Yerbolat Khassanov
Dual-Pipeline with Low-Rank Adaptation for New Language Integration in Multilingual ASR
Jun 12, 2024Abstract:This paper addresses challenges in integrating new languages into a pre-trained multilingual automatic speech recognition (mASR) system, particularly in scenarios where training data for existing languages is limited or unavailable. The proposed method employs a dual-pipeline with low-rank adaptation (LoRA). It maintains two data flow pipelines-one for existing languages and another for new languages. The primary pipeline follows the standard flow through the pre-trained parameters of mASR, while the secondary pipeline additionally utilizes language-specific parameters represented by LoRA and a separate output decoder module. Importantly, the proposed approach minimizes the performance degradation of existing languages and enables a language-agnostic operation mode, facilitated by a decoder selection strategy. We validate the effectiveness of the proposed method by extending the pre-trained Whisper model to 19 new languages from the FLEURS dataset
Multilingual Text-to-Speech Synthesis for Turkic Languages Using Transliteration
May 25, 2023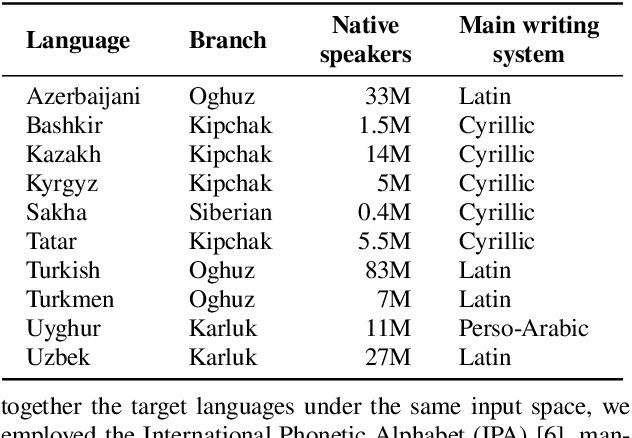
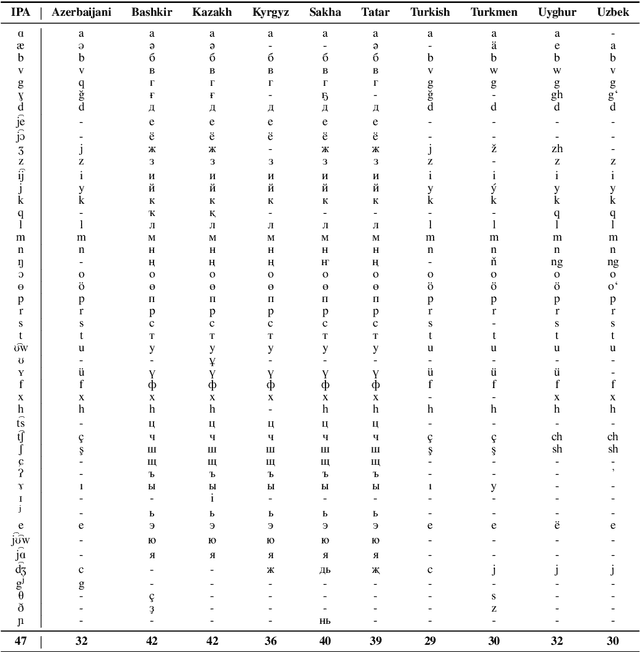
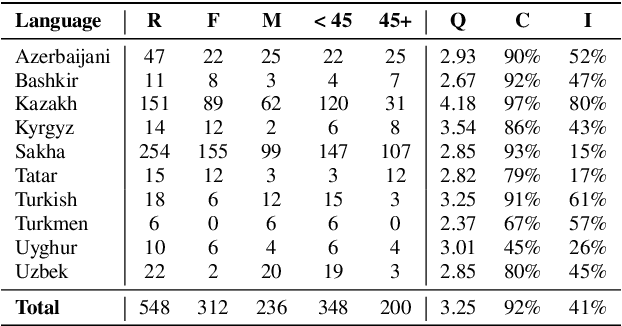
Abstract:This work aims to build a multilingual text-to-speech (TTS) synthesis system for ten lower-resourced Turkic languages: Azerbaijani, Bashkir, Kazakh, Kyrgyz, Sakha, Tatar, Turkish, Turkmen, Uyghur, and Uzbek. We specifically target the zero-shot learning scenario, where a TTS model trained using the data of one language is applied to synthesise speech for other, unseen languages. An end-to-end TTS system based on the Tacotron 2 architecture was trained using only the available data of the Kazakh language. To generate speech for the other Turkic languages, we first mapped the letters of the Turkic alphabets onto the symbols of the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA), which were then converted to the Kazakh alphabet letters. To demonstrate the feasibility of the proposed approach, we evaluated the multilingual Turkic TTS model subjectively and obtained promising results. To enable replication of the experiments, we make our code and dataset publicly available in our GitHub repository.
Improving short-video speech recognition using random utterance concatenation
Oct 28, 2022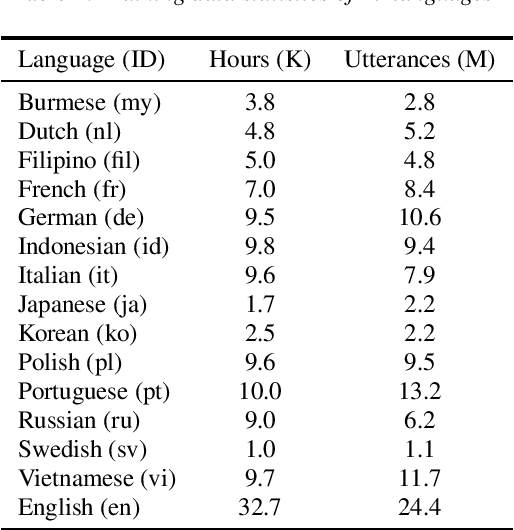
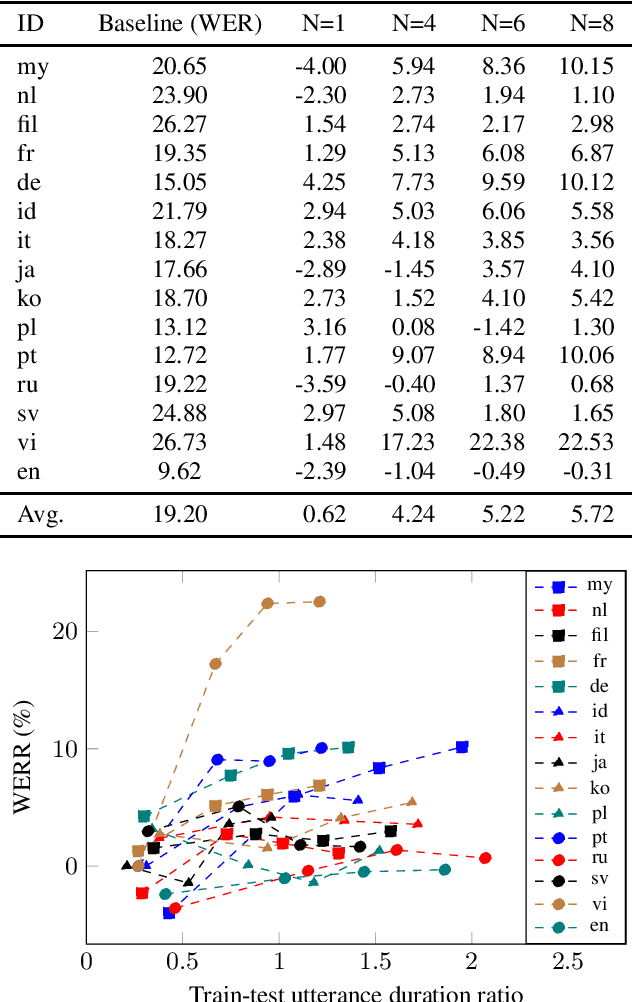
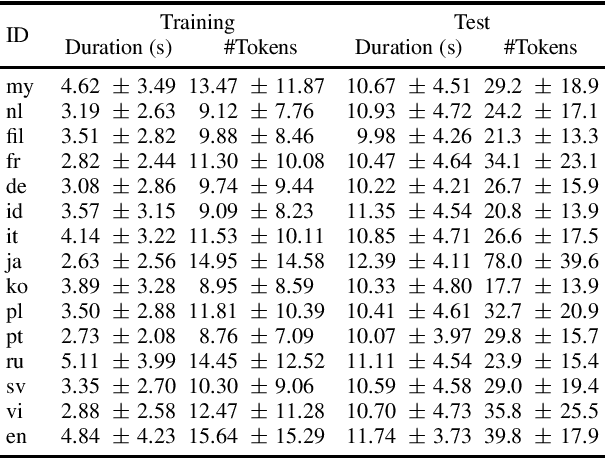
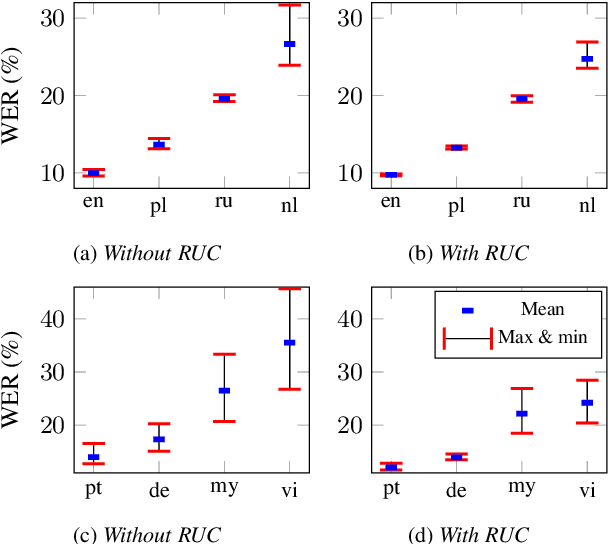
Abstract:One of the limitations in end-to-end automatic speech recognition framework is its performance would be compromised if train-test utterance lengths are mismatched. In this paper, we propose a random utterance concatenation (RUC) method to alleviate train-test utterance length mismatch issue for short-video speech recognition task. Specifically, we are motivated by observations our human-transcribed training utterances tend to be much shorter for short-video spontaneous speech (~3 seconds on average), while our test utterance generated from voice activity detection front-end is much longer (~10 seconds on average). Such a mismatch can lead to sub-optimal performance. Experimentally, by using the proposed RUC method, the best word error rate reduction (WERR) can be achieved with around three fold training data size increase as well as two utterance concatenation for each. In practice, the proposed method consistently outperforms the strong baseline models, where 3.64% average WERR is achieved on 14 languages.
KazakhTTS2: Extending the Open-Source Kazakh TTS Corpus With More Data, Speakers, and Topics
Jan 15, 2022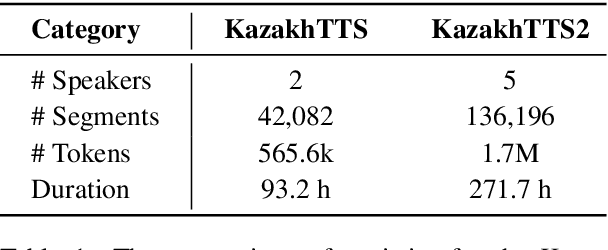
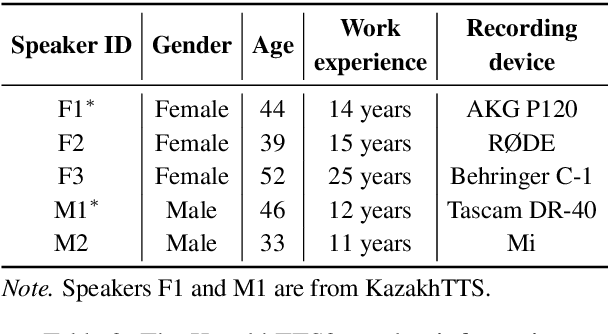
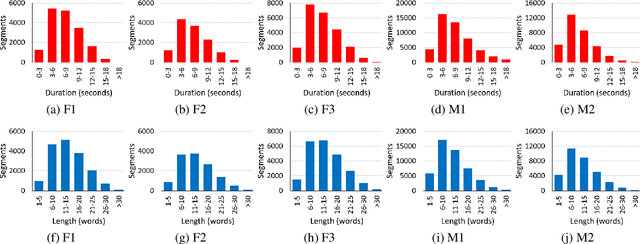
Abstract:We present an expanded version of our previously released Kazakh text-to-speech (KazakhTTS) synthesis corpus. In the new KazakhTTS2 corpus, the overall size is increased from 93 hours to 271 hours, the number of speakers has risen from two to five (three females and two males), and the topic coverage is diversified with the help of new sources, including a book and Wikipedia articles. This corpus is necessary for building high-quality TTS systems for Kazakh, a Central Asian agglutinative language from the Turkic family, which presents several linguistic challenges. We describe the corpus construction process and provide the details of the training and evaluation procedures for the TTS system. Our experimental results indicate that the constructed corpus is sufficient to build robust TTS models for real-world applications, with a subjective mean opinion score of above 4.0 for all the five speakers. We believe that our corpus will facilitate speech and language research for Kazakh and other Turkic languages, which are widely considered to be low-resource due to the limited availability of free linguistic data. The constructed corpus, code, and pretrained models are publicly available in our GitHub repository.
KazNERD: Kazakh Named Entity Recognition Dataset
Nov 26, 2021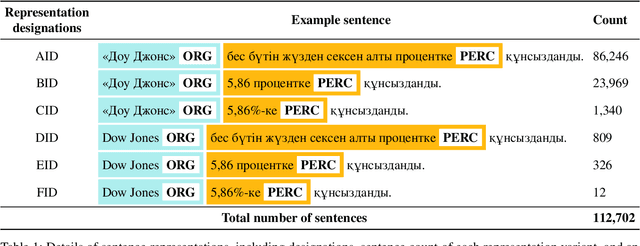
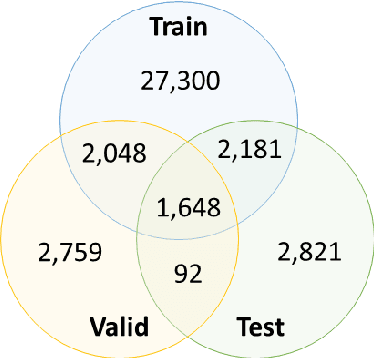
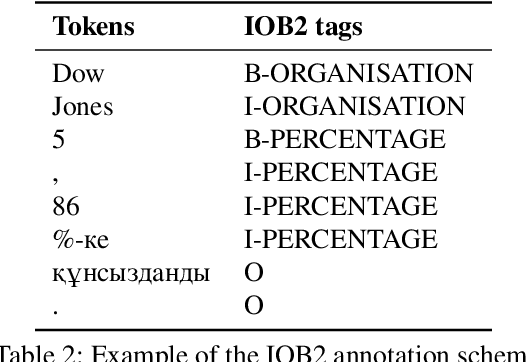
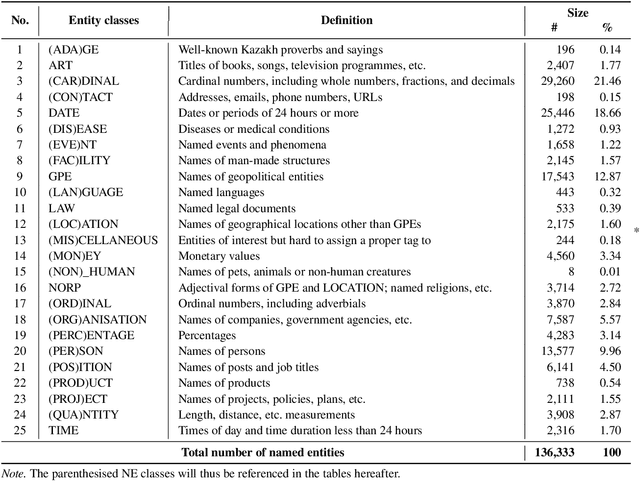
Abstract:We present the development of a dataset for Kazakh named entity recognition. The dataset was built as there is a clear need for publicly available annotated corpora in Kazakh, as well as annotation guidelines containing straightforward--but rigorous--rules and examples. The dataset annotation, based on the IOB2 scheme, was carried out on television news text by two native Kazakh speakers under the supervision of the first author. The resulting dataset contains 112,702 sentences and 136,333 annotations for 25 entity classes. State-of-the-art machine learning models to automatise Kazakh named entity recognition were also built, with the best-performing model achieving an exact match F1-score of 97.22% on the test set. The annotated dataset, guidelines, and codes used to train the models are freely available for download under the CC BY 4.0 licence from https://github.com/IS2AI/KazNERD.
A Study of Multimodal Person Verification Using Audio-Visual-Thermal Data
Oct 23, 2021
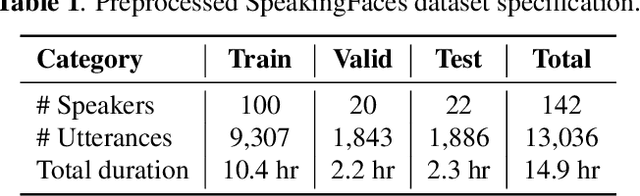
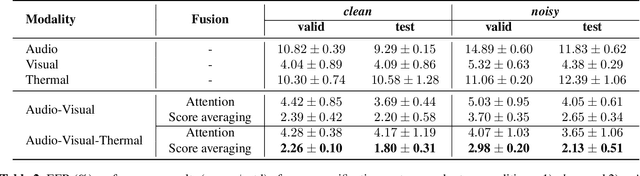
Abstract:In this paper, we study an approach to multimodal person verification using audio, visual, and thermal modalities. The combination of audio and visual modalities has already been shown to be effective for robust person verification. From this perspective, we investigate the impact of further increasing the number of modalities by supplementing thermal images. In particular, we implemented unimodal, bimodal, and trimodal verification systems using the state-of-the-art deep learning architectures and compared their performance under clean and noisy conditions. We also compared two popular fusion approaches based on simple score averaging and soft attention mechanism. The experiment conducted on the SpeakingFaces dataset demonstrates the superiority of the trimodal verification system over both unimodal and bimodal systems. To enable the reproducibility of the experiment and facilitate research into multimodal person verification, we make our code, pretrained models and preprocessed dataset freely available in our GitHub repository.
A Study of Multilingual End-to-End Speech Recognition for Kazakh, Russian, and English
Aug 03, 2021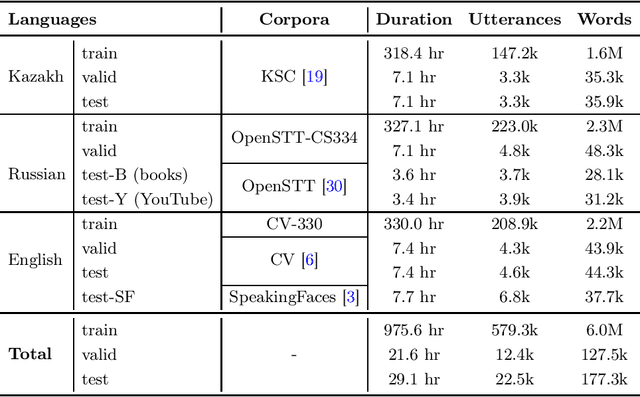
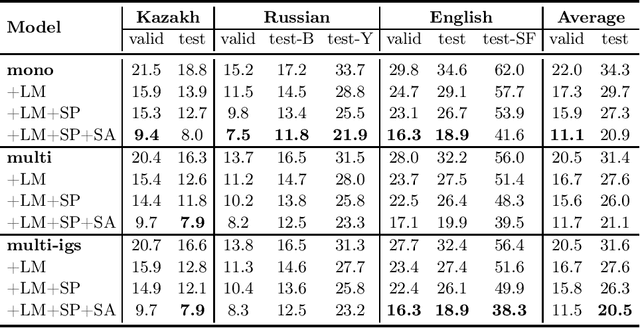
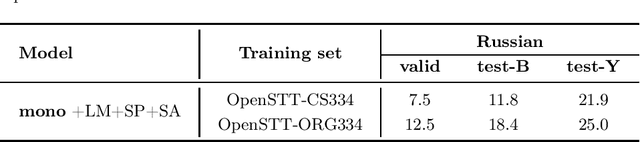
Abstract:We study training a single end-to-end (E2E) automatic speech recognition (ASR) model for three languages used in Kazakhstan: Kazakh, Russian, and English. We first describe the development of multilingual E2E ASR based on Transformer networks and then perform an extensive assessment on the aforementioned languages. We also compare two variants of output grapheme set construction: combined and independent. Furthermore, we evaluate the impact of LMs and data augmentation techniques on the recognition performance of the multilingual E2E ASR. In addition, we present several datasets for training and evaluation purposes. Experiment results show that the multilingual models achieve comparable performances to the monolingual baselines with a similar number of parameters. Our best monolingual and multilingual models achieved 20.9% and 20.5% average word error rates on the combined test set, respectively. To ensure the reproducibility of our experiments and results, we share our training recipes, datasets, and pre-trained models.
USC: An Open-Source Uzbek Speech Corpus and Initial Speech Recognition Experiments
Jul 30, 2021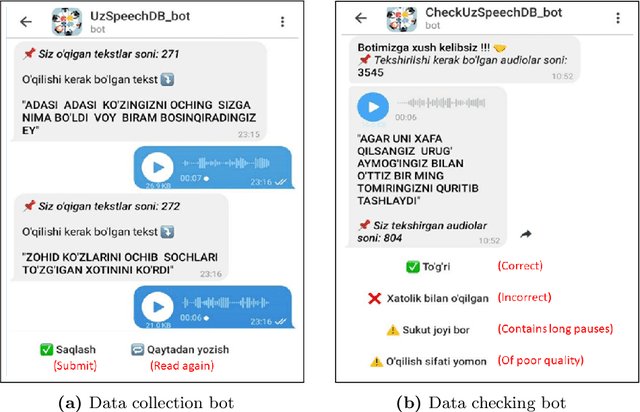
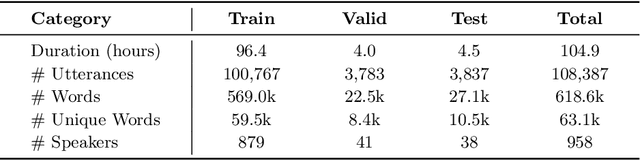
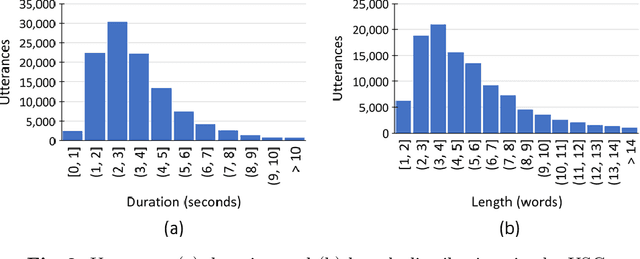
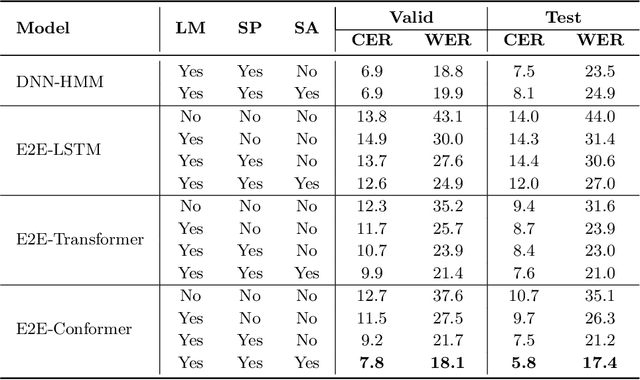
Abstract:We present a freely available speech corpus for the Uzbek language and report preliminary automatic speech recognition (ASR) results using both the deep neural network hidden Markov model (DNN-HMM) and end-to-end (E2E) architectures. The Uzbek speech corpus (USC) comprises 958 different speakers with a total of 105 hours of transcribed audio recordings. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first open-source Uzbek speech corpus dedicated to the ASR task. To ensure high quality, the USC has been manually checked by native speakers. We first describe the design and development procedures of the USC, and then explain the conducted ASR experiments in detail. The experimental results demonstrate promising results for the applicability of the USC for ASR. Specifically, 18.1% and 17.4% word error rates were achieved on the validation and test sets, respectively. To enable experiment reproducibility, we share the USC dataset, pre-trained models, and training recipes in our GitHub repository.
KazakhTTS: An Open-Source Kazakh Text-to-Speech Synthesis Dataset
Apr 26, 2021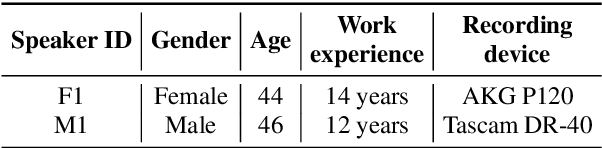
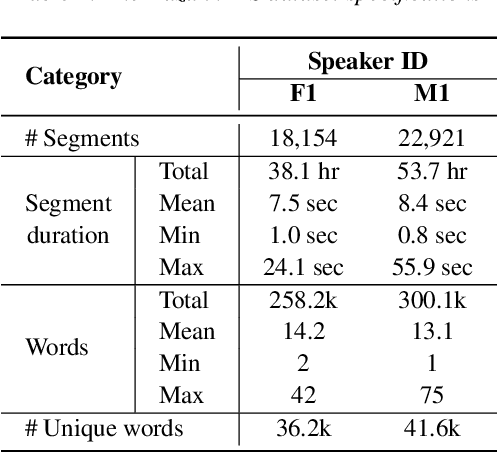
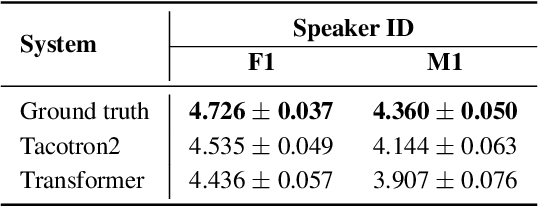
Abstract:This paper introduces a high-quality open-source speech synthesis dataset for Kazakh, a low-resource language spoken by over 13 million people worldwide. The dataset consists of about 93 hours of transcribed audio recordings spoken by two professional speakers (female and male). It is the first publicly available large-scale dataset developed to promote Kazakh text-to-speech (TTS) applications in both academia and industry. In this paper, we share our experience by describing the dataset development procedures and faced challenges, and discuss important future directions. To demonstrate the reliability of our dataset, we built baseline end-to-end TTS models and evaluated them using the subjective mean opinion score (MOS) measure. Evaluation results show that the best TTS models trained on our dataset achieve MOS above 4 for both speakers, which makes them applicable for practical use. The dataset, training recipe, and pretrained TTS models are freely available.
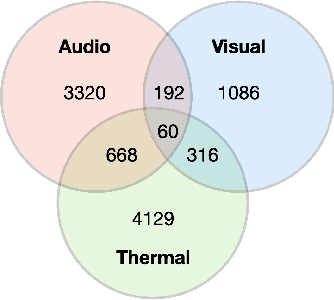
SpeakingFaces: A Large-Scale Multimodal Dataset of Voice Commands with Visual and Thermal Video Streams
Dec 18, 2020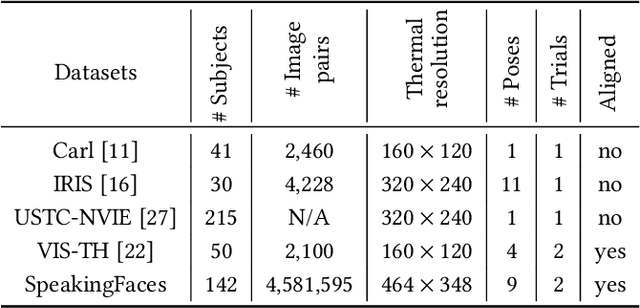
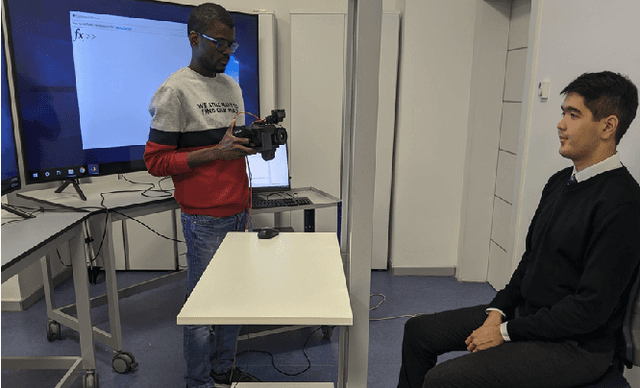
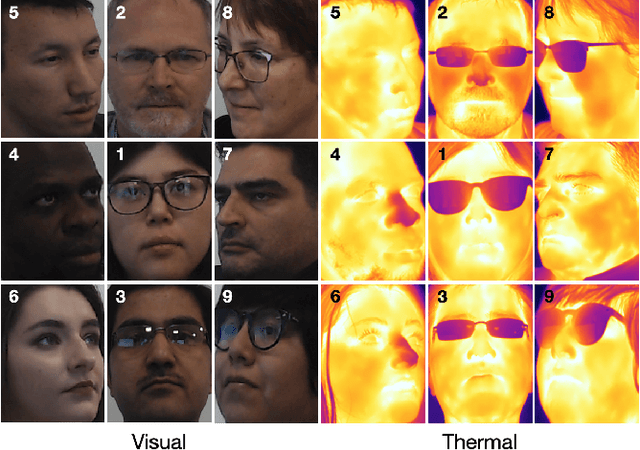
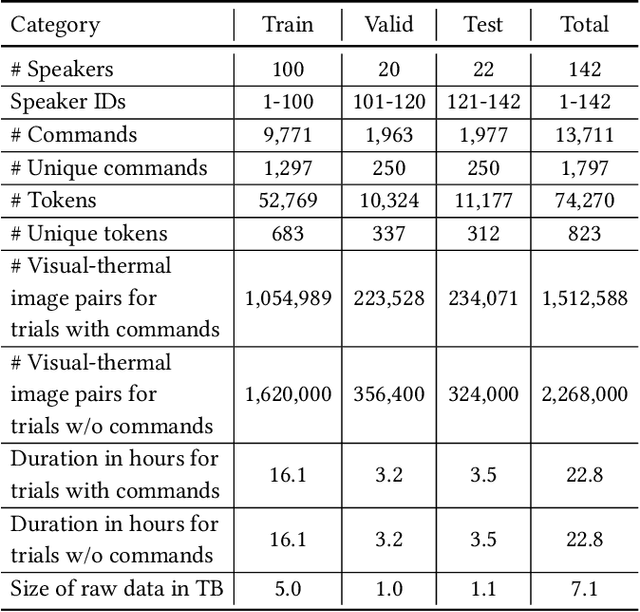
Abstract:We present SpeakingFaces as a publicly-available large-scale dataset developed to support multimodal machine learning research in contexts that utilize a combination of thermal, visual, and audio data streams; examples include human-computer interaction (HCI), biometric authentication, recognition systems, domain transfer, and speech recognition. SpeakingFaces is comprised of well-aligned high-resolution thermal and visual spectra image streams of fully-framed faces synchronized with audio recordings of each subject speaking approximately 100 imperative phrases. Data were collected from 142 subjects, yielding over 13,000 instances of synchronized data (~3.8 TB). For technical validation, we demonstrate two baseline examples. The first baseline shows classification by gender, utilizing different combinations of the three data streams in both clean and noisy environments. The second example consists of thermal-to-visual facial image translation, as an instance of domain transfer.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge