Van Tung Pham
A Comprehensive Solution to Connect Speech Encoder and Large Language Model for ASR
Jun 25, 2024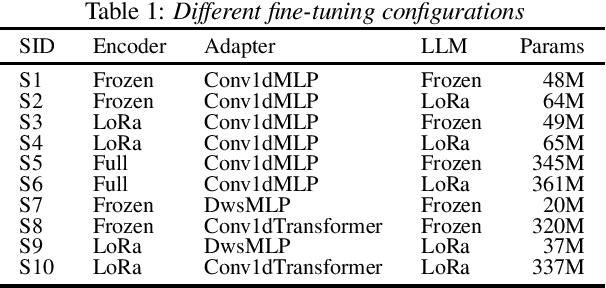
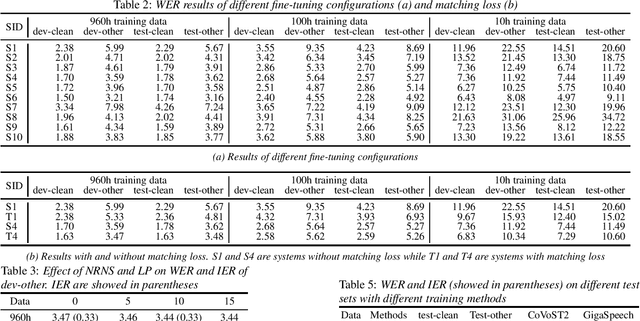
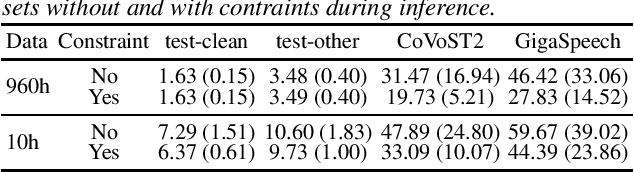
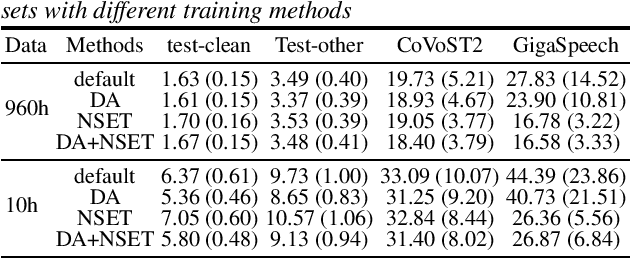
Abstract:Recent works have shown promising results in connecting speech encoders to large language models (LLMs) for speech recognition. However, several limitations persist, including limited fine-tuning options, a lack of mechanisms to enforce speech-text alignment, and high insertion errors especially in domain mismatch conditions. This paper presents a comprehensive solution to address these issues. We begin by investigating more thoughtful fine-tuning schemes. Next, we propose a matching loss to enhance alignment between modalities. Finally, we explore training and inference methods to mitigate high insertion errors. Experimental results on the Librispeech corpus demonstrate that partially fine-tuning the encoder and LLM using parameter-efficient methods, such as LoRA, is the most cost-effective approach. Additionally, the matching loss improves modality alignment, enhancing performance. The proposed training and inference methods significantly reduce insertion errors.
RdimKD: Generic Distillation Paradigm by Dimensionality Reduction
Dec 14, 2023



Abstract:Knowledge Distillation (KD) emerges as one of the most promising compression technologies to run advanced deep neural networks on resource-limited devices. In order to train a small network (student) under the guidance of a large network (teacher), the intuitive method is regularizing the feature maps or logits of the student using the teacher's information. However, existing methods either over-restrict the student to learn all information from the teacher, which lead to some bad local minimum, or use various fancy and elaborate modules to process and align features, which are complex and lack generality. In this work, we proposed an abstract and general paradigm for the KD task, referred to as DIMensionality Reduction KD (RdimKD), which solely relies on dimensionality reduction, with a very minor modification to naive L2 loss. RdimKD straightforwardly utilizes a projection matrix to project both the teacher's and student's feature maps onto a low-dimensional subspace, which are then optimized during training. RdimKD achieves the goal in the simplest way that not only does the student get valuable information from the teacher, but it also ensures sufficient flexibility to adapt to the student's low-capacity reality. Our extensive empirical findings indicate the effectiveness of RdimKD across various learning tasks and diverse network architectures.
Improving short-video speech recognition using random utterance concatenation
Oct 28, 2022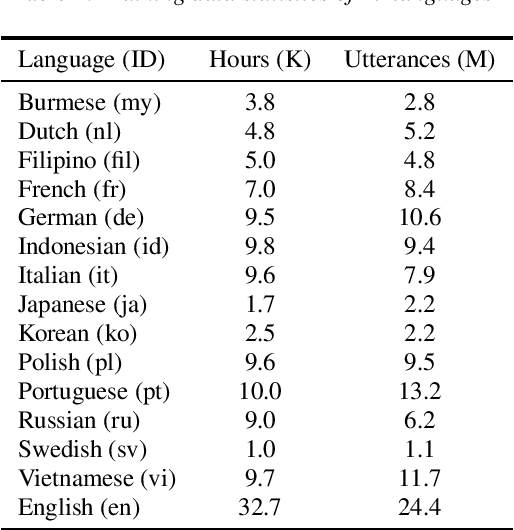
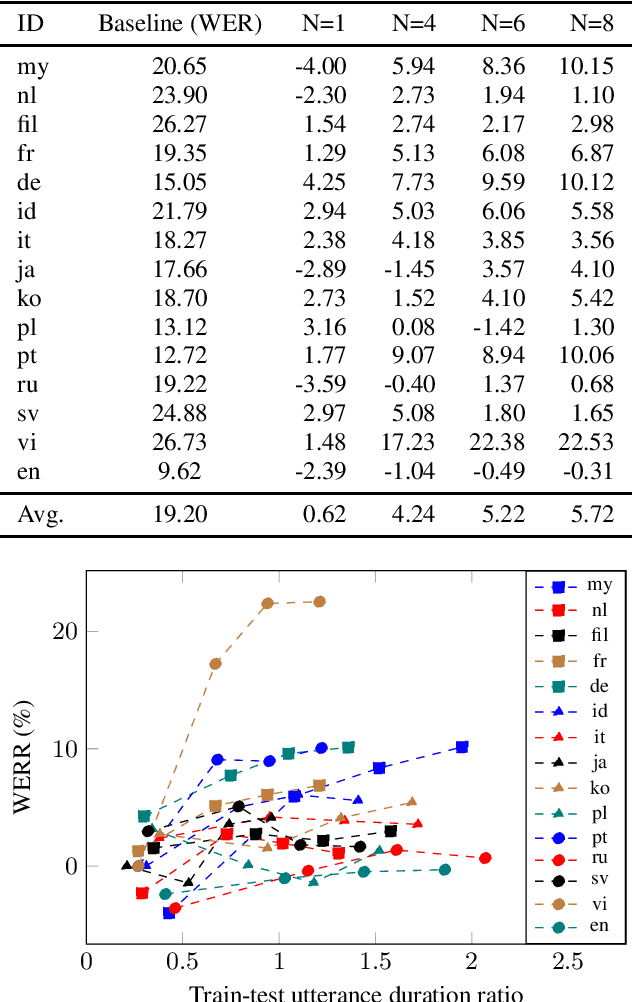
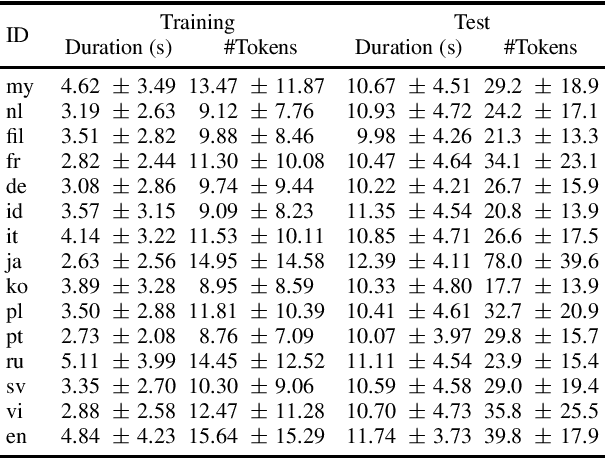
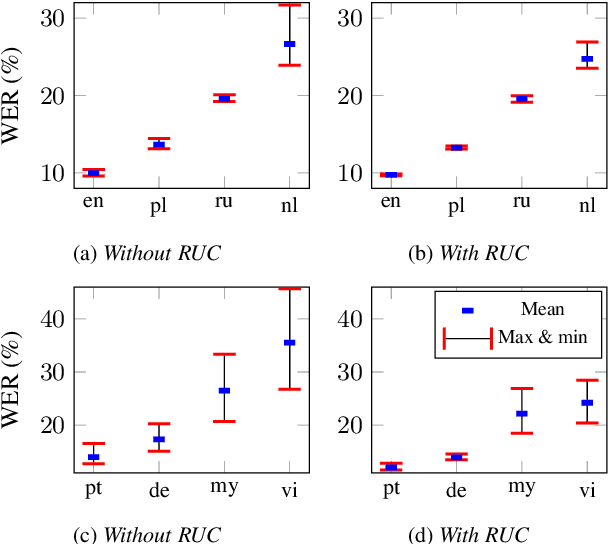
Abstract:One of the limitations in end-to-end automatic speech recognition framework is its performance would be compromised if train-test utterance lengths are mismatched. In this paper, we propose a random utterance concatenation (RUC) method to alleviate train-test utterance length mismatch issue for short-video speech recognition task. Specifically, we are motivated by observations our human-transcribed training utterances tend to be much shorter for short-video spontaneous speech (~3 seconds on average), while our test utterance generated from voice activity detection front-end is much longer (~10 seconds on average). Such a mismatch can lead to sub-optimal performance. Experimentally, by using the proposed RUC method, the best word error rate reduction (WERR) can be achieved with around three fold training data size increase as well as two utterance concatenation for each. In practice, the proposed method consistently outperforms the strong baseline models, where 3.64% average WERR is achieved on 14 languages.
Multitask-Based Joint Learning Approach To Robust ASR For Radio Communication Speech
Jul 22, 2021
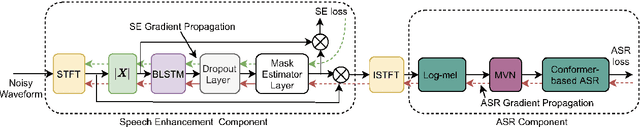

Abstract:To realize robust end-to-end Automatic Speech Recognition(E2E ASR) under radio communication condition, we propose a multitask-based method to joint train a Speech Enhancement (SE) module as the front-end and an E2E ASR model as the back-end in this paper. One of the advantage of the proposed method is that the entire system can be trained from scratch. Different from prior works, either component here doesn't need to perform pre-training and fine-tuning processes separately. Through analysis, we found that the success of the proposed method lies in the following aspects. Firstly, multitask learning is essential, that is the SE network is not only learning to produce more Intelligent speech, it is also aimed to generate speech that is beneficial to recognition. Secondly, we also found speech phase preserved from noisy speech is critical for improving ASR performance. Thirdly, we propose a dual channel data augmentation training method to obtain further improvement.Specifically, we combine the clean and enhanced speech to train the whole system. We evaluate the proposed method on the RATS English data set, achieving a relative WER reduction of 4.6% with the joint training method, and up to a relative WER reduction of 11.2% with the proposed data augmentation method.
End-to-End Speaker Height and age estimation using Attention Mechanism with LSTM-RNN
Jan 13, 2021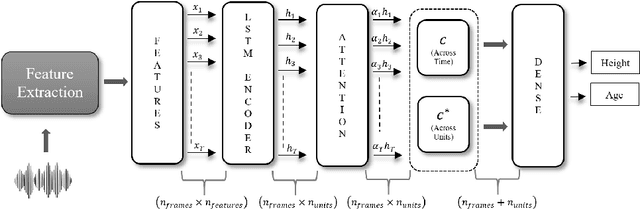
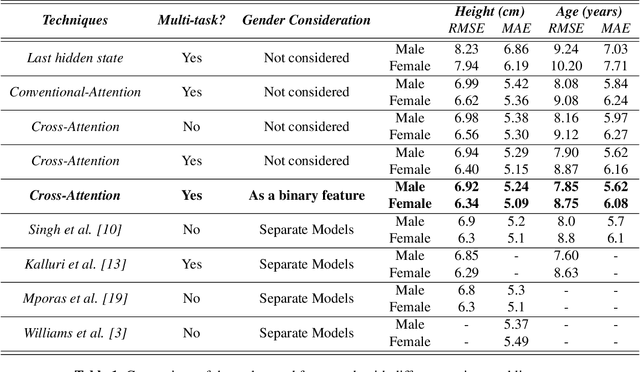
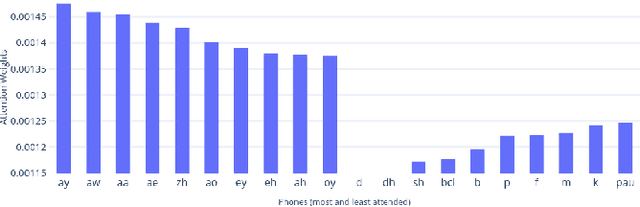
Abstract:Automatic height and age estimation of speakers using acoustic features is widely used for the purpose of human-computer interaction, forensics, etc. In this work, we propose a novel approach of using attention mechanism to build an end-to-end architecture for height and age estimation. The attention mechanism is combined with Long Short-Term Memory(LSTM) encoder which is able to capture long-term dependencies in the input acoustic features. We modify the conventionally used Attention -- which calculates context vectors the sum of attention only across timeframes -- by introducing a modified context vector which takes into account total attention across encoder units as well, giving us a new cross-attention mechanism. Apart from this, we also investigate a multi-task learning approach for jointly estimating speaker height and age. We train and test our model on the TIMIT corpus. Our model outperforms several approaches in the literature. We achieve a root mean square error (RMSE) of 6.92cm and6.34cm for male and female heights respectively and RMSE of 7.85years and 8.75years for male and females ages respectively. By tracking the attention weights allocated to different phones, we find that Vowel phones are most important whistlestop phones are least important for the estimation task.
Leveraging Text Data Using Hybrid Transformer-LSTM Based End-to-End ASR in Transfer Learning
May 28, 2020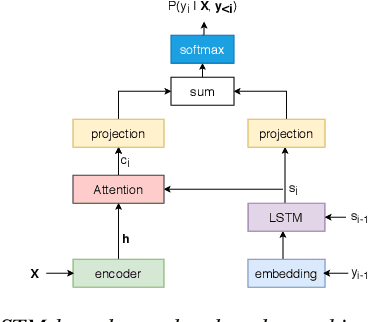
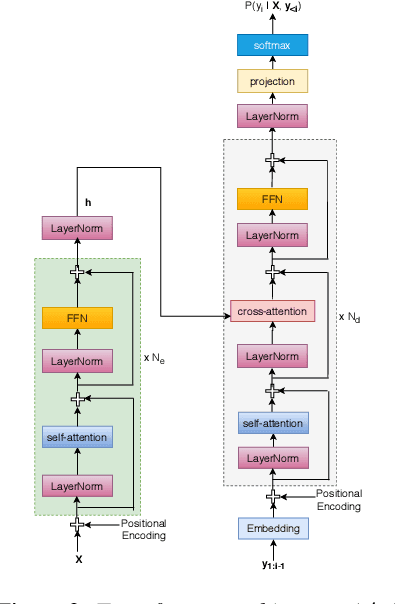
Abstract:In this work, we study leveraging extra text data to improve low-resource end-to-end ASR under cross-lingual transfer learning setting. To this end, we extend our prior work [1], and propose a hybrid Transformer-LSTM based architecture. This architecture not only takes advantage of the highly effective encoding capacity of the Transformer network but also benefits from extra text data due to the LSTM-based independent language model network. We conduct experiments on our in-house Malay corpus which contains limited labeled data and a large amount of extra text. Results show that the proposed architecture outperforms the previous LSTM-based architecture [1] by 24.2% relative word error rate (WER) when both are trained using limited labeled data. Starting from this, we obtain further 25.4% relative WER reduction by transfer learning from another resource-rich language. Moreover, we obtain additional 13.6% relative WER reduction by boosting the LSTM decoder of the transferred model with the extra text data. Overall, our best model outperforms the vanilla Transformer ASR by 11.9% relative WER. Last but not least, the proposed hybrid architecture offers much faster inference compared to both LSTM and Transformer architectures.
Approaches to Improving Recognition of Underrepresented Named Entities in Hybrid ASR Systems
May 18, 2020


Abstract:In this paper, we present a series of complementary approaches to improve the recognition of underrepresented named entities (NE) in hybrid ASR systems without compromising overall word error rate performance. The underrepresented words correspond to rare or out-of-vocabulary (OOV) words in the training data, and thereby can't be modeled reliably. We begin with graphemic lexicon which allows to drop the necessity of phonetic models in hybrid ASR. We study it under different settings and demonstrate its effectiveness in dealing with underrepresented NEs. Next, we study the impact of neural language model (LM) with letter-based features derived to handle infrequent words. After that, we attempt to enrich representations of underrepresented NEs in pretrained neural LM by borrowing the embedding representations of rich-represented words. This let us gain significant performance improvement on underrepresented NE recognition. Finally, we boost the likelihood scores of utterances containing NEs in the word lattices rescored by neural LMs and gain further performance improvement. The combination of the aforementioned approaches improves NE recognition by up to 42% relatively.
Independent language modeling architecture for end-to-end ASR
Nov 25, 2019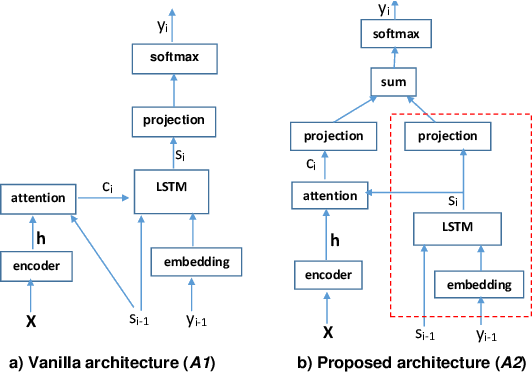
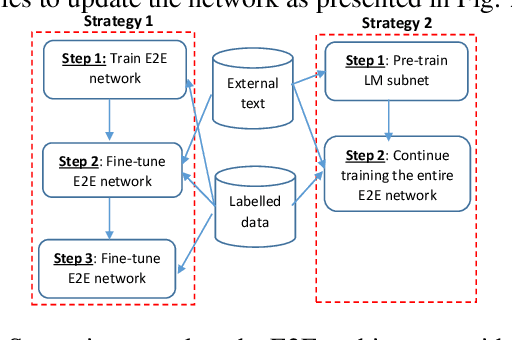
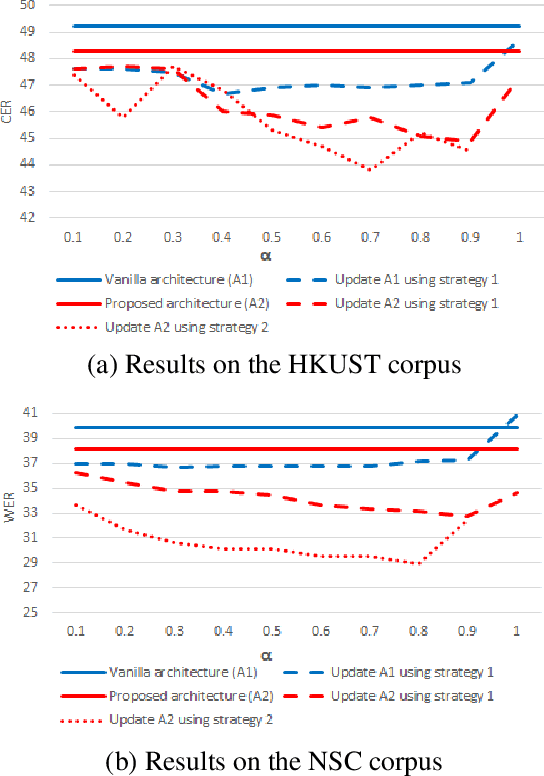
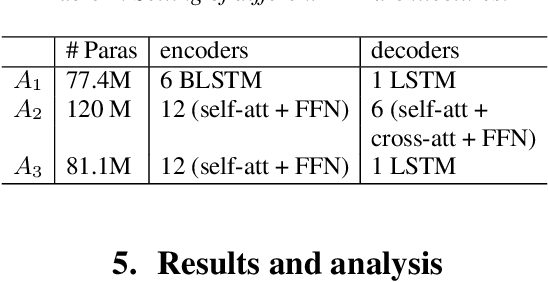
Abstract:The attention-based end-to-end (E2E) automatic speech recognition (ASR) architecture allows for joint optimization of acoustic and language models within a single network. However, in a vanilla E2E ASR architecture, the decoder sub-network (subnet), which incorporates the role of the language model (LM), is conditioned on the encoder output. This means that the acoustic encoder and the language model are entangled that doesn't allow language model to be trained separately from external text data. To address this problem, in this work, we propose a new architecture that separates the decoder subnet from the encoder output. In this way, the decoupled subnet becomes an independently trainable LM subnet, which can easily be updated using the external text data. We study two strategies for updating the new architecture. Experimental results show that, 1) the independent LM architecture benefits from external text data, achieving 9.3% and 22.8% relative character and word error rate reduction on Mandarin HKUST and English NSC datasets respectively; 2)the proposed architecture works well with external LM and can be generalized to different amount of labelled data.
Constrained Output Embeddings for End-to-End Code-Switching Speech Recognition with Only Monolingual Data
Apr 08, 2019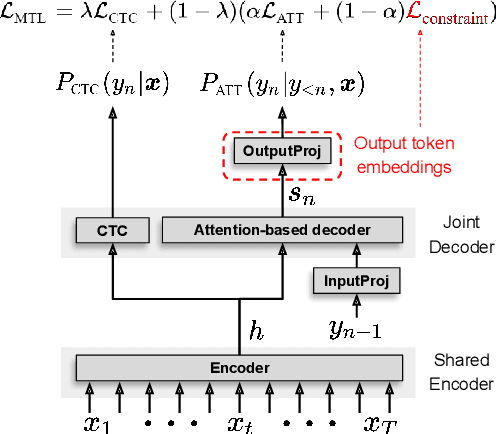
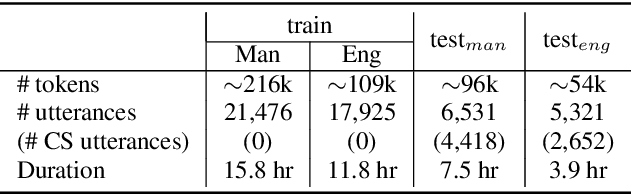
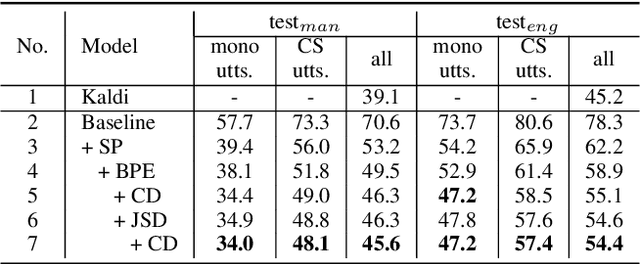
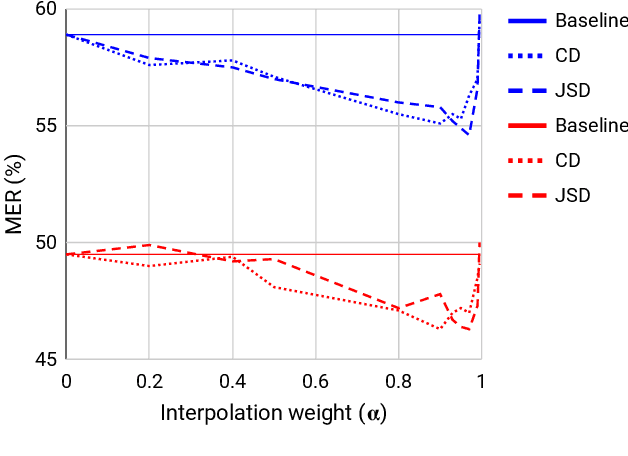
Abstract:The lack of code-switch training data is one of the major concerns in the development of end-to-end code-switching automatic speech recognition (ASR) models. In this work, we propose a method to train an improved end-to-end code-switching ASR using only monolingual data. Our method encourages the distributions of output token embeddings of monolingual languages to be similar, and hence, promotes the ASR model to easily code-switch between languages. Specifically, we propose to use Jensen-Shannon divergence and cosine distance based constraints. The former will enforce output embeddings of monolingual languages to possess similar distributions, while the later simply brings the centroids of two distributions to be close to each other. Experimental results demonstrate high effectiveness of the proposed method, yielding up to 4.5% absolute mixed error rate improvement on Mandarin-English code-switching ASR task.
Enriching Rare Word Representations in Neural Language Models by Embedding Matrix Augmentation
Apr 08, 2019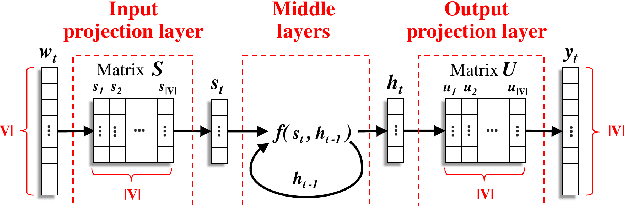
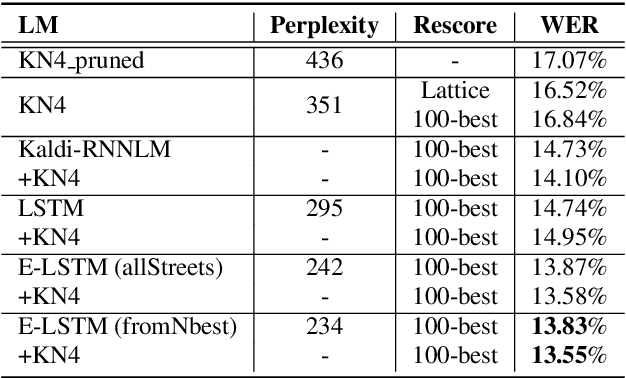

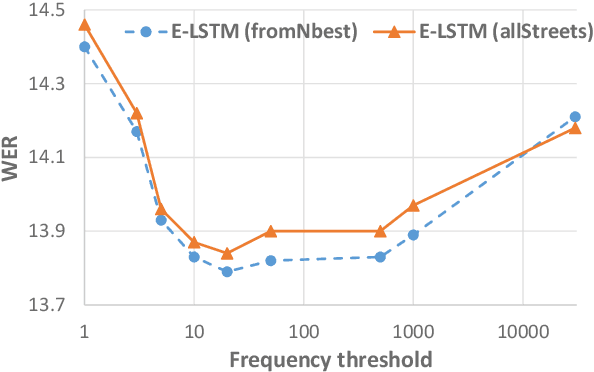
Abstract:The neural language models (NLM) achieve strong generalization capability by learning the dense representation of words and using them to estimate probability distribution function. However, learning the representation of rare words is a challenging problem causing the NLM to produce unreliable probability estimates. To address this problem, we propose a method to enrich representations of rare words in pre-trained NLM and consequently improve its probability estimation performance. The proposed method augments the word embedding matrices of pre-trained NLM while keeping other parameters unchanged. Specifically, our method updates the embedding vectors of rare words using embedding vectors of other semantically and syntactically similar words. To evaluate the proposed method, we enrich the rare street names in the pre-trained NLM and use it to rescore 100-best hypotheses output from the Singapore English speech recognition system. The enriched NLM reduces the word error rate by 6% relative and improves the recognition accuracy of the rare words by 16% absolute as compared to the baseline NLM.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge