Yexin Yang
MinMo: A Multimodal Large Language Model for Seamless Voice Interaction
Jan 10, 2025



Abstract:Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) and multimodal speech-text models have laid the groundwork for seamless voice interactions, enabling real-time, natural, and human-like conversations. Previous models for voice interactions are categorized as native and aligned. Native models integrate speech and text processing in one framework but struggle with issues like differing sequence lengths and insufficient pre-training. Aligned models maintain text LLM capabilities but are often limited by small datasets and a narrow focus on speech tasks. In this work, we introduce MinMo, a Multimodal Large Language Model with approximately 8B parameters for seamless voice interaction. We address the main limitations of prior aligned multimodal models. We train MinMo through multiple stages of speech-to-text alignment, text-to-speech alignment, speech-to-speech alignment, and duplex interaction alignment, on 1.4 million hours of diverse speech data and a broad range of speech tasks. After the multi-stage training, MinMo achieves state-of-the-art performance across various benchmarks for voice comprehension and generation while maintaining the capabilities of text LLMs, and also facilitates full-duplex conversation, that is, simultaneous two-way communication between the user and the system. Moreover, we propose a novel and simple voice decoder that outperforms prior models in voice generation. The enhanced instruction-following capabilities of MinMo supports controlling speech generation based on user instructions, with various nuances including emotions, dialects, and speaking rates, and mimicking specific voices. For MinMo, the speech-to-text latency is approximately 100ms, full-duplex latency is approximately 600ms in theory and 800ms in practice. The MinMo project web page is https://funaudiollm.github.io/minmo, and the code and models will be released soon.
CosyVoice 2: Scalable Streaming Speech Synthesis with Large Language Models
Dec 13, 2024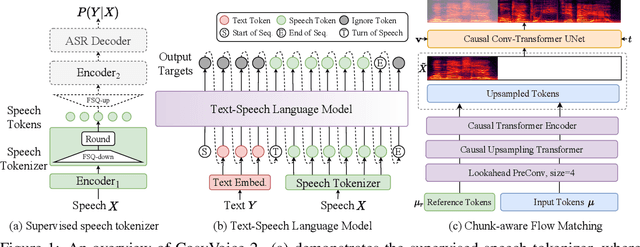

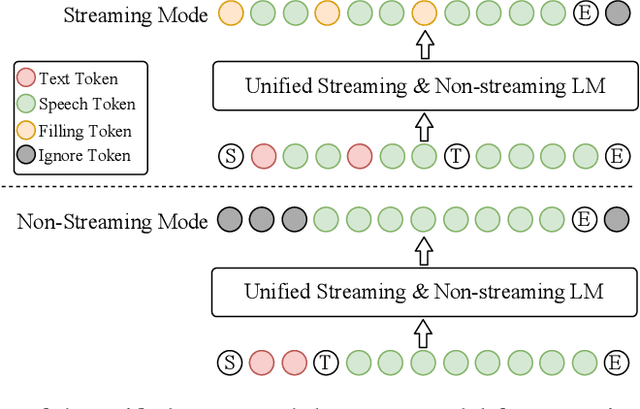

Abstract:In our previous work, we introduced CosyVoice, a multilingual speech synthesis model based on supervised discrete speech tokens. By employing progressive semantic decoding with two popular generative models, language models (LMs) and Flow Matching, CosyVoice demonstrated high prosody naturalness, content consistency, and speaker similarity in speech in-context learning. Recently, significant progress has been made in multi-modal large language models (LLMs), where the response latency and real-time factor of speech synthesis play a crucial role in the interactive experience. Therefore, in this report, we present an improved streaming speech synthesis model, CosyVoice 2, which incorporates comprehensive and systematic optimizations. Specifically, we introduce finite-scalar quantization to improve the codebook utilization of speech tokens. For the text-speech LM, we streamline the model architecture to allow direct use of a pre-trained LLM as the backbone. In addition, we develop a chunk-aware causal flow matching model to support various synthesis scenarios, enabling both streaming and non-streaming synthesis within a single model. By training on a large-scale multilingual dataset, CosyVoice 2 achieves human-parity naturalness, minimal response latency, and virtually lossless synthesis quality in the streaming mode. We invite readers to listen to the demos at https://funaudiollm.github.io/cosyvoice2.
CosyVoice: A Scalable Multilingual Zero-shot Text-to-speech Synthesizer based on Supervised Semantic Tokens
Jul 09, 2024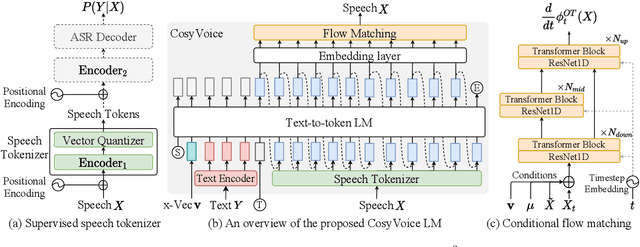
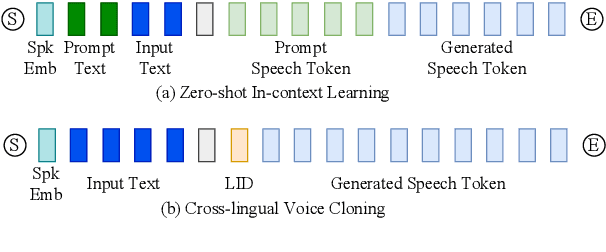
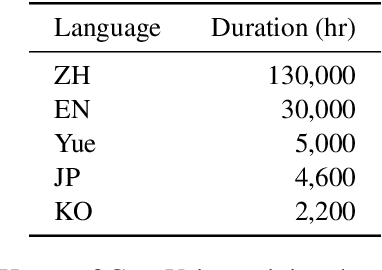
Abstract:Recent years have witnessed a trend that large language model (LLM) based text-to-speech (TTS) emerges into the mainstream due to their high naturalness and zero-shot capacity. In this paradigm, speech signals are discretized into token sequences, which are modeled by an LLM with text as prompts and reconstructed by a token-based vocoder to waveforms. Obviously, speech tokens play a critical role in LLM-based TTS models. Current speech tokens are learned in an unsupervised manner, which lacks explicit semantic information and alignment to the text. In this paper, we propose to represent speech with supervised semantic tokens, which are derived from a multilingual speech recognition model by inserting vector quantization into the encoder. Based on the tokens, we further propose a scalable zero-shot TTS synthesizer, CosyVoice, which consists of an LLM for text-to-token generation and a conditional flow matching model for token-to-speech synthesis. Experimental results show that supervised semantic tokens significantly outperform existing unsupervised tokens in terms of content consistency and speaker similarity for zero-shot voice cloning. Moreover, we find that utilizing large-scale data further improves the synthesis performance, indicating the scalable capacity of CosyVoice. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first attempt to involve supervised speech tokens into TTS models.
SeACo-Paraformer: A Non-Autoregressive ASR System with Flexible and Effective Hotword Customization Ability
Aug 16, 2023



Abstract:Hotword customization is one of the important issues remained in ASR field - it is of value to enable users of ASR systems to customize names of entities, persons and other phrases. The past few years have seen both implicit and explicit modeling strategies for ASR contextualization developed. While these approaches have performed adequately, they still exhibit certain shortcomings such as instability in effectiveness. In this paper we propose Semantic-augmented Contextual-Paraformer (SeACo-Paraformer) a novel NAR based ASR system with flexible and effective hotword customization ability. It combines the accuracy of the AED-based model, the efficiency of the NAR model, and the excellent performance in contextualization. In 50,000 hours industrial big data experiments, our proposed model outperforms strong baselines in customization and general ASR tasks. Besides, we explore an efficient way to filter large scale incoming hotwords for further improvement. The source codes and industrial models proposed and compared are all opened as well as two hotword test sets.
AISPEECH-SJTU accent identification system for the Accented English Speech Recognition Challenge
Feb 19, 2021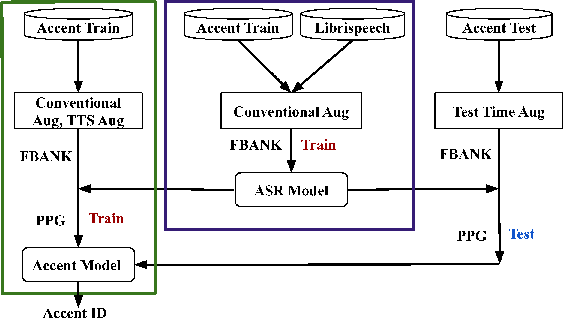
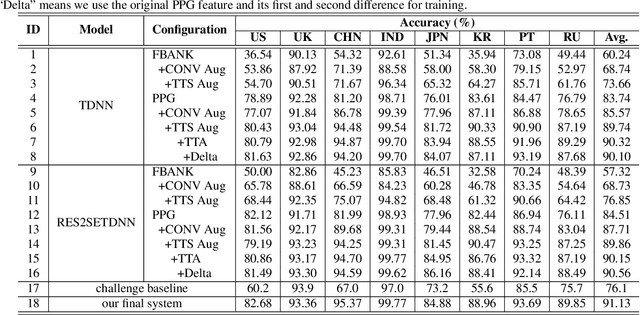
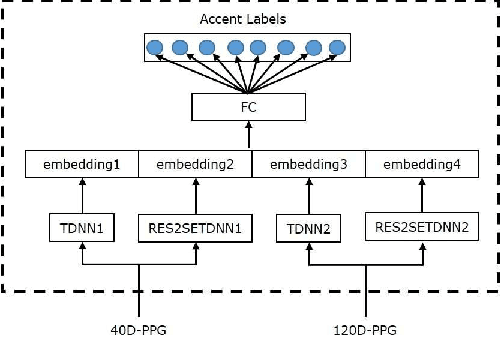
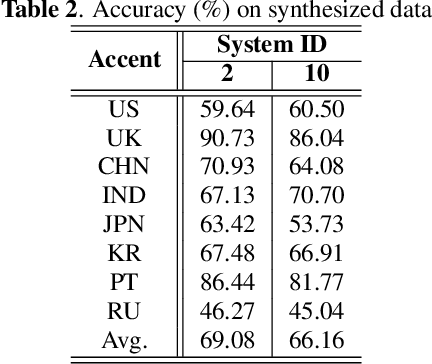
Abstract:This paper describes the AISpeech-SJTU system for the accent identification track of the Interspeech-2020 Accented English Speech Recognition Challenge. In this challenge track, only 160-hour accented English data collected from 8 countries and the auxiliary Librispeech dataset are provided for training. To build an accurate and robust accent identification system, we explore the whole system pipeline in detail. First, we introduce the ASR based phone posteriorgram (PPG) feature to accent identification and verify its efficacy. Then, a novel TTS based approach is carefully designed to augment the very limited accent training data for the first time. Finally, we propose the test time augmentation and embedding fusion schemes to further improve the system performance. Our final system is ranked first in the challenge and outperforms all the other participants by a large margin. The submitted system achieves 83.63\% average accuracy on the challenge evaluation data, ahead of the others by more than 10\% in absolute terms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge