William Thong
Query by Activity Video in the Wild
Nov 23, 2023Abstract:This paper focuses on activity retrieval from a video query in an imbalanced scenario. In current query-by-activity-video literature, a common assumption is that all activities have sufficient labelled examples when learning an embedding. This assumption does however practically not hold, as only a portion of activities have many examples, while other activities are only described by few examples. In this paper, we propose a visual-semantic embedding network that explicitly deals with the imbalanced scenario for activity retrieval. Our network contains two novel modules. The visual alignment module performs a global alignment between the input video and fixed-sized visual bank representations for all activities. The semantic module performs an alignment between the input video and fixed-sized semantic activity representations. By matching videos with both visual and semantic activity representations that are of equal size over all activities, we no longer ignore infrequent activities during retrieval. Experiments on a new imbalanced activity retrieval benchmark show the effectiveness of our approach for all types of activities.
Beyond Skin Tone: A Multidimensional Measure of Apparent Skin Color
Sep 10, 2023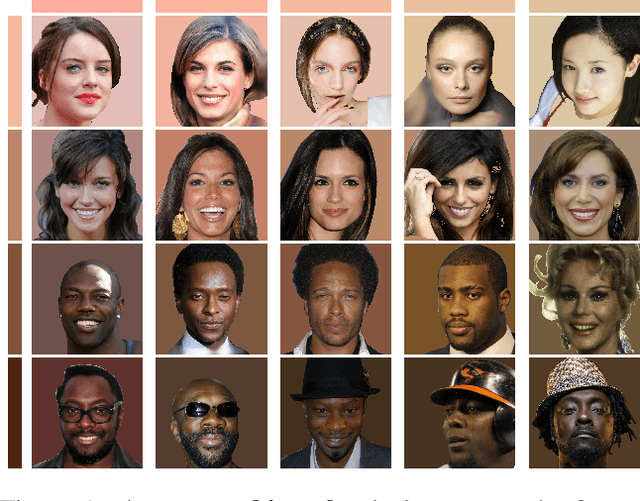
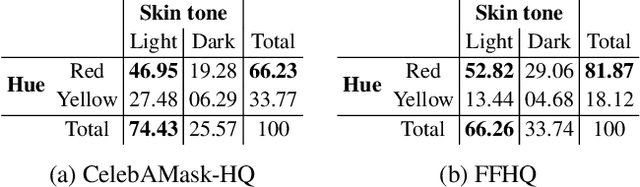

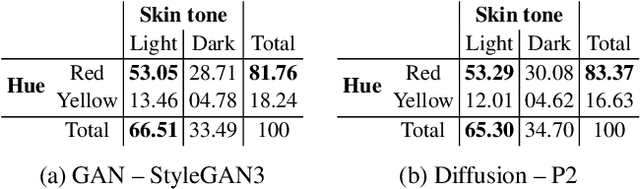
Abstract:This paper strives to measure apparent skin color in computer vision, beyond a unidimensional scale on skin tone. In their seminal paper Gender Shades, Buolamwini and Gebru have shown how gender classification systems can be biased against women with darker skin tones. Subsequently, fairness researchers and practitioners have adopted the Fitzpatrick skin type classification as a common measure to assess skin color bias in computer vision systems. While effective, the Fitzpatrick scale only focuses on the skin tone ranging from light to dark. Towards a more comprehensive measure of skin color, we introduce the hue angle ranging from red to yellow. When applied to images, the hue dimension reveals additional biases related to skin color in both computer vision datasets and models. We then recommend multidimensional skin color scales, relying on both skin tone and hue, for fairness assessments.
Ethical Considerations for Collecting Human-Centric Image Datasets
Feb 07, 2023
Abstract:Human-centric image datasets are critical to the development of computer vision technologies. However, recent investigations have foregrounded significant ethical issues related to privacy and bias, which have resulted in the complete retraction, or modification, of several prominent datasets. Recent works have tried to reverse this trend, for example, by proposing analytical frameworks for ethically evaluating datasets, the standardization of dataset documentation and curation practices, privacy preservation methodologies, as well as tools for surfacing and mitigating representational biases. Little attention, however, has been paid to the realities of operationalizing ethical data collection. To fill this gap, we present a set of key ethical considerations and practical recommendations for collecting more ethically-minded human-centric image data. Our research directly addresses issues of privacy and bias by contributing to the research community best practices for ethical data collection, covering purpose, privacy and consent, as well as diversity. We motivate each consideration by drawing on lessons from current practices, dataset withdrawals and audits, and analytical ethical frameworks. Our research is intended to augment recent scholarship, representing an important step toward more responsible data curation practices.
Content-Diverse Comparisons improve IQA
Nov 09, 2022



Abstract:Image quality assessment (IQA) forms a natural and often straightforward undertaking for humans, yet effective automation of the task remains highly challenging. Recent metrics from the deep learning community commonly compare image pairs during training to improve upon traditional metrics such as PSNR or SSIM. However, current comparisons ignore the fact that image content affects quality assessment as comparisons only occur between images of similar content. This restricts the diversity and number of image pairs that the model is exposed to during training. In this paper, we strive to enrich these comparisons with content diversity. Firstly, we relax comparison constraints, and compare pairs of images with differing content. This increases the variety of available comparisons. Secondly, we introduce listwise comparisons to provide a holistic view to the model. By including differentiable regularizers, derived from correlation coefficients, models can better adjust predicted scores relative to one another. Evaluation on multiple benchmarks, covering a wide range of distortions and image content, shows the effectiveness of our learning scheme for training image quality assessment models.
Feature and Label Embedding Spaces Matter in Addressing Image Classifier Bias
Oct 27, 2021



Abstract:This paper strives to address image classifier bias, with a focus on both feature and label embedding spaces. Previous works have shown that spurious correlations from protected attributes, such as age, gender, or skin tone, can cause adverse decisions. To balance potential harms, there is a growing need to identify and mitigate image classifier bias. First, we identify in the feature space a bias direction. We compute class prototypes of each protected attribute value for every class, and reveal an existing subspace that captures the maximum variance of the bias. Second, we mitigate biases by mapping image inputs to label embedding spaces. Each value of the protected attribute has its projection head where classes are embedded through a latent vector representation rather than a common one-hot encoding. Once trained, we further reduce in the feature space the bias effect by removing its direction. Evaluation on biased image datasets, for multi-class, multi-label and binary classifications, shows the effectiveness of tackling both feature and label embedding spaces in improving the fairness of the classifier predictions, while preserving classification performance.
NTIRE 2021 Challenge on Perceptual Image Quality Assessment
May 11, 2021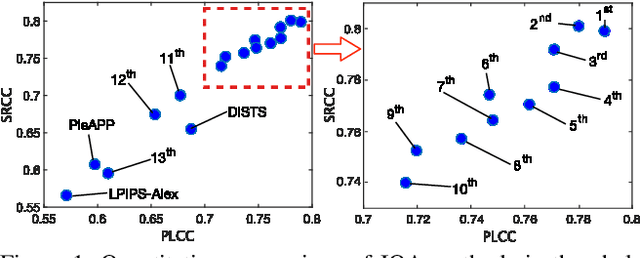
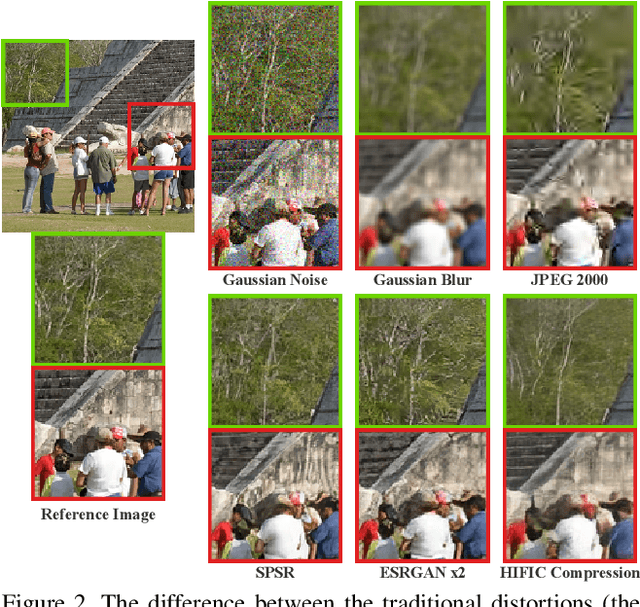
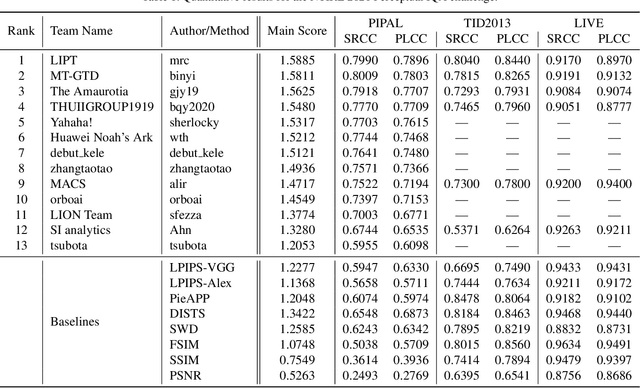

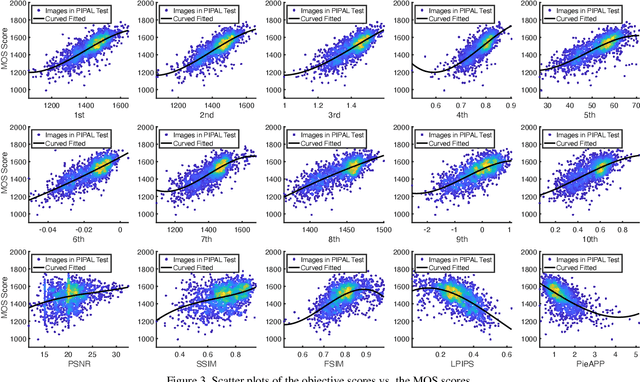
Abstract:This paper reports on the NTIRE 2021 challenge on perceptual image quality assessment (IQA), held in conjunction with the New Trends in Image Restoration and Enhancement workshop (NTIRE) workshop at CVPR 2021. As a new type of image processing technology, perceptual image processing algorithms based on Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) have produced images with more realistic textures. These output images have completely different characteristics from traditional distortions, thus pose a new challenge for IQA methods to evaluate their visual quality. In comparison with previous IQA challenges, the training and testing datasets in this challenge include the outputs of perceptual image processing algorithms and the corresponding subjective scores. Thus they can be used to develop and evaluate IQA methods on GAN-based distortions. The challenge has 270 registered participants in total. In the final testing stage, 13 participating teams submitted their models and fact sheets. Almost all of them have achieved much better results than existing IQA methods, while the winning method can demonstrate state-of-the-art performance.
Object Priors for Classifying and Localizing Unseen Actions
Apr 10, 2021



Abstract:This work strives for the classification and localization of human actions in videos, without the need for any labeled video training examples. Where existing work relies on transferring global attribute or object information from seen to unseen action videos, we seek to classify and spatio-temporally localize unseen actions in videos from image-based object information only. We propose three spatial object priors, which encode local person and object detectors along with their spatial relations. On top we introduce three semantic object priors, which extend semantic matching through word embeddings with three simple functions that tackle semantic ambiguity, object discrimination, and object naming. A video embedding combines the spatial and semantic object priors. It enables us to introduce a new video retrieval task that retrieves action tubes in video collections based on user-specified objects, spatial relations, and object size. Experimental evaluation on five action datasets shows the importance of spatial and semantic object priors for unseen actions. We find that persons and objects have preferred spatial relations that benefit unseen action localization, while using multiple languages and simple object filtering directly improves semantic matching, leading to state-of-the-art results for both unseen action classification and localization.
Bias-Awareness for Zero-Shot Learning the Seen and Unseen
Aug 25, 2020



Abstract:Generalized zero-shot learning recognizes inputs from both seen and unseen classes. Yet, existing methods tend to be biased towards the classes seen during training. In this paper, we strive to mitigate this bias. We propose a bias-aware learner to map inputs to a semantic embedding space for generalized zero-shot learning. During training, the model learns to regress to real-valued class prototypes in the embedding space with temperature scaling, while a margin-based bidirectional entropy term regularizes seen and unseen probabilities. Relying on a real-valued semantic embedding space provides a versatile approach, as the model can operate on different types of semantic information for both seen and unseen classes. Experiments are carried out on four benchmarks for generalized zero-shot learning and demonstrate the benefits of the proposed bias-aware classifier, both as a stand-alone method or in combination with generated features.
Open Cross-Domain Visual Search
Nov 19, 2019



Abstract:This paper introduces open cross-domain visual search, where categories in any target domain are retrieved based on queries from any source domain. Current works usually tackle cross-domain visual search as a domain adaptation problem. This limits the search to a closed setting, with one fixed source domain and one fixed target domain. To make the step towards an open setting where multiple visual domains are available, we introduce a simple yet effective approach. We formulate the search as one of mapping examples from every visual domain to a common semantic space, where categories are represented by hyperspherical prototypes. Cross-domain search is then performed by searching in the common space, regardless of which domains are used as source or target. Having separate mappings for every domain allows us to search in an open setting, and to incrementally add new domains over time without retraining existing mapping functions. Experimentally, we show our capability to perform open cross-domain visual search. Our approach is competitive with respect to traditional closed settings, where we obtain state-of-the-art results on six benchmarks for three sketch-based search tasks.
Cooperative Embeddings for Instance, Attribute and Category Retrieval
Apr 02, 2019



Abstract:The goal of this paper is to retrieve an image based on instance, attribute and category similarity notions. Different from existing works, which usually address only one of these entities in isolation, we introduce a cooperative embedding to integrate them while preserving their specific level of semantic representation. An algebraic structure defines a superspace filled with instances. Attributes are axis-aligned to form subspaces, while categories influence the arrangement of similar instances. These relationships enable them to cooperate for their mutual benefits for image retrieval. We derive a proxy-based softmax embedding loss to learn simultaneously all similarity measures in both superspace and subspaces. We evaluate our model on datasets from two different domains. Experiments on image retrieval tasks show the benefits of the cooperative embeddings for modeling multiple image similarities, and for discovering style evolution of instances between- and within-categories.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge