Weilong Chen
Recurrent Feature Mining and Keypoint Mixup Padding for Category-Agnostic Pose Estimation
Mar 27, 2025Abstract:Category-agnostic pose estimation aims to locate keypoints on query images according to a few annotated support images for arbitrary novel classes. Existing methods generally extract support features via heatmap pooling, and obtain interacted features from support and query via cross-attention. Hence, these works neglect to mine fine-grained and structure-aware (FGSA) features from both support and query images, which are crucial for pixel-level keypoint localization. To this end, we propose a novel yet concise framework, which recurrently mines FGSA features from both support and query images. Specifically, we design a FGSA mining module based on deformable attention mechanism. On the one hand, we mine fine-grained features by applying deformable attention head over multi-scale feature maps. On the other hand, we mine structure-aware features by offsetting the reference points of keypoints to their linked keypoints. By means of above module, we recurrently mine FGSA features from support and query images, and thus obtain better support features and query estimations. In addition, we propose to use mixup keypoints to pad various classes to a unified keypoint number, which could provide richer supervision than the zero padding used in existing works. We conduct extensive experiments and in-depth studies on large-scale MP-100 dataset, and outperform SOTA method dramatically (+3.2\%PCK@0.05). Code is avaiable at https://github.com/chenbys/FMMP.
Large-Scale AI in Telecom: Charting the Roadmap for Innovation, Scalability, and Enhanced Digital Experiences
Mar 06, 2025Abstract:This white paper discusses the role of large-scale AI in the telecommunications industry, with a specific focus on the potential of generative AI to revolutionize network functions and user experiences, especially in the context of 6G systems. It highlights the development and deployment of Large Telecom Models (LTMs), which are tailored AI models designed to address the complex challenges faced by modern telecom networks. The paper covers a wide range of topics, from the architecture and deployment strategies of LTMs to their applications in network management, resource allocation, and optimization. It also explores the regulatory, ethical, and standardization considerations for LTMs, offering insights into their future integration into telecom infrastructure. The goal is to provide a comprehensive roadmap for the adoption of LTMs to enhance scalability, performance, and user-centric innovation in telecom networks.
Trend-Based SAC Beam Control Method with Zero-Shot in Superconducting Linear Accelerator
May 25, 2023Abstract:The superconducting linear accelerator is a highly flexiable facility for modern scientific discoveries, necessitating weekly reconfiguration and tuning. Accordingly, minimizing setup time proves essential in affording users with ample experimental time. We propose a trend-based soft actor-critic(TBSAC) beam control method with strong robustness, allowing the agents to be trained in a simulated environment and applied to the real accelerator directly with zero-shot. To validate the effectiveness of our method, two different typical beam control tasks were performed on China Accelerator Facility for Superheavy Elements (CAFe II) and a light particle injector(LPI) respectively. The orbit correction tasks were performed in three cryomodules in CAFe II seperately, the time required for tuning has been reduced to one-tenth of that needed by human experts, and the RMS values of the corrected orbit were all less than 1mm. The other transmission efficiency optimization task was conducted in the LPI, our agent successfully optimized the transmission efficiency of radio-frequency quadrupole(RFQ) to over $85\%$ within 2 minutes. The outcomes of these two experiments offer substantiation that our proposed TBSAC approach can efficiently and effectively accomplish beam commissioning tasks while upholding the same standard as skilled human experts. As such, our method exhibits potential for future applications in other accelerator commissioning fields.
Deep Reinforcement Learning-Assisted Federated Learning for Robust Short-term Utility Demand Forecasting in Electricity Wholesale Markets
Jun 23, 2022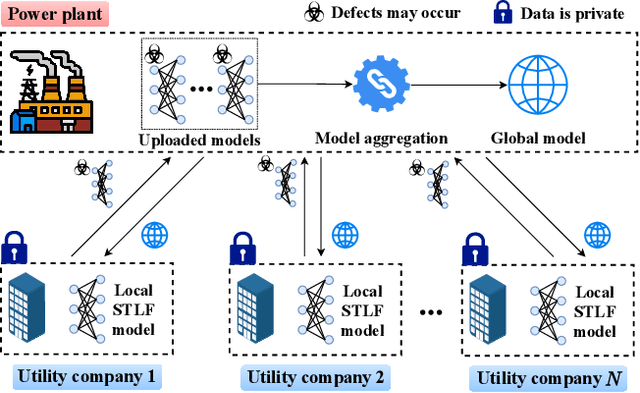
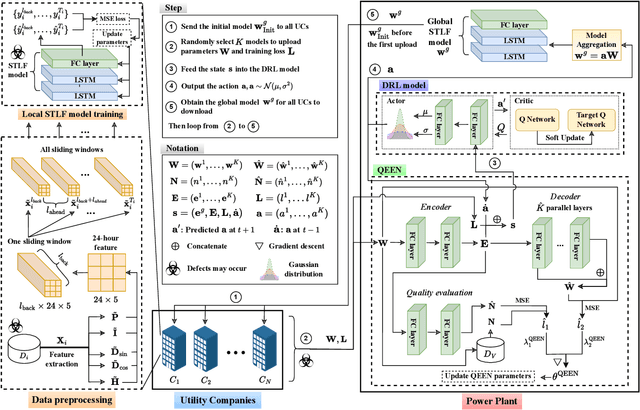
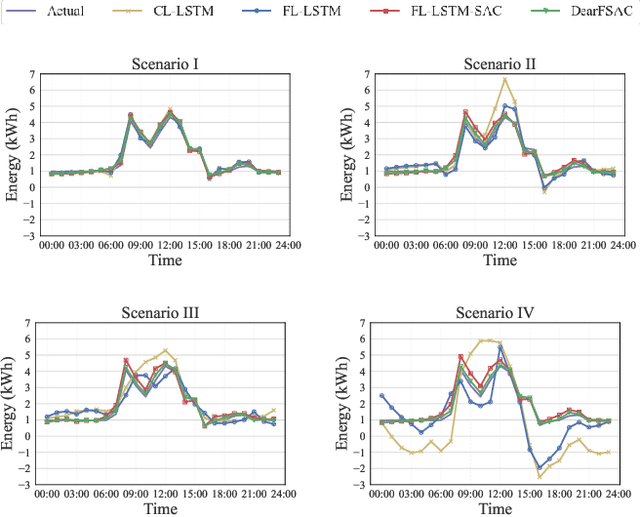
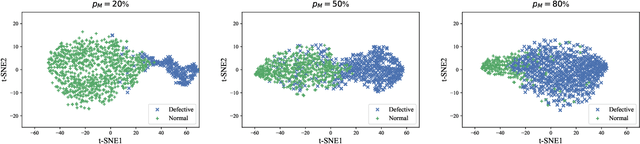
Abstract:Short-term load forecasting (STLF) plays a significant role in the operation of electricity trading markets. Considering the growing concern of data privacy, federated learning (FL) is increasingly adopted to train STLF models for utility companies (UCs) in recent research. Inspiringly, in wholesale markets, as it is not realistic for power plants (PPs) to access UCs' data directly, FL is definitely a feasible solution of obtaining an accurate STLF model for PPs. However, due to FL's distributed nature and intense competition among UCs, defects increasingly occur and lead to poor performance of the STLF model, indicating that simply adopting FL is not enough. In this paper, we propose a DRL-assisted FL approach, DEfect-AwaRe federated soft actor-critic (DearFSAC), to robustly train an accurate STLF model for PPs to forecast precise short-term utility electricity demand. Firstly. we design a STLF model based on long short-term memory (LSTM) using just historical load data and time data. Furthermore, considering the uncertainty of defects occurrence, a deep reinforcement learning (DRL) algorithm is adopted to assist FL by alleviating model degradation caused by defects. In addition, for faster convergence of FL training, an auto-encoder is designed for both dimension reduction and quality evaluation of uploaded models. In the simulations, we validate our approach on real data of Helsinki's UCs in 2019. The results show that DearFSAC outperforms all the other approaches no matter if defects occur or not.
DearFSAC: An Approach to Optimizing Unreliable Federated Learning via Deep Reinforcement Learning
Jan 30, 2022Abstract:In federated learning (FL), model aggregation has been widely adopted for data privacy. In recent years, assigning different weights to local models has been used to alleviate the FL performance degradation caused by differences between local datasets. However, when various defects make the FL process unreliable, most existing FL approaches expose weak robustness. In this paper, we propose the DEfect-AwaRe federated soft actor-critic (DearFSAC) to dynamically assign weights to local models to improve the robustness of FL. The deep reinforcement learning algorithm soft actor-critic is adopted for near-optimal performance and stable convergence. Besides, an auto-encoder is trained to output low-dimensional embedding vectors that are further utilized to evaluate model quality. In the experiments, DearFSAC outperforms three existing approaches on four datasets for both independent and identically distributed (IID) and non-IID settings under defective scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge