Vincenzo Lippiello
HATPIC: An Open-Source Single Axis Haptic Joystick for Robotic Development
Feb 24, 2025
Abstract:Humans process significantly more information through the sense of touch than through vision. Consequently, haptics for telemanipulation is poised to become essential in the coming years, as it offers operators an additional sensory channel crucial for interpretation in extreme conditions. However, current haptic device setups are either difficult to access or provide low-quality force feedback rendering. This work proposes the design of a single-axis, open-source setup for telemanipulation development, aimed at addressing these issues. We first introduce the haptic device and demonstrate its integration with common robotic tools. The proposed joystick has the potential to accelerate the development and deployment of haptic technology in a wide range of robotics applications, enhancing operator feedback and control.
Assisted Physical Interaction: Autonomous Aerial Robots with Neural Network Detection, Navigation, and Safety Layers
Oct 21, 2024



Abstract:The paper introduces a novel framework for safe and autonomous aerial physical interaction in industrial settings. It comprises two main components: a neural network-based target detection system enhanced with edge computing for reduced onboard computational load, and a control barrier function (CBF)-based controller for safe and precise maneuvering. The target detection system is trained on a dataset under challenging visual conditions and evaluated for accuracy across various unseen data with changing lighting conditions. Depth features are utilized for target pose estimation, with the entire detection framework offloaded into low-latency edge computing. The CBF-based controller enables the UAV to converge safely to the target for precise contact. Simulated evaluations of both the controller and target detection are presented, alongside an analysis of real-world detection performance.
* 8 pages,14 figures, ICUAS 2024
Design of a Flexible Robot Arm for Safe Aerial Physical Interaction
Oct 21, 2024



Abstract:This paper introduces a novel compliant mechanism combining lightweight and energy dissipation for aerial physical interaction. Weighting 400~g at take-off, the mechanism is actuated in the forward body direction, enabling precise position control for force interaction and various other aerial manipulation tasks. The robotic arm, structured as a closed-loop kinematic chain, employs two deported servomotors. Each joint is actuated with a single tendon for active motion control in compression of the arm at the end-effector. Its elasto-mechanical design reduces weight and provides flexibility, allowing passive-compliant interactions without impacting the motors' integrity. Notably, the arm's damping can be adjusted based on the proposed inner frictional bulges. Experimental applications showcase the aerial system performance in both free-flight and physical interaction. The presented work may open safer applications for \ac{MAV} in real environments subject to perturbations during interaction.
* 6 pages, 7 figures, ROBOSOFT 2024
Design and Control of an Omnidirectional Aerial Robot with a Miniaturized Haptic Joystick for Physical Interaction
Oct 11, 2024Abstract:Fully actuated aerial robot proved their superiority for Aerial Physical Interaction (APhI) over the past years. This work proposes a minimal setup for aerial telemanipulation, enhancing accessibility of these technologies. The design and the control of a 6-DoF joystick with 4-DoF haptic feedback is detailed. It is the first haptic device with standard Remote Controller (RC) form factor for APhI. By miniaturizing haptic device, it enhances RC with the sense of touch, increasing physical awareness. The goal is to give operators an extra sense, other than vision and sound, to help to perform safe APhI. To the best of the authors knowledge, this is the first teleoperation system able to decouple each single axis input command. On the omnidirectional quadrotor, by reducing the number of components with a new design, we aim a simplified maintenance, and improved force and thrust to weight ratio. Open-sourced physic based simulation and successful preliminary flight tests highlighted the tool as promising for future APhI applications.
Development of a semi-autonomous framework for NDT inspection with a tilting aerial platform
Jul 03, 2024
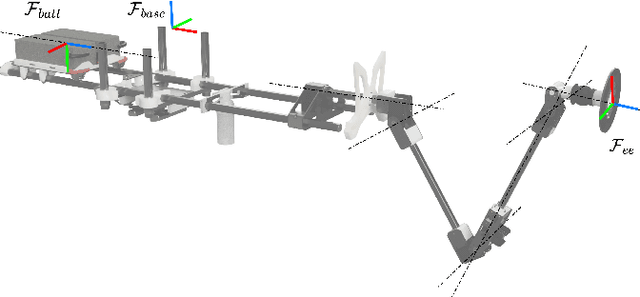
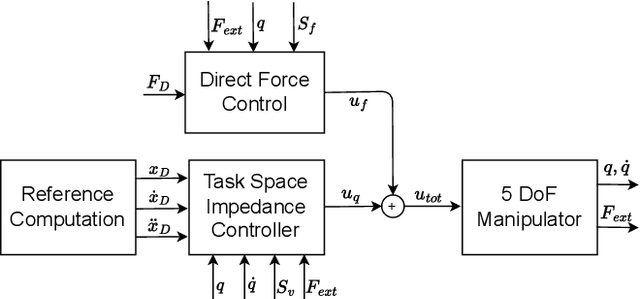
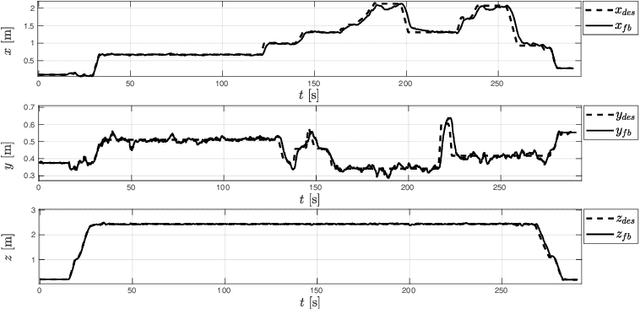
Abstract:This letter investigates the problem of controlling an aerial manipulator, composed of an omnidirectional tilting drone equipped with a five-degrees-of-freedom robotic arm. The robot has to interact with the environment to inspect structures and perform non-destructive measurements. A parallel force-impedance control technique is developed to establish contact with the designed surface with a desired force profile. During the interaction, a pushing phase is required to create a vacuum between the surface and the echometer sensor mounted at the end-effector, to measure the thickness of the interaction surface. Repetitive measures are performed to show the repeatability of the algorithm.
AERIAL-CORE: AI-Powered Aerial Robots for Inspection and Maintenance of Electrical Power Infrastructures
Jan 04, 2024Abstract:Large-scale infrastructures are prone to deterioration due to age, environmental influences, and heavy usage. Ensuring their safety through regular inspections and maintenance is crucial to prevent incidents that can significantly affect public safety and the environment. This is especially pertinent in the context of electrical power networks, which, while essential for energy provision, can also be sources of forest fires. Intelligent drones have the potential to revolutionize inspection and maintenance, eliminating the risks for human operators, increasing productivity, reducing inspection time, and improving data collection quality. However, most of the current methods and technologies in aerial robotics have been trialed primarily in indoor testbeds or outdoor settings under strictly controlled conditions, always within the line of sight of human operators. Additionally, these methods and technologies have typically been evaluated in isolation, lacking comprehensive integration. This paper introduces the first autonomous system that combines various innovative aerial robots. This system is designed for extended-range inspections beyond the visual line of sight, features aerial manipulators for maintenance tasks, and includes support mechanisms for human operators working at elevated heights. The paper further discusses the successful validation of this system on numerous electrical power lines, with aerial robots executing flights over 10 kilometers away from their ground control stations.
Beyond Jacobian-based tasks: Extended set-based tasks for multi-task execution and prioritization
Oct 24, 2023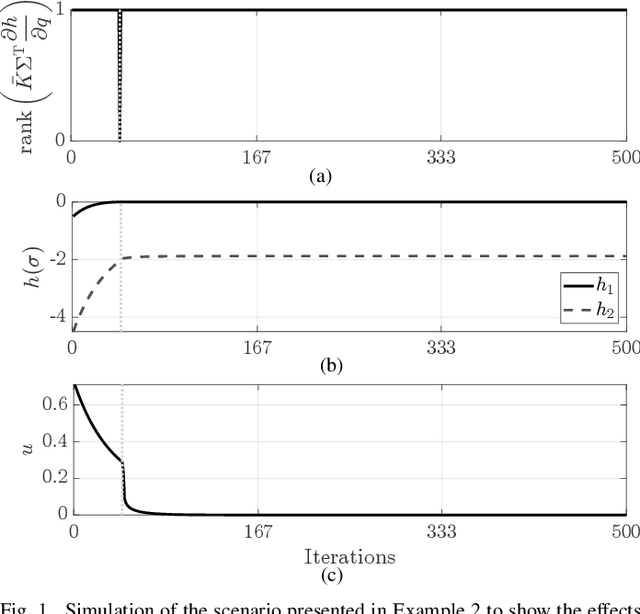
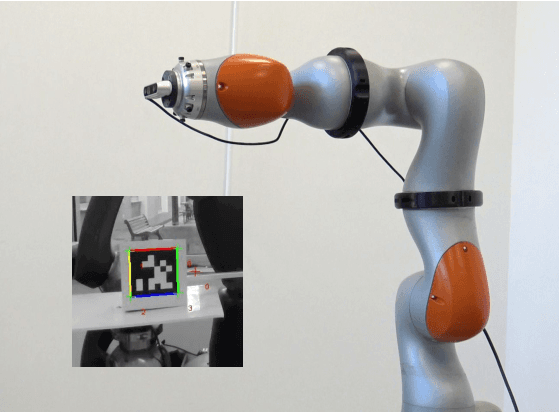
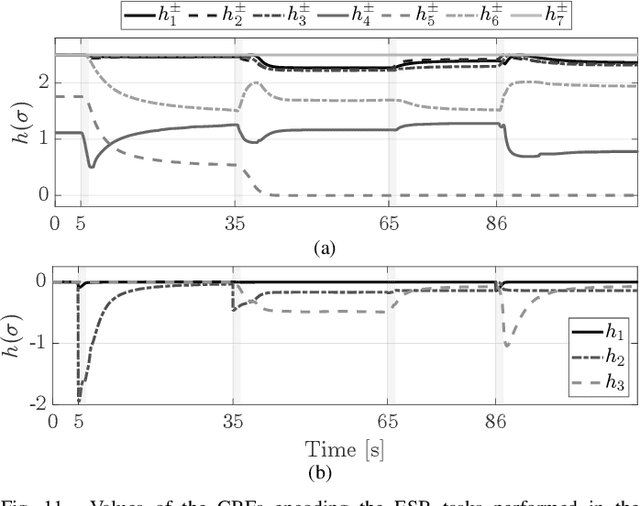
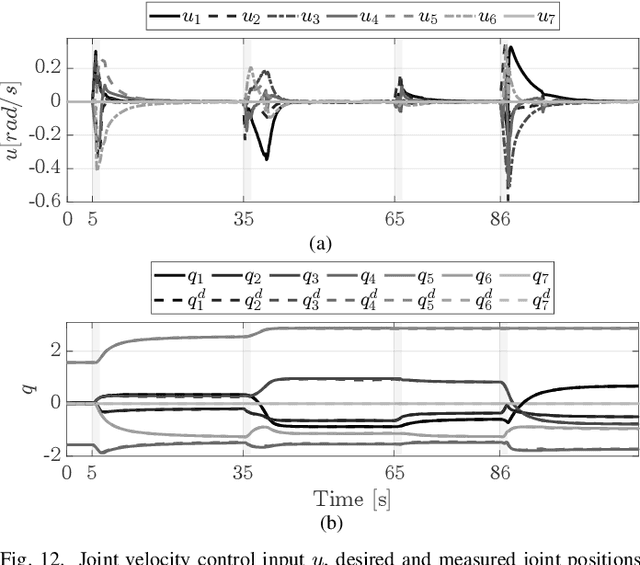
Abstract:The ability of executing multiple tasks simultaneously is an important feature of redundant robotic systems. As a matter of fact, complex behaviors can often be obtained as a result of the execution of several tasks. Moreover, in safety-critical applications, tasks designed to ensure the safety of the robot and its surroundings have to be executed along with other nominal tasks. In such cases, it is also important to prioritize the former over the latter. In this paper, we formalize the definition of extended set-based tasks, i.e., tasks which can be executed by rendering subsets of the task space asymptotically stable or forward invariant. We propose a mathematical representation of such tasks that allows for the execution of more complex and time-varying prioritized stacks of tasks using kinematic and dynamic robot models alike. We present and analyze an optimization-based framework which is computationally efficient, accounts for input bounds, and allows for the stable execution of time-varying prioritized stacks of extended set-based tasks. The proposed framework is validated using extensive simulations and experiments with robotic manipulators.
Multimodal Interaction with Multiple Co-located Drones in Search and Rescue Missions
May 24, 2016
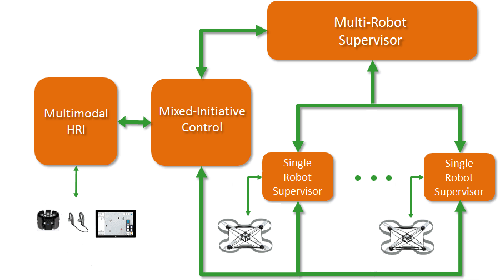
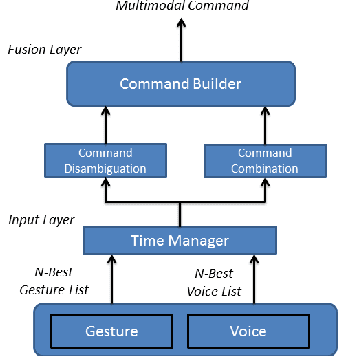
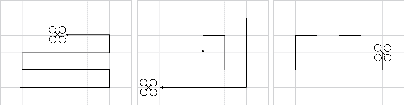
Abstract:We present a multimodal interaction framework suitable for a human rescuer that operates in proximity with a set of co-located drones during search missions. This work is framed in the context of the SHERPA project whose goal is to develop a mixed ground and aerial robotic platform to support search and rescue activities in a real-world alpine scenario. Differently from typical human-drone interaction settings, here the operator is not fully dedicated to the drones, but involved in search and rescue tasks, hence only able to provide sparse, incomplete, although high-value, instructions to the robots. This operative scenario requires a human-interaction framework that supports multimodal communication along with an effective and natural mixed-initiative interaction between the human and the robots. In this work, we illustrate the domain and the proposed multimodal interaction framework discussing the system at work in a simulated case study.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge