Wenge Liu
Integrative Decoding: Improve Factuality via Implicit Self-consistency
Oct 02, 2024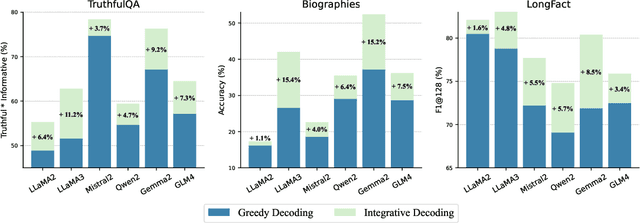
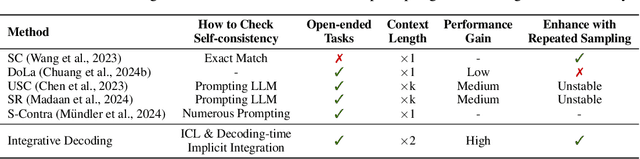
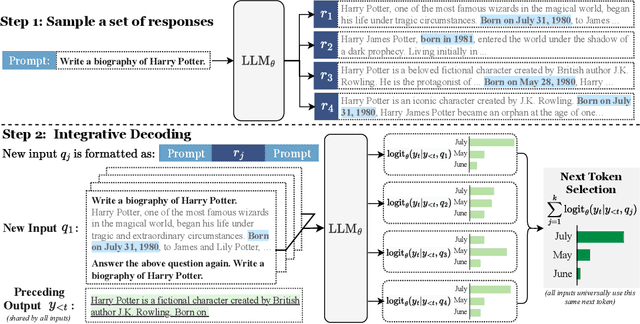
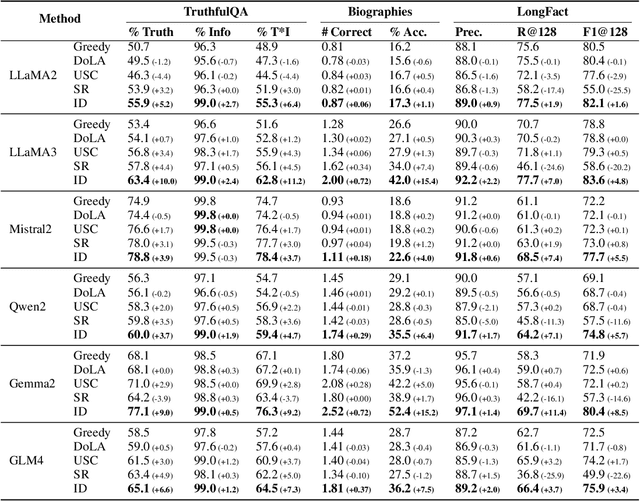
Abstract:Self-consistency-based approaches, which involve repeatedly sampling multiple outputs and selecting the most consistent one as the final response, prove to be remarkably effective in improving the factual accuracy of large language models. Nonetheless, existing methods usually have strict constraints on the task format, largely limiting their applicability. In this paper, we present Integrative Decoding (ID), to unlock the potential of self-consistency in open-ended generation tasks. ID operates by constructing a set of inputs, each prepended with a previously sampled response, and then processes them concurrently, with the next token being selected by aggregating of all their corresponding predictions at each decoding step. In essence, this simple approach implicitly incorporates self-consistency in the decoding objective. Extensive evaluation shows that ID consistently enhances factuality over a wide range of language models, with substantial improvements on the TruthfulQA (+11.2%), Biographies (+15.4%) and LongFact (+8.5%) benchmarks. The performance gains amplify progressively as the number of sampled responses increases, indicating the potential of ID to scale up with repeated sampling.
Evolving to be Your Soulmate: Personalized Dialogue Agents with Dynamically Adapted Personas
Jun 20, 2024
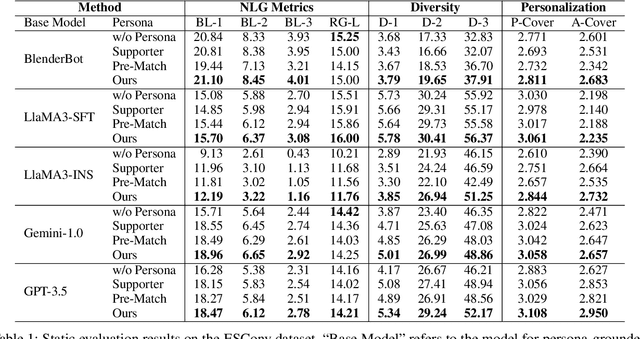
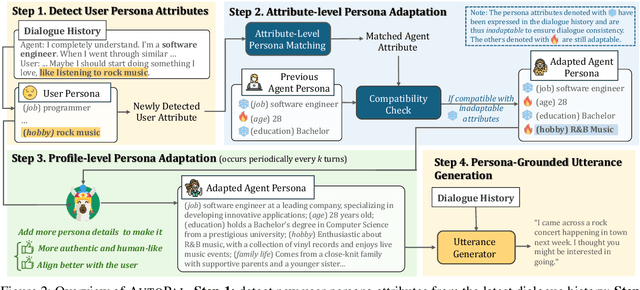
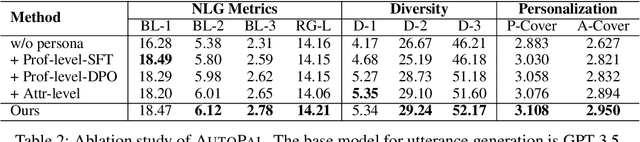
Abstract:Previous research on persona-based dialogue agents typically preset the agent's persona before deployment, which remains static thereafter. In this paper, we take a step further and explore a new paradigm called Self-evolving Personalized Dialogue Agents (SPDA), where the agent continuously evolves during the conversation to better align with the user's anticipation by dynamically adapting its persona. This paradigm could enable better personalization for each user, but also introduce unique challenges, which mainly lie in the process of persona adaptation. Two key issues include how to achieve persona alignment with the user and how to ensure smooth transition in the adaptation process. To address them, we propose a novel framework that refines the persona at hierarchical levels to progressively align better with the user in a controllable way. Experiments show that integrating the personas adapted by our framework consistently enhances personalization and overall dialogue performance across various base systems.
COOPER: Coordinating Specialized Agents towards a Complex Dialogue Goal
Dec 19, 2023



Abstract:In recent years, there has been a growing interest in exploring dialogues with more complex goals, such as negotiation, persuasion, and emotional support, which go beyond traditional service-focused dialogue systems. Apart from the requirement for much more sophisticated strategic reasoning and communication skills, a significant challenge of these tasks lies in the difficulty of objectively measuring the achievement of their goals in a quantifiable way, making it difficult for existing research to directly optimize the dialogue procedure towards them. In our work, we emphasize the multifaceted nature of complex dialogue goals and argue that it is more feasible to accomplish them by comprehensively considering and jointly promoting their different aspects. To this end, we propose a novel dialogue framework, Cooper, which coordinates multiple specialized agents, each dedicated to a specific dialogue goal aspect separately, to approach the complex objective. Through this divide-and-conquer manner, we make complex dialogue goals more approachable and elicit greater intelligence via the collaboration of individual agents. Experiments on persuasion and emotional support dialogues demonstrate the superiority of our method over a set of competitive baselines.
Improving Multi-turn Emotional Support Dialogue Generation with Lookahead Strategy Planning
Oct 09, 2022



Abstract:Providing Emotional Support (ES) to soothe people in emotional distress is an essential capability in social interactions. Most existing researches on building ES conversation systems only considered single-turn interactions with users, which was over-simplified. In comparison, multi-turn ES conversation systems can provide ES more effectively, but face several new technical challenges, including: (1) how to adopt appropriate support strategies to achieve the long-term dialogue goal of comforting the user's emotion; (2) how to dynamically model the user's state. In this paper, we propose a novel system MultiESC to address these issues. For strategy planning, drawing inspiration from the A* search algorithm, we propose lookahead heuristics to estimate the future user feedback after using particular strategies, which helps to select strategies that can lead to the best long-term effects. For user state modeling, MultiESC focuses on capturing users' subtle emotional expressions and understanding their emotion causes. Extensive experiments show that MultiESC significantly outperforms competitive baselines in both dialogue generation and strategy planning. Our codes are available at https://github.com/lwgkzl/MultiESC.
"My nose is running.""Are you also coughing?": Building A Medical Diagnosis Agent with Interpretable Inquiry Logics
May 02, 2022



Abstract:With the rise of telemedicine, the task of developing Dialogue Systems for Medical Diagnosis (DSMD) has received much attention in recent years. Different from early researches that needed to rely on extra human resources and expertise to help construct the system, recent researches focused on how to build DSMD in a purely data-driven manner. However, the previous data-driven DSMD methods largely overlooked the system interpretability, which is critical for a medical application, and they also suffered from the data sparsity issue at the same time. In this paper, we explore how to bring interpretability to data-driven DSMD. Specifically, we propose a more interpretable decision process to implement the dialogue manager of DSMD by reasonably mimicking real doctors' inquiry logics, and we devise a model with highly transparent components to conduct the inference. Moreover, we collect a new DSMD dataset, which has a much larger scale, more diverse patterns and is of higher quality than the existing ones. The experiments show that our method obtains 7.7%, 10.0%, 3.0% absolute improvement in diagnosis accuracy respectively on three datasets, demonstrating the effectiveness of its rational decision process and model design. Our codes and the GMD-12 dataset are available at https://github.com/lwgkzl/BR-Agent.
MedDG: A Large-scale Medical Consultation Dataset for Building Medical Dialogue System
Oct 15, 2020



Abstract:Developing conversational agents to interact with patients and provide primary clinical advice has attracted increasing attention due to its huge application potential, especially in the time of COVID-19 Pandemic. However, the training of end-to-end neural-based medical dialogue system is restricted by an insufficient quantity of medical dialogue corpus. In this work, we make the first attempt to build and release a large-scale high-quality Medical Dialogue dataset related to 12 types of common Gastrointestinal diseases named MedDG, with more than 17K conversations collected from the online health consultation community. Five different categories of entities, including diseases, symptoms, attributes, tests, and medicines, are annotated in each conversation of MedDG as additional labels. To push forward the future research on building expert-sensitive medical dialogue system, we proposes two kinds of medical dialogue tasks based on MedDG dataset. One is the next entity prediction and the other is the doctor response generation. To acquire a clear comprehension on these two medical dialogue tasks, we implement several state-of-the-art benchmarks, as well as design two dialogue models with a further consideration on the predicted entities. Experimental results show that the pre-train language models and other baselines struggle on both tasks with poor performance in our dataset, and the response quality can be enhanced with the help of auxiliary entity information. From human evaluation, the simple retrieval model outperforms several state-of-the-art generative models, indicating that there still remains a large room for improvement on generating medically meaningful responses.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge