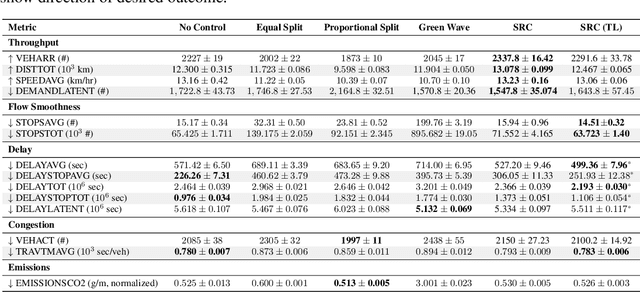
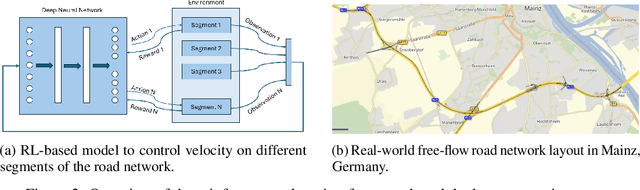
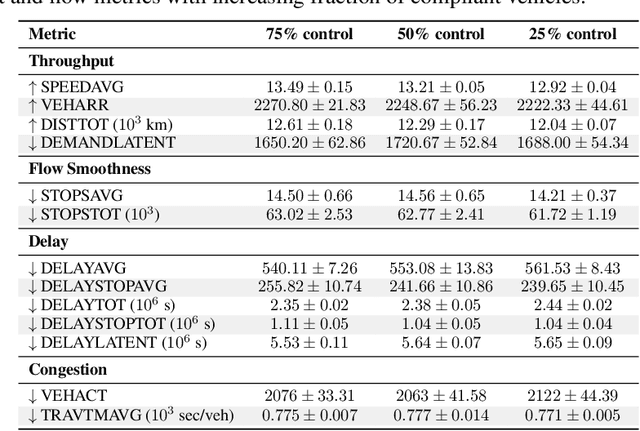
Abstract:Free-flow road networks, such as suburban highways, are increasingly experiencing traffic congestion due to growing commuter inflow and limited infrastructure. Traditional control mechanisms, such as traffic signals or local heuristics, are ineffective or infeasible in these high-speed, signal-free environments. We introduce self-regulating cars, a reinforcement learning-based traffic control protocol that dynamically modulates vehicle speeds to optimize throughput and prevent congestion, without requiring new physical infrastructure. Our approach integrates classical traffic flow theory, gap acceptance models, and microscopic simulation into a physics-informed RL framework. By abstracting roads into super-segments, the agent captures emergent flow dynamics and learns robust speed modulation policies from instantaneous traffic observations. Evaluated in the high-fidelity PTV Vissim simulator on a real-world highway network, our method improves total throughput by 5%, reduces average delay by 13%, and decreases total stops by 3% compared to the no-control setting. It also achieves smoother, congestion-resistant flow while generalizing across varied traffic patterns, demonstrating its potential for scalable, ML-driven traffic management.
EduBot -- Can LLMs Solve Personalized Learning and Programming Assignments?
Apr 23, 2025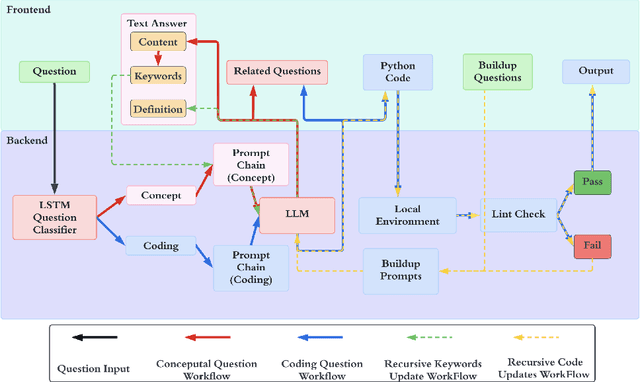
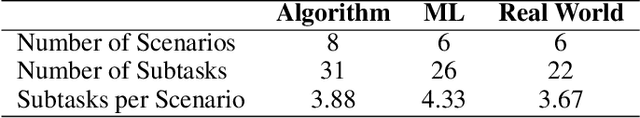
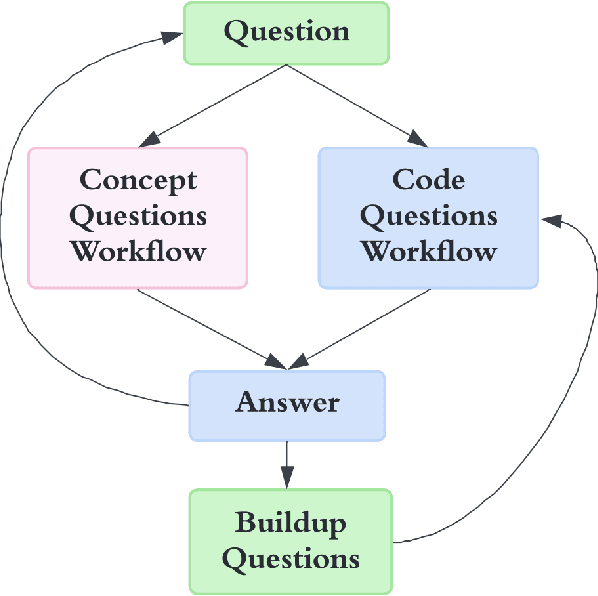

Abstract:The prevalence of Large Language Models (LLMs) is revolutionizing the process of writing code. General and code LLMs have shown impressive performance in generating standalone functions and code-completion tasks with one-shot queries. However, the ability to solve comprehensive programming tasks with recursive requests and bug fixes remains questionable. In this paper, we propose EduBot, an intelligent automated assistant system that combines conceptual knowledge teaching, end-to-end code development, personalized programming through recursive prompt-driven methods, and debugging with limited human interventions powered by LLMs. We show that EduBot can solve complicated programming tasks consisting of sub-tasks with increasing difficulties ranging from conceptual to coding questions by recursive automatic prompt-driven systems without finetuning on LLMs themselves. To further evaluate EduBot's performance, we design and conduct a benchmark suite consisting of 20 scenarios in algorithms, machine learning, and real-world problems. The result shows that EduBot can complete most scenarios in less than 20 minutes. Based on the benchmark suites, we perform a comparative study to take different LLMs as the backbone and to verify EduBot's compatibility and robustness across LLMs with varying capabilities. We believe that EduBot is an exploratory approach to explore the potential of pre-trained LLMs in multi-step reasoning and code generation for solving personalized assignments with knowledge learning and code generation.
Discovering Hidden Pollution Hotspots Using Sparse Sensor Measurements
Oct 05, 2024Abstract:Effective air pollution management in urban areas relies on both monitoring and mitigation strategies, yet high costs often limit sensor networks to a few key pollution hotspots. In this paper, we show that New Delhi's public sensor network is insufficient for identifying all pollution hotspots. To address this, we augmented the city's network with 28 low-cost sensors, monitoring PM 2.5 concentrations over 30 months (May 2018 to November 2020). Our analysis uncovered 189 additional hotspots, supplementing the 660 already detected by the government network. We observed that Space-Time Kriging with limited but accurate sensor data provides a more robust and generalizable approach for identifying these hotspots, as compared to deep learning models that require large amounts of fine-grained multi-modal data (emissions inventory, meteorology, etc.) which was not reliably, frequently and accurately available in the New Delhi context. Using Space-Time Kriging, we achieved 98% precision and 95.4% recall in detecting hotspots with 50% sensor failure. Furthermore, this method proved effective in predicting hotspots in areas without sensors, achieving 95.3% precision and 88.5% recall in the case of 50% missing sensors. Our findings revealed that a significant portion of New Delhi's population, around 23 million people, was exposed to pollution hotspots for at least half of the study period. We also identified areas beyond the reach of the public sensor network that should be prioritized for pollution control. These results highlight the need for more comprehensive monitoring networks and suggest Space-Time Kriging as a viable solution for cities facing similar resource constraints.
NaijaHate: Evaluating Hate Speech Detection on Nigerian Twitter Using Representative Data
Mar 28, 2024



Abstract:To address the global issue of hateful content proliferating in online platforms, hate speech detection (HSD) models are typically developed on datasets collected in the United States, thereby failing to generalize to English dialects from the Majority World. Furthermore, HSD models are often evaluated on curated samples, raising concerns about overestimating model performance in real-world settings. In this work, we introduce NaijaHate, the first dataset annotated for HSD which contains a representative sample of Nigerian tweets. We demonstrate that HSD evaluated on biased datasets traditionally used in the literature largely overestimates real-world performance on representative data. We also propose NaijaXLM-T, a pretrained model tailored to the Nigerian Twitter context, and establish the key role played by domain-adaptive pretraining and finetuning in maximizing HSD performance. Finally, we show that in this context, a human-in-the-loop approach to content moderation where humans review 1% of Nigerian tweets flagged as hateful would enable to moderate 60% of all hateful content. Taken together, these results pave the way towards robust HSD systems and a better protection of social media users from hateful content in low-resource settings.
Designing Informative Metrics for Few-Shot Example Selection
Mar 06, 2024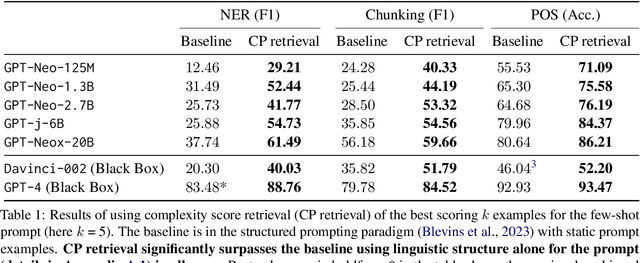
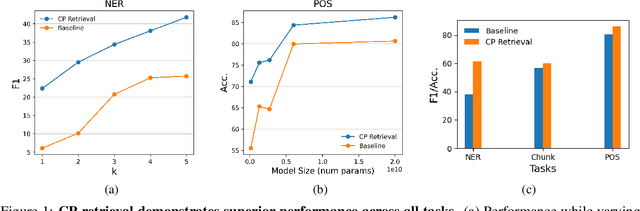
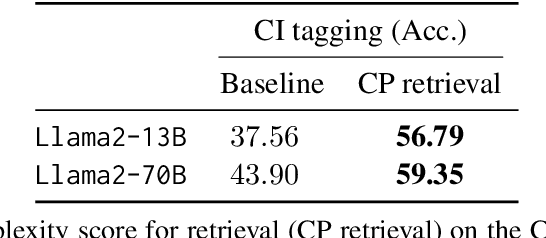
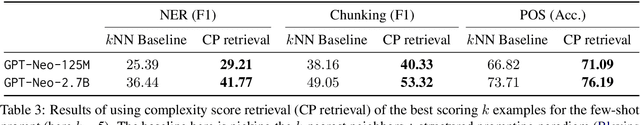
Abstract:Pretrained language models (PLMs) have shown remarkable few-shot learning capabilities when provided with properly formatted examples. However, selecting the "best" examples remains an open challenge. We propose a complexity-based prompt selection approach for sequence tagging tasks. This approach avoids the training of a dedicated model for selection of examples, and instead uses certain metrics to align the syntactico-semantic complexity of test sentences and examples. We use both sentence- and word-level metrics to match the complexity of examples to the (test) sentence being considered. Our results demonstrate that our approach extracts greater performance from PLMs: it achieves state-of-the-art performance on few-shot NER, achieving a 5% absolute improvement in F1 score on the CoNLL2003 dataset for GPT-4. We also see large gains of upto 28.85 points (F1/Acc.) in smaller models like GPT-j-6B.
Generation of a Compendium of Transcription Factor Cascades and Identification of Potential Therapeutic Targets using Graph Machine Learning
Nov 29, 2023



Abstract:Transcription factors (TFs) play a vital role in the regulation of gene expression thereby making them critical to many cellular processes. In this study, we used graph machine learning methods to create a compendium of TF cascades using data extracted from the STRING database. A TF cascade is a sequence of TFs that regulate each other, forming a directed path in the TF network. We constructed a knowledge graph of 81,488 unique TF cascades, with the longest cascade consisting of 62 TFs. Our results highlight the complex and intricate nature of TF interactions, where multiple TFs work together to regulate gene expression. We also identified 10 TFs with the highest regulatory influence based on centrality measurements, providing valuable information for researchers interested in studying specific TFs. Furthermore, our pathway enrichment analysis revealed significant enrichment of various pathways and functional categories, including those involved in cancer and other diseases, as well as those involved in development, differentiation, and cell signaling. The enriched pathways identified in this study may have potential as targets for therapeutic intervention in diseases associated with dysregulation of transcription factors. We have released the dataset, knowledge graph, and graphML methods for the TF cascades, and created a website to display the results, which can be accessed by researchers interested in using this dataset. Our study provides a valuable resource for understanding the complex network of interactions between TFs and their regulatory roles in cellular processes.
Fine-grained prediction of food insecurity using news streams
Nov 17, 2021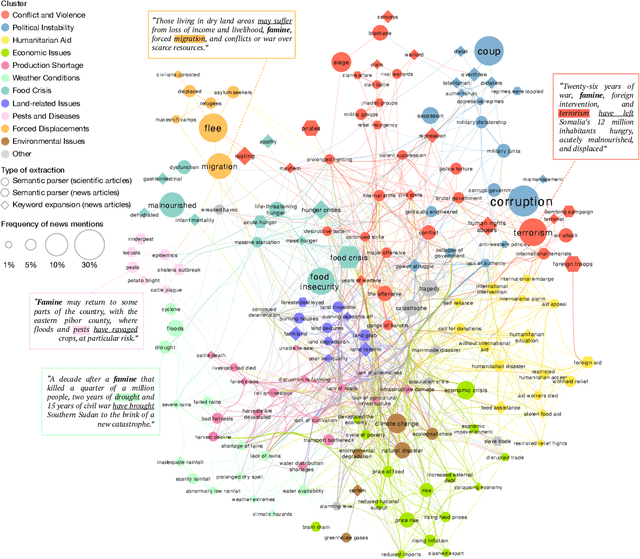
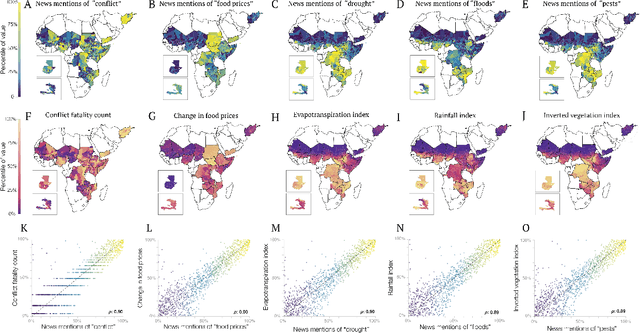

Abstract:Anticipating the outbreak of a food crisis is crucial to efficiently allocate emergency relief and reduce human suffering. However, existing food insecurity early warning systems rely on risk measures that are often delayed, outdated, or incomplete. Here, we leverage recent advances in deep learning to extract high-frequency precursors to food crises from the text of a large corpus of news articles about fragile states published between 1980 and 2020. Our text features are causally grounded, interpretable, validated by existing data, and allow us to predict 32% more food crises than existing models up to three months ahead of time at the district level across 15 fragile states. These results could have profound implications on how humanitarian aid gets allocated and open new avenues for machine learning to improve decision making in data-scarce environments.
DICE: Deep Significance Clustering for Outcome-Aware Stratification
Jan 07, 2021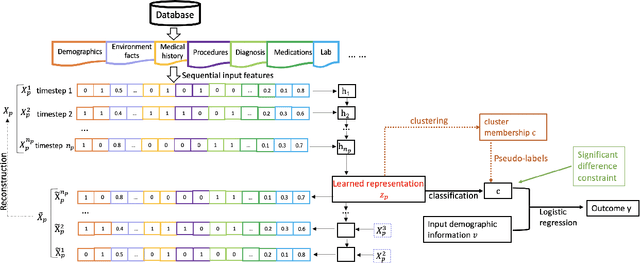
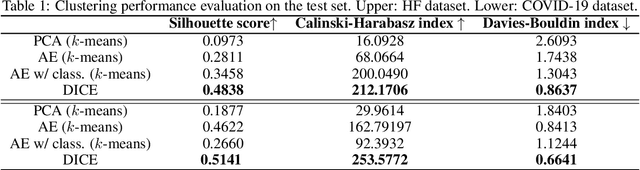
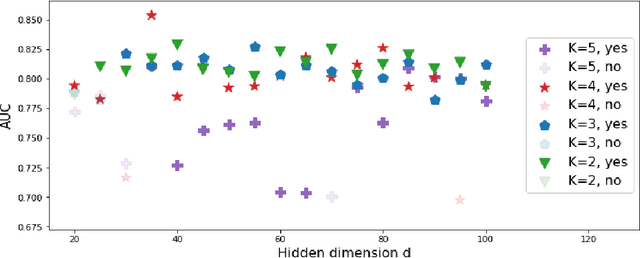
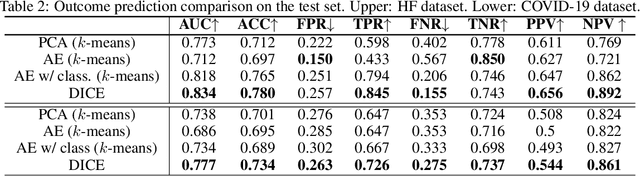
Abstract:We present deep significance clustering (DICE), a framework for jointly performing representation learning and clustering for "outcome-aware" stratification. DICE is intended to generate cluster membership that may be used to categorize a population by individual risk level for a targeted outcome. Following the representation learning and clustering steps, we embed the objective function in DICE with a constraint which requires a statistically significant association between the outcome and cluster membership of learned representations. DICE further includes a neural architecture search step to maximize both the likelihood of representation learning and outcome classification accuracy with cluster membership as the predictor. To demonstrate its utility in medicine for patient risk-stratification, the performance of DICE was evaluated using two datasets with different outcome ratios extracted from real-world electronic health records. Outcomes are defined as acute kidney injury (30.4\%) among a cohort of COVID-19 patients, and discharge disposition (36.8\%) among a cohort of heart failure patients, respectively. Extensive results demonstrate that DICE has superior performance as measured by the difference in outcome distribution across clusters, Silhouette score, Calinski-Harabasz index, and Davies-Bouldin index for clustering, and Area under the ROC Curve (AUC) for outcome classification compared to several baseline approaches.
Beyond The Text: Analysis of Privacy Statements through Syntactic and Semantic Role Labeling
Oct 01, 2020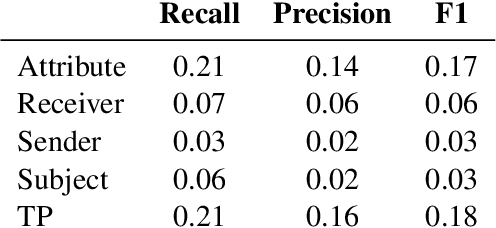
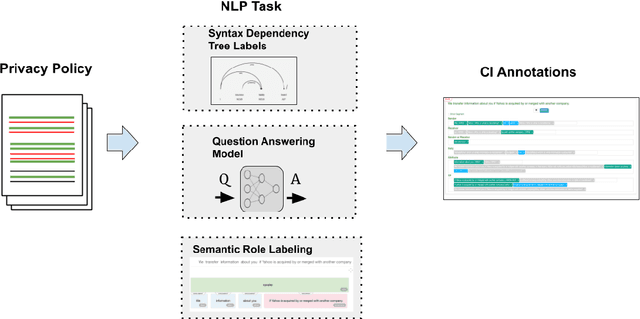
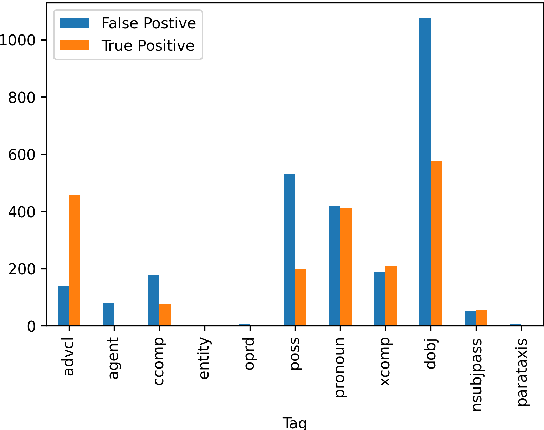

Abstract:This paper formulates a new task of extracting privacy parameters from a privacy policy, through the lens of Contextual Integrity, an established social theory framework for reasoning about privacy norms. Privacy policies, written by lawyers, are lengthy and often comprise incomplete and vague statements. In this paper, we show that traditional NLP tasks, including the recently proposed Question-Answering based solutions, are insufficient to address the privacy parameter extraction problem and provide poor precision and recall. We describe 4 different types of conventional methods that can be partially adapted to address the parameter extraction task with varying degrees of success: Hidden Markov Models, BERT fine-tuned models, Dependency Type Parsing (DP) and Semantic Role Labeling (SRL). Based on a detailed evaluation across 36 real-world privacy policies of major enterprises, we demonstrate that a solution combining syntactic DP coupled with type-specific SRL tasks provides the highest accuracy for retrieving contextual privacy parameters from privacy statements. We also observe that incorporating domain-specific knowledge is critical to achieving high precision and recall, thus inspiring new NLP research to address this important problem in the privacy domain.
What is Fair? Exploring Pareto-Efficiency for Fairness Constrained Classifiers
Oct 30, 2019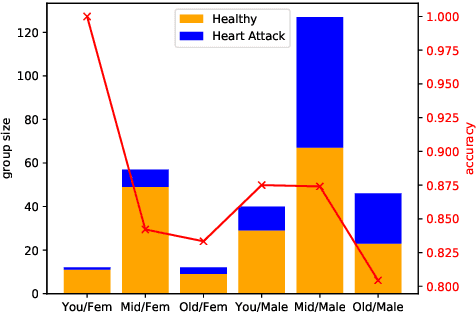
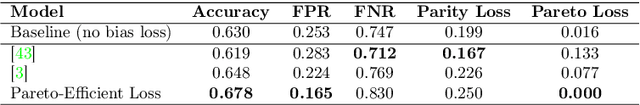
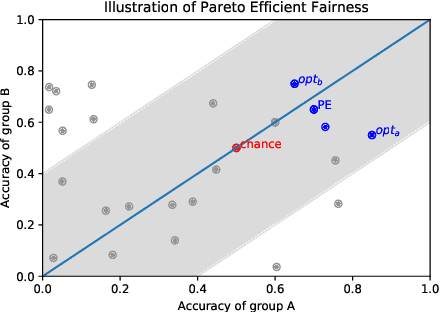
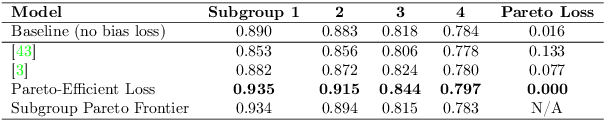
Abstract:The potential for learned models to amplify existing societal biases has been broadly recognized. Fairness-aware classifier constraints, which apply equality metrics of performance across subgroups defined on sensitive attributes such as race and gender, seek to rectify inequity but can yield non-uniform degradation in performance for skewed datasets. In certain domains, imbalanced degradation of performance can yield another form of unintentional bias. In the spirit of constructing fairness-aware algorithms as societal imperative, we explore an alternative: Pareto-Efficient Fairness (PEF). Theoretically, we prove that PEF identifies the operating point on the Pareto curve of subgroup performances closest to the fairness hyperplane, maximizing multiple subgroup accuracy. Empirically we demonstrate that PEF outperforms by achieving Pareto levels in accuracy for all subgroups compared to strict fairness constraints in several UCI datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge