Tian Shen
PathOrchestra: A Comprehensive Foundation Model for Computational Pathology with Over 100 Diverse Clinical-Grade Tasks
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:The complexity and variability inherent in high-resolution pathological images present significant challenges in computational pathology. While pathology foundation models leveraging AI have catalyzed transformative advancements, their development demands large-scale datasets, considerable storage capacity, and substantial computational resources. Furthermore, ensuring their clinical applicability and generalizability requires rigorous validation across a broad spectrum of clinical tasks. Here, we present PathOrchestra, a versatile pathology foundation model trained via self-supervised learning on a dataset comprising 300K pathological slides from 20 tissue and organ types across multiple centers. The model was rigorously evaluated on 112 clinical tasks using a combination of 61 private and 51 public datasets. These tasks encompass digital slide preprocessing, pan-cancer classification, lesion identification, multi-cancer subtype classification, biomarker assessment, gene expression prediction, and the generation of structured reports. PathOrchestra demonstrated exceptional performance across 27,755 WSIs and 9,415,729 ROIs, achieving over 0.950 accuracy in 47 tasks, including pan-cancer classification across various organs, lymphoma subtype diagnosis, and bladder cancer screening. Notably, it is the first model to generate structured reports for high-incidence colorectal cancer and diagnostically complex lymphoma-areas that are infrequently addressed by foundational models but hold immense clinical potential. Overall, PathOrchestra exemplifies the feasibility and efficacy of a large-scale, self-supervised pathology foundation model, validated across a broad range of clinical-grade tasks. Its high accuracy and reduced reliance on extensive data annotation underline its potential for clinical integration, offering a pathway toward more efficient and high-quality medical services.
MedFMC: A Real-world Dataset and Benchmark For Foundation Model Adaptation in Medical Image Classification
Jun 16, 2023Abstract:Foundation models, often pre-trained with large-scale data, have achieved paramount success in jump-starting various vision and language applications. Recent advances further enable adapting foundation models in downstream tasks efficiently using only a few training samples, e.g., in-context learning. Yet, the application of such learning paradigms in medical image analysis remains scarce due to the shortage of publicly accessible data and benchmarks. In this paper, we aim at approaches adapting the foundation models for medical image classification and present a novel dataset and benchmark for the evaluation, i.e., examining the overall performance of accommodating the large-scale foundation models downstream on a set of diverse real-world clinical tasks. We collect five sets of medical imaging data from multiple institutes targeting a variety of real-world clinical tasks (22,349 images in total), i.e., thoracic diseases screening in X-rays, pathological lesion tissue screening, lesion detection in endoscopy images, neonatal jaundice evaluation, and diabetic retinopathy grading. Results of multiple baseline methods are demonstrated using the proposed dataset from both accuracy and cost-effective perspectives.
CoDiM: Learning with Noisy Labels via Contrastive Semi-Supervised Learning
Nov 23, 2021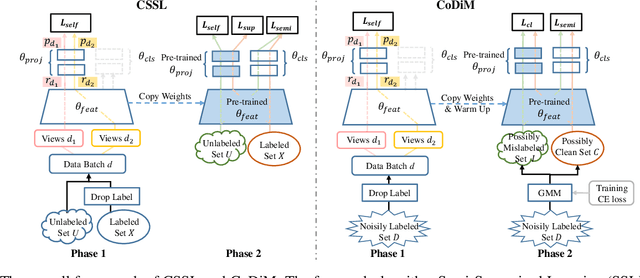
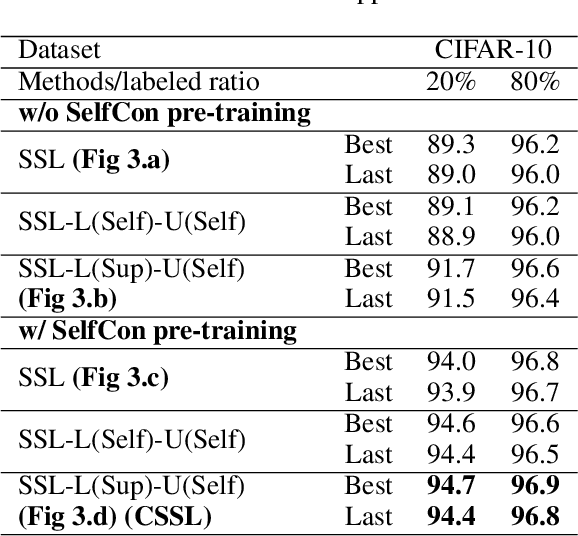
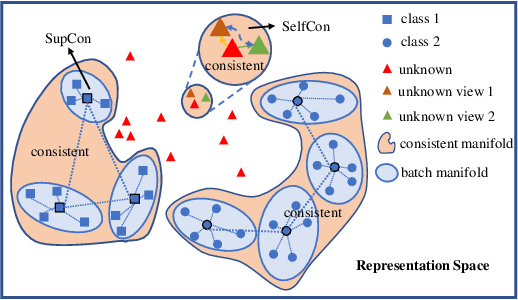
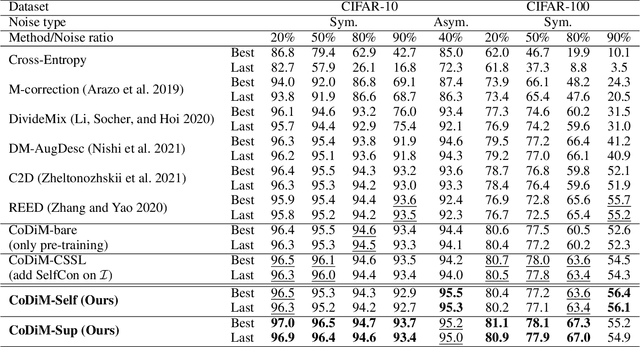
Abstract:Labels are costly and sometimes unreliable. Noisy label learning, semi-supervised learning, and contrastive learning are three different strategies for designing learning processes requiring less annotation cost. Semi-supervised learning and contrastive learning have been recently demonstrated to improve learning strategies that address datasets with noisy labels. Still, the inner connections between these fields as well as the potential to combine their strengths together have only started to emerge. In this paper, we explore further ways and advantages to fuse them. Specifically, we propose CSSL, a unified Contrastive Semi-Supervised Learning algorithm, and CoDiM (Contrastive DivideMix), a novel algorithm for learning with noisy labels. CSSL leverages the power of classical semi-supervised learning and contrastive learning technologies and is further adapted to CoDiM, which learns robustly from multiple types and levels of label noise. We show that CoDiM brings consistent improvements and achieves state-of-the-art results on multiple benchmarks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge