Tongjia Chen
PointDiffuse: A Dual-Conditional Diffusion Model for Enhanced Point Cloud Semantic Segmentation
Mar 11, 2025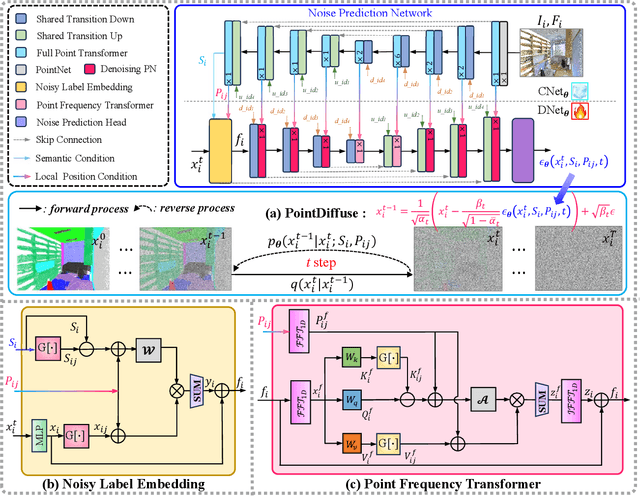

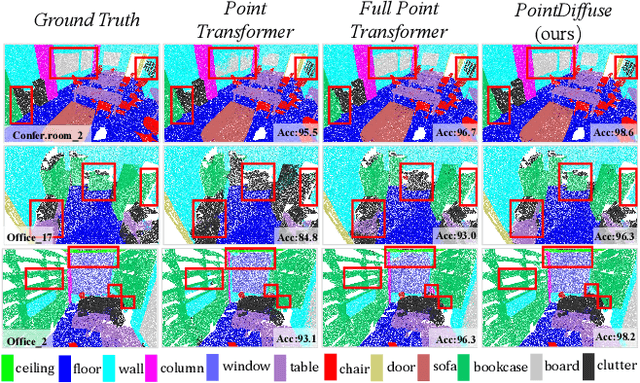

Abstract:Diffusion probabilistic models are traditionally used to generate colors at fixed pixel positions in 2D images. Building on this, we extend diffusion models to point cloud semantic segmentation, where point positions also remain fixed, and the diffusion model generates point labels instead of colors. To accelerate the denoising process in reverse diffusion, we introduce a noisy label embedding mechanism. This approach integrates semantic information into the noisy label, providing an initial semantic reference that improves the reverse diffusion efficiency. Additionally, we propose a point frequency transformer that enhances the adjustment of high-level context in point clouds. To reduce computational complexity, we introduce the position condition into MLP and propose denoising PointNet to process the high-resolution point cloud without sacrificing geometric details. Finally, we integrate the proposed noisy label embedding, point frequency transformer and denoising PointNet in our proposed dual conditional diffusion model-based network (PointDiffuse) to perform large-scale point cloud semantic segmentation. Extensive experiments on five benchmarks demonstrate the superiority of PointDiffuse, achieving the state-of-the-art mIoU of 74.2\% on S3DIS Area 5, 81.2\% on S3DIS 6-fold and 64.8\% on SWAN dataset.
Motion-Grounded Video Reasoning: Understanding and Perceiving Motion at Pixel Level
Nov 15, 2024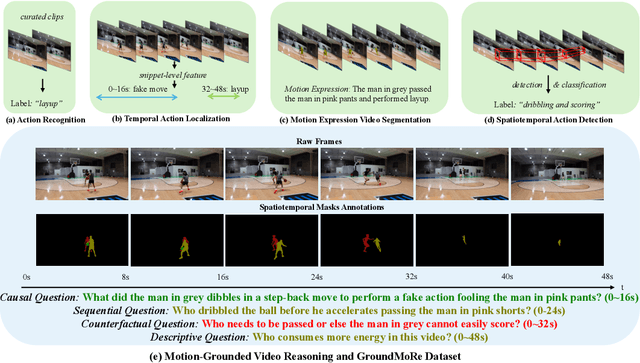

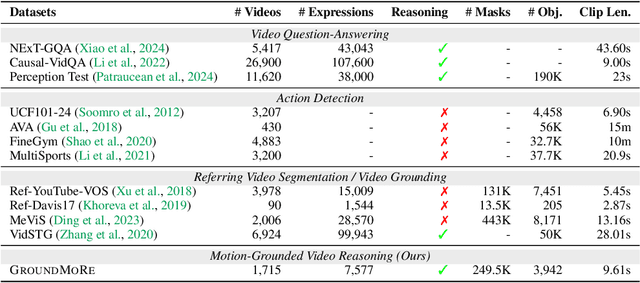
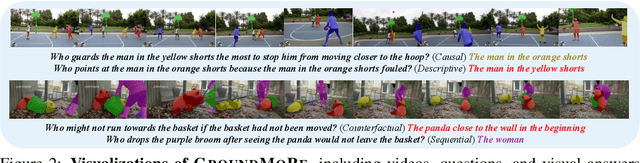
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce Motion-Grounded Video Reasoning, a new motion understanding task that requires generating visual answers (video segmentation masks) according to the input question, and hence needs implicit spatiotemporal reasoning and grounding. This task extends existing spatiotemporal grounding work focusing on explicit action/motion grounding, to a more general format by enabling implicit reasoning via questions. To facilitate the development of the new task, we collect a large-scale dataset called GROUNDMORE, which comprises 1,715 video clips, 249K object masks that are deliberately designed with 4 question types (Causal, Sequential, Counterfactual, and Descriptive) for benchmarking deep and comprehensive motion reasoning abilities. GROUNDMORE uniquely requires models to generate visual answers, providing a more concrete and visually interpretable response than plain texts. It evaluates models on both spatiotemporal grounding and reasoning, fostering to address complex challenges in motion-related video reasoning, temporal perception, and pixel-level understanding. Furthermore, we introduce a novel baseline model named Motion-Grounded Video Reasoning Assistant (MORA). MORA incorporates the multimodal reasoning ability from the Multimodal LLM, the pixel-level perception capability from the grounding model (SAM), and the temporal perception ability from a lightweight localization head. MORA achieves respectable performance on GROUNDMORE outperforming the best existing visual grounding baseline model by an average of 21.5% relatively. We hope this novel and challenging task will pave the way for future advancements in robust and general motion understanding via video reasoning segmentation
Soft Masked Transformer for Point Cloud Processing with Skip Attention-Based Upsampling
Mar 21, 2024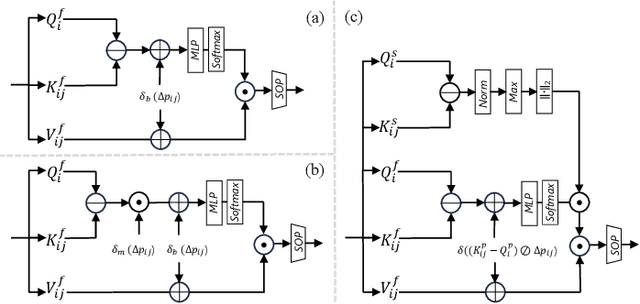
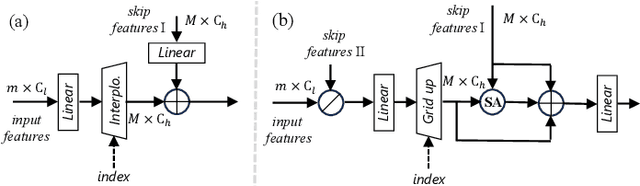
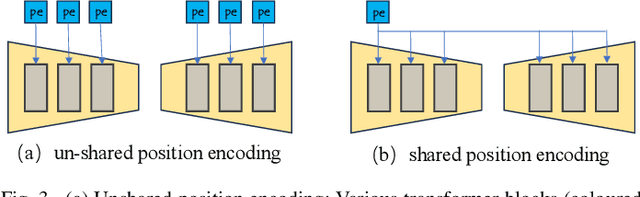
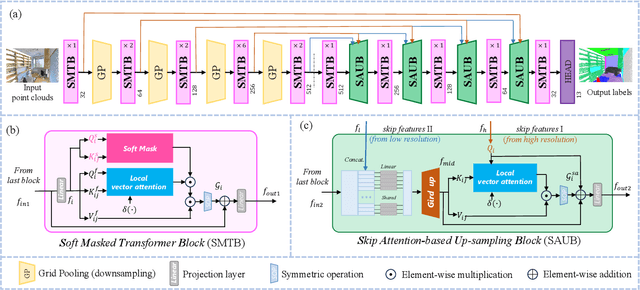
Abstract:Point cloud processing methods leverage local and global point features %at the feature level to cater to downstream tasks, yet they often overlook the task-level context inherent in point clouds during the encoding stage. We argue that integrating task-level information into the encoding stage significantly enhances performance. To that end, we propose SMTransformer which incorporates task-level information into a vector-based transformer by utilizing a soft mask generated from task-level queries and keys to learn the attention weights. Additionally, to facilitate effective communication between features from the encoding and decoding layers in high-level tasks such as segmentation, we introduce a skip-attention-based up-sampling block. This block dynamically fuses features from various resolution points across the encoding and decoding layers. To mitigate the increase in network parameters and training time resulting from the complexity of the aforementioned blocks, we propose a novel shared position encoding strategy. This strategy allows various transformer blocks to share the same position information over the same resolution points, thereby reducing network parameters and training time without compromising accuracy.Experimental comparisons with existing methods on multiple datasets demonstrate the efficacy of SMTransformer and skip-attention-based up-sampling for point cloud processing tasks, including semantic segmentation and classification. In particular, we achieve state-of-the-art semantic segmentation results of 73.4% mIoU on S3DIS Area 5 and 62.4% mIoU on SWAN dataset
OST: Refining Text Knowledge with Optimal Spatio-Temporal Descriptor for General Video Recognition
Nov 30, 2023Abstract:Due to the resource-intensive nature of training vision-language models on expansive video data, a majority of studies have centered on adapting pre-trained image-language models to the video domain. Dominant pipelines propose to tackle the visual discrepancies with additional temporal learners while overlooking the substantial discrepancy for web-scaled descriptive narratives and concise action category names, leading to less distinct semantic space and potential performance limitations. In this work, we prioritize the refinement of text knowledge to facilitate generalizable video recognition. To address the limitations of the less distinct semantic space of category names, we prompt a large language model (LLM) to augment action class names into Spatio-Temporal Descriptors thus bridging the textual discrepancy and serving as a knowledge base for general recognition. Moreover, to assign the best descriptors with different video instances, we propose Optimal Descriptor Solver, forming the video recognition problem as solving the optimal matching flow across frame-level representations and descriptors. Comprehensive evaluations in zero-shot, few-shot, and fully supervised video recognition highlight the effectiveness of our approach. Our best model achieves a state-of-the-art zero-shot accuracy of 75.1% on Kinetics-600.
Multi-scale Alternated Attention Transformer for Generalized Stereo Matching
Aug 06, 2023Abstract:Recent stereo matching networks achieves dramatic performance by introducing epipolar line constraint to limit the matching range of dual-view. However, in complicated real-world scenarios, the feature information based on intra-epipolar line alone is too weak to facilitate stereo matching. In this paper, we present a simple but highly effective network called Alternated Attention U-shaped Transformer (AAUformer) to balance the impact of epipolar line in dual and single view respectively for excellent generalization performance. Compared to other models, our model has several main designs: 1) to better liberate the local semantic features of the single-view at pixel level, we introduce window self-attention to break the limits of intra-row self-attention and completely replace the convolutional network for denser features before cross-matching; 2) the multi-scale alternated attention backbone network was designed to extract invariant features in order to achieves the coarse-to-fine matching process for hard-to-discriminate regions. We performed a series of both comparative studies and ablation studies on several mainstream stereo matching datasets. The results demonstrate that our model achieves state-of-the-art on the Scene Flow dataset, and the fine-tuning performance is competitive on the KITTI 2015 dataset. In addition, for cross generalization experiments on synthetic and real-world datasets, our model outperforms several state-of-the-art works.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge