Changyan Xiao
Multi-scale Alternated Attention Transformer for Generalized Stereo Matching
Aug 06, 2023Abstract:Recent stereo matching networks achieves dramatic performance by introducing epipolar line constraint to limit the matching range of dual-view. However, in complicated real-world scenarios, the feature information based on intra-epipolar line alone is too weak to facilitate stereo matching. In this paper, we present a simple but highly effective network called Alternated Attention U-shaped Transformer (AAUformer) to balance the impact of epipolar line in dual and single view respectively for excellent generalization performance. Compared to other models, our model has several main designs: 1) to better liberate the local semantic features of the single-view at pixel level, we introduce window self-attention to break the limits of intra-row self-attention and completely replace the convolutional network for denser features before cross-matching; 2) the multi-scale alternated attention backbone network was designed to extract invariant features in order to achieves the coarse-to-fine matching process for hard-to-discriminate regions. We performed a series of both comparative studies and ablation studies on several mainstream stereo matching datasets. The results demonstrate that our model achieves state-of-the-art on the Scene Flow dataset, and the fine-tuning performance is competitive on the KITTI 2015 dataset. In addition, for cross generalization experiments on synthetic and real-world datasets, our model outperforms several state-of-the-art works.
A grid-point detection method based on U-net for a structured light system
Dec 05, 2020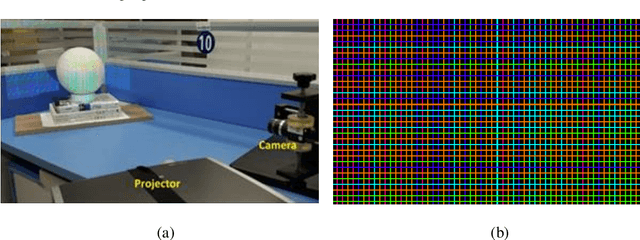
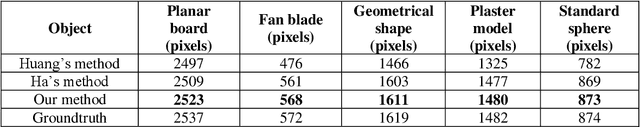
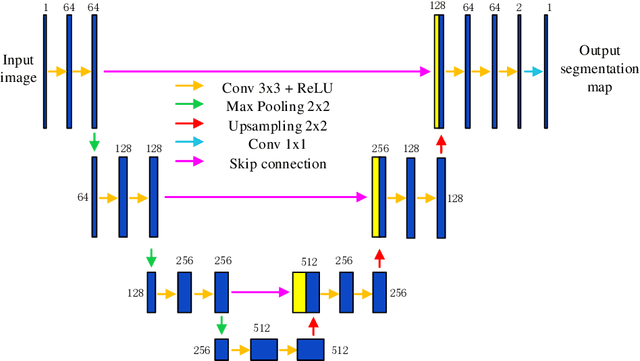
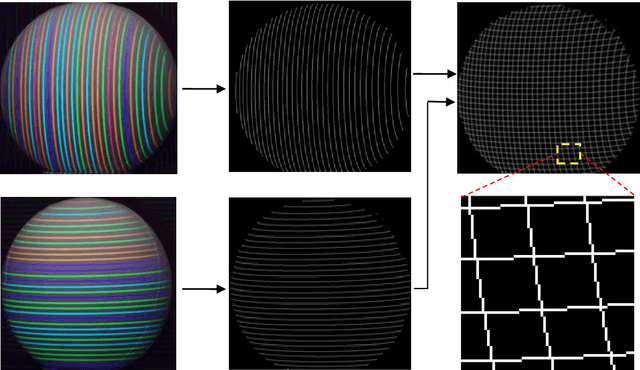
Abstract:Accurate detection of the feature points of the projected pattern plays an extremely important role in one-shot 3D reconstruction systems, especially for the ones using a grid pattern. To solve this problem, this paper proposes a grid-point detection method based on U-net. A specific dataset is designed that includes the images captured with the two-shot imaging method and the ones acquired with the one-shot imaging method. Among them, the images in the first group after labeled as the ground truth images and the images captured at the same pose with the one-shot method are cut into small patches with the size of 64x64 pixels then feed to the training set. The remaining of the images in the second group is the test set. The experimental results show that our method can achieve a better detecting performance with higher accuracy in comparison with the previous methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge