Qian Da
MedFMC: A Real-world Dataset and Benchmark For Foundation Model Adaptation in Medical Image Classification
Jun 16, 2023Abstract:Foundation models, often pre-trained with large-scale data, have achieved paramount success in jump-starting various vision and language applications. Recent advances further enable adapting foundation models in downstream tasks efficiently using only a few training samples, e.g., in-context learning. Yet, the application of such learning paradigms in medical image analysis remains scarce due to the shortage of publicly accessible data and benchmarks. In this paper, we aim at approaches adapting the foundation models for medical image classification and present a novel dataset and benchmark for the evaluation, i.e., examining the overall performance of accommodating the large-scale foundation models downstream on a set of diverse real-world clinical tasks. We collect five sets of medical imaging data from multiple institutes targeting a variety of real-world clinical tasks (22,349 images in total), i.e., thoracic diseases screening in X-rays, pathological lesion tissue screening, lesion detection in endoscopy images, neonatal jaundice evaluation, and diabetic retinopathy grading. Results of multiple baseline methods are demonstrated using the proposed dataset from both accuracy and cost-effective perspectives.
Signet Ring Cell Detection With a Semi-supervised Learning Framework
Jul 09, 2019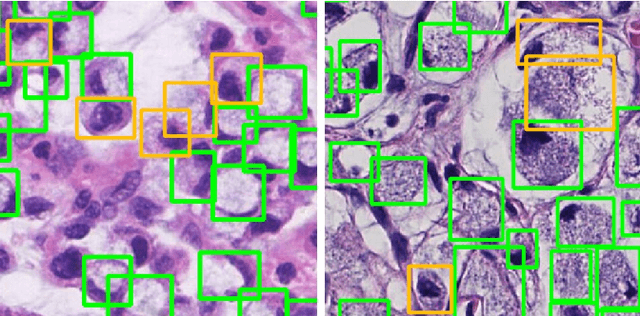


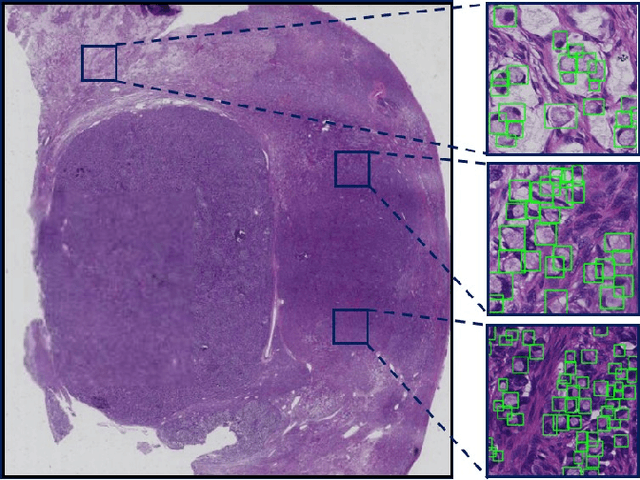
Abstract:Signet ring cell carcinoma is a type of rare adenocarcinoma with poor prognosis. Early detection leads to huge improvement of patients' survival rate. However, pathologists can only visually detect signet ring cells under the microscope. This procedure is not only laborious but also prone to omission. An automatic and accurate signet ring cell detection solution is thus important but has not been investigated before. In this paper, we take the first step to present a semi-supervised learning framework for the signet ring cell detection problem. Self-training is proposed to deal with the challenge of incomplete annotations, and cooperative-training is adapted to explore the unlabeled regions. Combining the two techniques, our semi-supervised learning framework can make better use of both labeled and unlabeled data. Experiments on large real clinical data demonstrate the effectiveness of our design. Our framework achieves accurate signet ring cell detection and can be readily applied in the clinical trails. The dataset will be released soon to facilitate the development of the area.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge