Stefano Rosa
Embodied Image Captioning: Self-supervised Learning Agents for Spatially Coherent Image Descriptions
Apr 11, 2025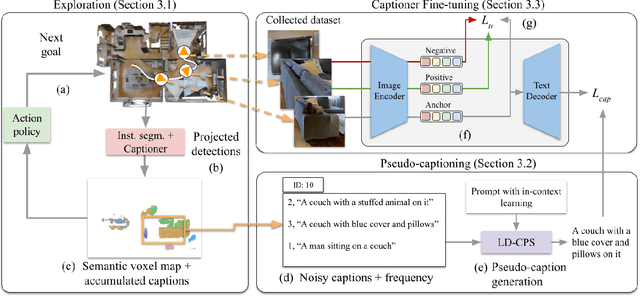
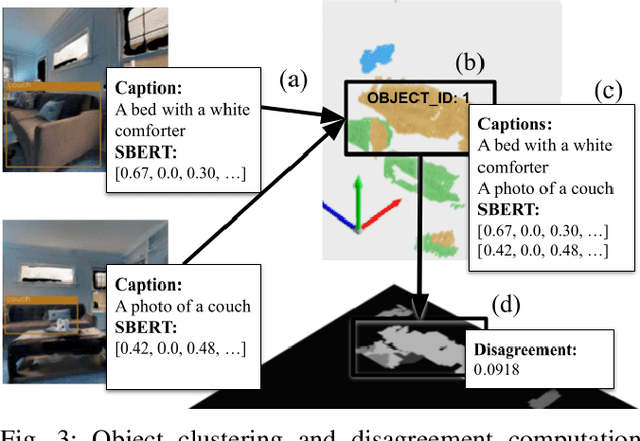
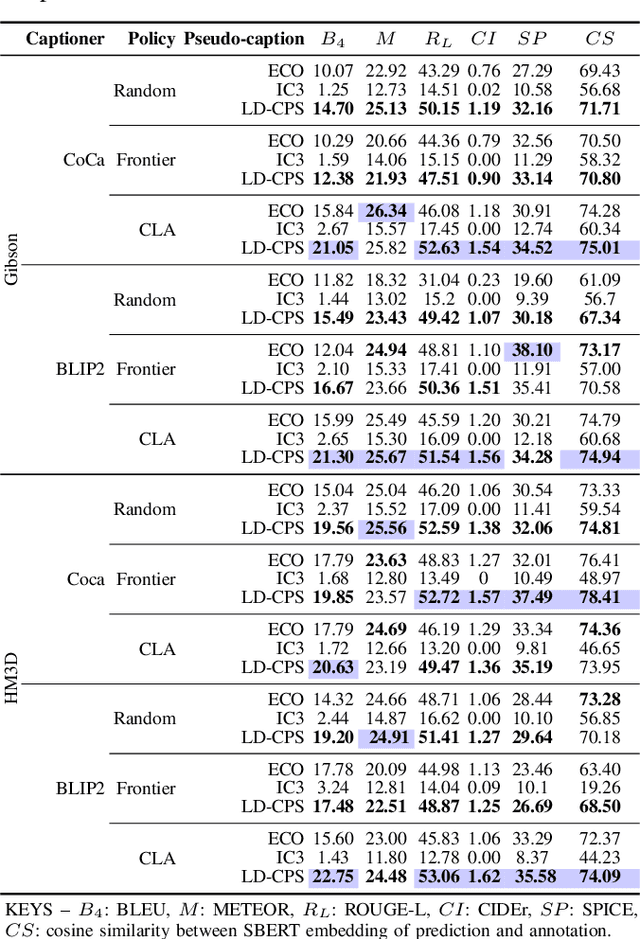

Abstract:We present a self-supervised method to improve an agent's abilities in describing arbitrary objects while actively exploring a generic environment. This is a challenging problem, as current models struggle to obtain coherent image captions due to different camera viewpoints and clutter. We propose a three-phase framework to fine-tune existing captioning models that enhances caption accuracy and consistency across views via a consensus mechanism. First, an agent explores the environment, collecting noisy image-caption pairs. Then, a consistent pseudo-caption for each object instance is distilled via consensus using a large language model. Finally, these pseudo-captions are used to fine-tune an off-the-shelf captioning model, with the addition of contrastive learning. We analyse the performance of the combination of captioning models, exploration policies, pseudo-labeling methods, and fine-tuning strategies, on our manually labeled test set. Results show that a policy can be trained to mine samples with higher disagreement compared to classical baselines. Our pseudo-captioning method, in combination with all policies, has a higher semantic similarity compared to other existing methods, and fine-tuning improves caption accuracy and consistency by a significant margin. Code and test set annotations available at https://hsp-iit.github.io/embodied-captioning/
I2EDL: Interactive Instruction Error Detection and Localization
Jun 07, 2024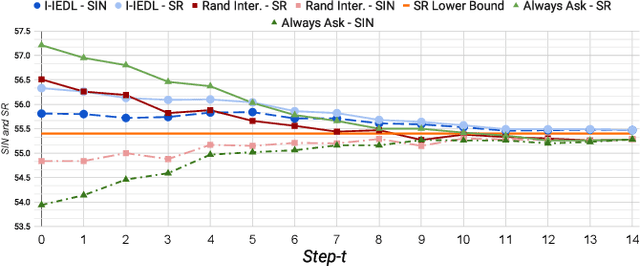
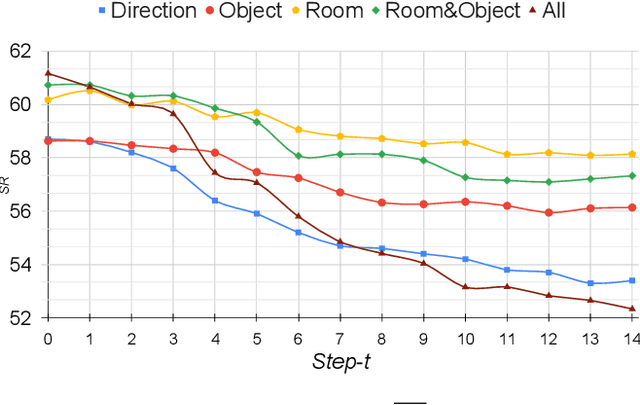
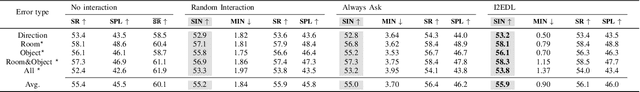
Abstract:In the Vision-and-Language Navigation in Continuous Environments (VLN-CE) task, the human user guides an autonomous agent to reach a target goal via a series of low-level actions following a textual instruction in natural language. However, most existing methods do not address the likely case where users may make mistakes when providing such instruction (e.g. "turn left" instead of "turn right"). In this work, we address a novel task of Interactive VLN in Continuous Environments (IVLN-CE), which allows the agent to interact with the user during the VLN-CE navigation to verify any doubts regarding the instruction errors. We propose an Interactive Instruction Error Detector and Localizer (I2EDL) that triggers the user-agent interaction upon the detection of instruction errors during the navigation. We leverage a pre-trained module to detect instruction errors and pinpoint them in the instruction by cross-referencing the textual input and past observations. In such way, the agent is able to query the user for a timely correction, without demanding the user's cognitive load, as we locate the probable errors to a precise part of the instruction. We evaluate the proposed I2EDL on a dataset of instructions containing errors, and further devise a novel metric, the Success weighted by Interaction Number (SIN), to reflect both the navigation performance and the interaction effectiveness. We show how the proposed method can ask focused requests for corrections to the user, which in turn increases the navigation success, while minimizing the interactions.
Mind the Error! Detection and Localization of Instruction Errors in Vision-and-Language Navigation
Mar 15, 2024



Abstract:Vision-and-Language Navigation in Continuous Environments (VLN-CE) is one of the most intuitive yet challenging embodied AI tasks. Agents are tasked to navigate towards a target goal by executing a set of low-level actions, following a series of natural language instructions. All VLN-CE methods in the literature assume that language instructions are exact. However, in practice, instructions given by humans can contain errors when describing a spatial environment due to inaccurate memory or confusion. Current VLN-CE benchmarks do not address this scenario, making the state-of-the-art methods in VLN-CE fragile in the presence of erroneous instructions from human users. For the first time, we propose a novel benchmark dataset that introduces various types of instruction errors considering potential human causes. This benchmark provides valuable insight into the robustness of VLN systems in continuous environments. We observe a noticeable performance drop (up to -25%) in Success Rate when evaluating the state-of-the-art VLN-CE methods on our benchmark. Moreover, we formally define the task of Instruction Error Detection and Localization, and establish an evaluation protocol on top of our benchmark dataset. We also propose an effective method, based on a cross-modal transformer architecture, that achieves the best performance in error detection and localization, compared to baselines. Surprisingly, our proposed method has revealed errors in the validation set of the two commonly used datasets for VLN-CE, i.e., R2R-CE and RxR-CE, demonstrating the utility of our technique in other tasks. Code and dataset will be made available upon acceptance at https://intelligolabs.github.io/R2RIE-CE
Self-improving object detection via disagreement reconciliation
Feb 21, 2023



Abstract:Object detectors often experience a drop in performance when new environmental conditions are insufficiently represented in the training data. This paper studies how to automatically fine-tune a pre-existing object detector while exploring and acquiring images in a new environment without relying on human intervention, i.e., in a self-supervised fashion. In our setting, an agent initially explores the environment using a pre-trained off-the-shelf detector to locate objects and associate pseudo-labels. By assuming that pseudo-labels for the same object must be consistent across different views, we devise a novel mechanism for producing refined predictions from the consensus among observations. Our approach improves the off-the-shelf object detector by 2.66% in terms of mAP and outperforms the current state of the art without relying on ground-truth annotations.
Look around and learn: self-improving object detection by exploration
Feb 10, 2023Abstract:Object detectors often experience a drop in performance when new environmental conditions are insufficiently represented in the training data. This paper studies how to automatically fine-tune a pre-existing object detector while exploring and acquiring images in a new environment without relying on human intervention, i.e., in an utterly self-supervised fashion. In our setting, an agent initially learns to explore the environment using a pre-trained off-the-shelf detector to locate objects and associate pseudo-labels. By assuming that pseudo-labels for the same object must be consistent across different views, we learn an exploration policy mining hard samples and we devise a novel mechanism for producing refined predictions from the consensus among observations. Our approach outperforms the current state-of-the-art, and it closes the performance gap against a fully supervised setting without relying on ground-truth annotations. We also compare various exploration policies for the agent to gather more informative observations. Code and dataset will be made available upon paper acceptance
Learning Semantic Segmentation of Large-Scale Point Clouds with Random Sampling
Jul 06, 2021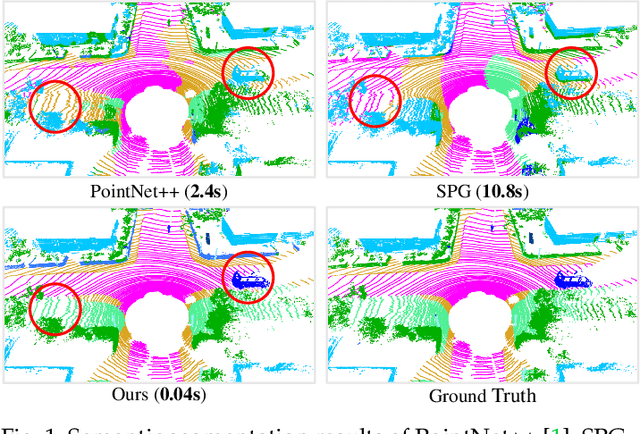
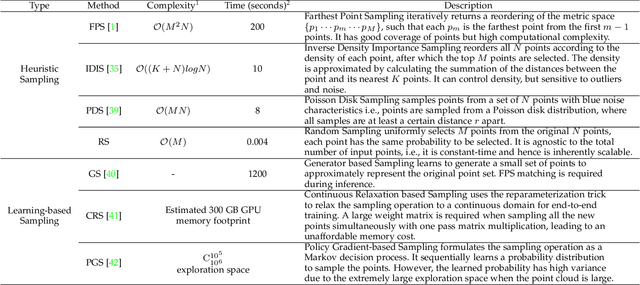
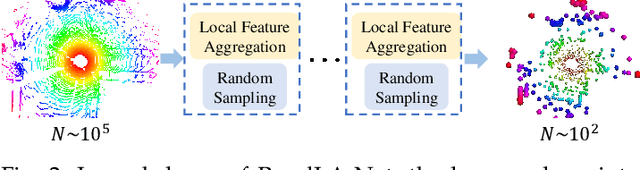
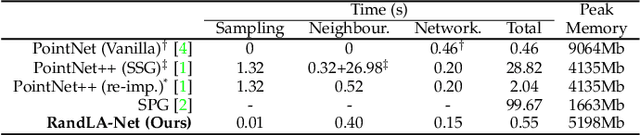
Abstract:We study the problem of efficient semantic segmentation of large-scale 3D point clouds. By relying on expensive sampling techniques or computationally heavy pre/post-processing steps, most existing approaches are only able to be trained and operate over small-scale point clouds. In this paper, we introduce RandLA-Net, an efficient and lightweight neural architecture to directly infer per-point semantics for large-scale point clouds. The key to our approach is to use random point sampling instead of more complex point selection approaches. Although remarkably computation and memory efficient, random sampling can discard key features by chance. To overcome this, we introduce a novel local feature aggregation module to progressively increase the receptive field for each 3D point, thereby effectively preserving geometric details. Comparative experiments show that our RandLA-Net can process 1 million points in a single pass up to 200x faster than existing approaches. Moreover, extensive experiments on five large-scale point cloud datasets, including Semantic3D, SemanticKITTI, Toronto3D, NPM3D and S3DIS, demonstrate the state-of-the-art semantic segmentation performance of our RandLA-Net.
SelectFusion: A Generic Framework to Selectively Learn Multisensory Fusion
Dec 30, 2019

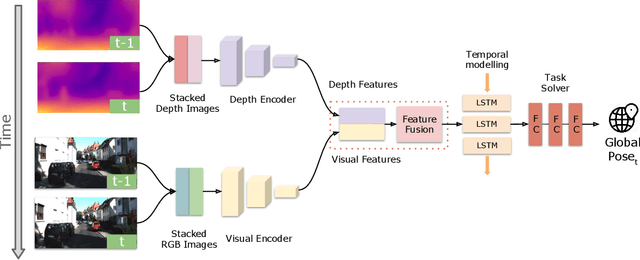

Abstract:Autonomous vehicles and mobile robotic systems are typically equipped with multiple sensors to provide redundancy. By integrating the observations from different sensors, these mobile agents are able to perceive the environment and estimate system states, e.g. locations and orientations. Although deep learning approaches for multimodal odometry estimation and localization have gained traction, they rarely focus on the issue of robust sensor fusion - a necessary consideration to deal with noisy or incomplete sensor observations in the real world. Moreover, current deep odometry models also suffer from a lack of interpretability. To this extent, we propose SelectFusion, an end-to-end selective sensor fusion module which can be applied to useful pairs of sensor modalities such as monocular images and inertial measurements, depth images and LIDAR point clouds. During prediction, the network is able to assess the reliability of the latent features from different sensor modalities and estimate both trajectory at scale and global pose. In particular, we propose two fusion modules based on different attention strategies: deterministic soft fusion and stochastic hard fusion, and we offer a comprehensive study of the new strategies compared to trivial direct fusion. We evaluate all fusion strategies in both ideal conditions and on progressively degraded datasets that present occlusions, noisy and missing data and time misalignment between sensors, and we investigate the effectiveness of the different fusion strategies in attending the most reliable features, which in itself, provides insights into the operation of the various models.
RandLA-Net: Efficient Semantic Segmentation of Large-Scale Point Clouds
Nov 25, 2019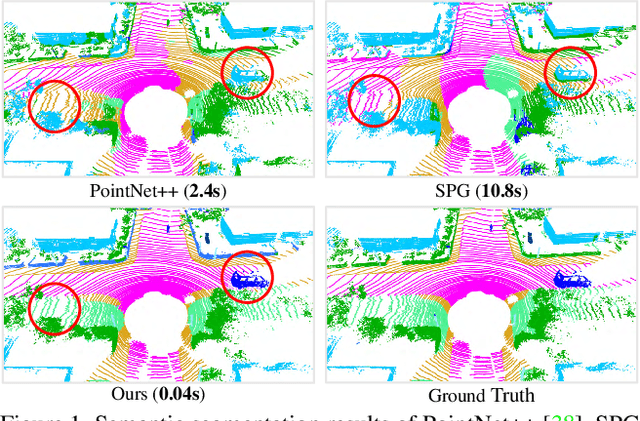
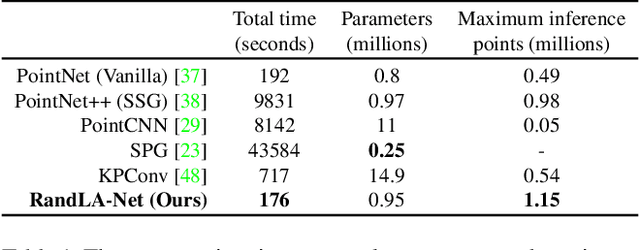
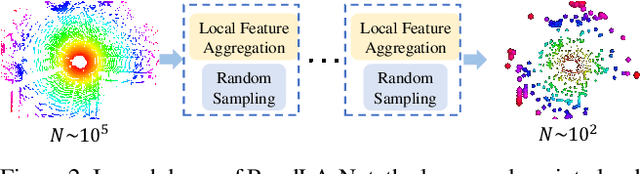
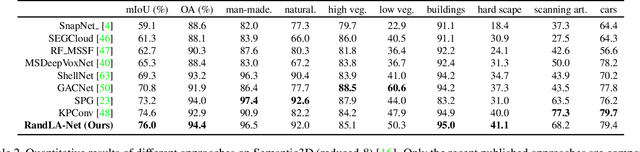
Abstract:We study the problem of efficient semantic segmentation for large-scale 3D point clouds. By relying on expensive sampling techniques or computationally heavy pre/post-processing steps, most existing approaches are only able to be trained and operate over small-scale point clouds. In this paper, we introduce RandLA-Net, an efficient and lightweight neural architecture to directly infer per-point semantics for large-scale point clouds. The key to our approach is to use random point sampling instead of more complex point selection approaches. Although remarkably computation and memory efficient, random sampling can discard key features by chance. To overcome this, we introduce a novel local feature aggregation module to progressively increase the receptive field for each 3D point, thereby effectively preserving geometric details. Extensive experiments show that our RandLA-Net can process 1 million points in a single pass with up to 200X faster than existing approaches. Moreover, our RandLA-Net clearly surpasses state-of-the-art approaches for semantic segmentation on two large-scale benchmarks Semantic3D and SemanticKITTI.
DeepTIO: A Deep Thermal-Inertial Odometry with Visual Hallucination
Sep 16, 2019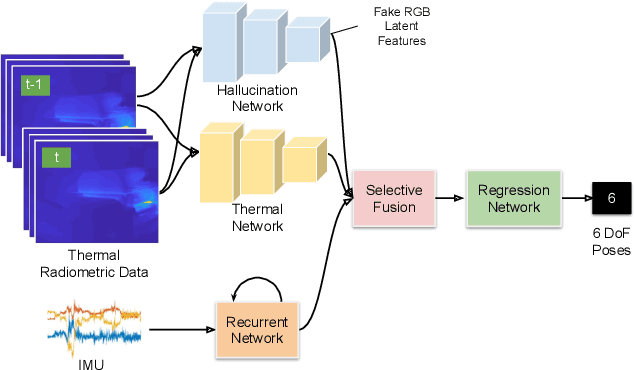
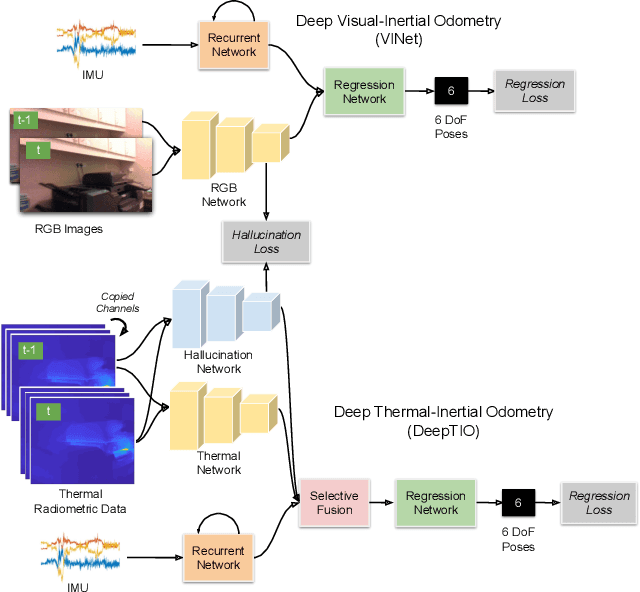
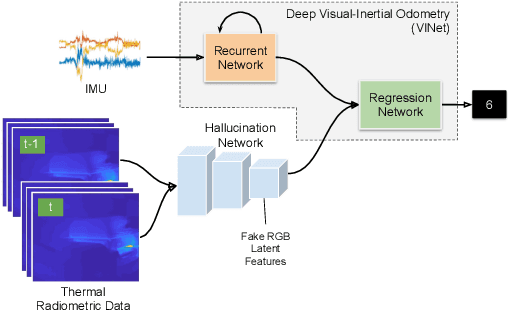
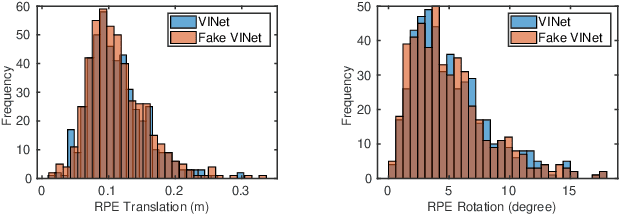
Abstract:Visual odometry shows excellent performance in a wide range of environments. However, in visually-denied scenarios (e.g. heavy smoke or darkness), pose estimates degrade or even fail. Thermal imaging cameras are commonly used for perception and inspection when the environment has low visibility. However, their use in odometry estimation is hampered by the lack of robust visual features. In part, this is as a result of the sensor measuring the ambient temperature profile rather than scene appearance and geometry. To overcome these issues, we propose a Deep Neural Network model for thermal-inertial odometry (DeepTIO) by incorporating a visual hallucination network to provide the thermal network with complementary information. The hallucination network is taught to predict fake visual features from thermal images by using the robust Huber loss. We also employ selective fusion to attentively fuse the features from three different modalities, i.e thermal, hallucination, and inertial features. Extensive experiments are performed in our large scale hand-held data in benign and smoke-filled environments, showing the efficacy of the proposed model.
Selective Sensor Fusion for Neural Visual-Inertial Odometry
Mar 04, 2019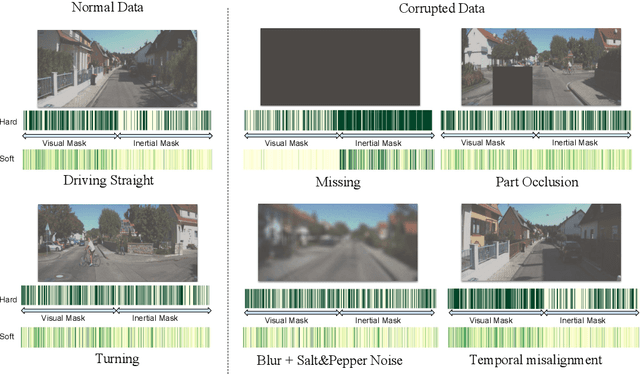
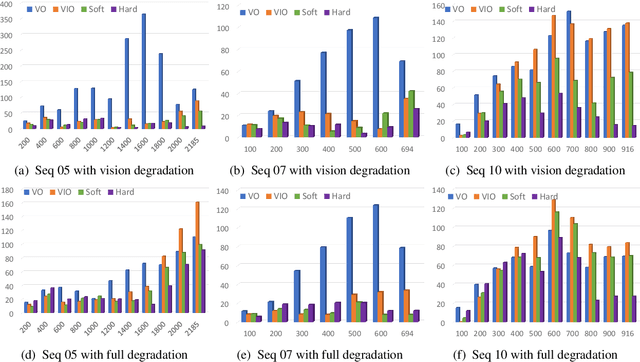
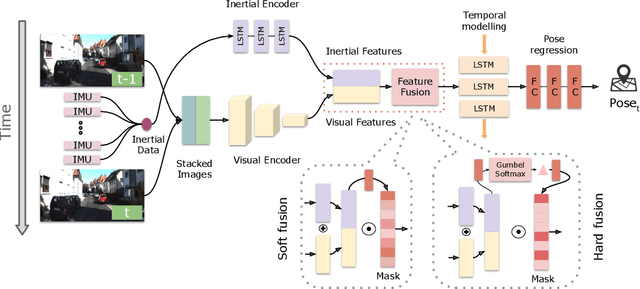

Abstract:Deep learning approaches for Visual-Inertial Odometry (VIO) have proven successful, but they rarely focus on incorporating robust fusion strategies for dealing with imperfect input sensory data. We propose a novel end-to-end selective sensor fusion framework for monocular VIO, which fuses monocular images and inertial measurements in order to estimate the trajectory whilst improving robustness to real-life issues, such as missing and corrupted data or bad sensor synchronization. In particular, we propose two fusion modalities based on different masking strategies: deterministic soft fusion and stochastic hard fusion, and we compare with previously proposed direct fusion baselines. During testing, the network is able to selectively process the features of the available sensor modalities and produce a trajectory at scale. We present a thorough investigation on the performances on three public autonomous driving, Micro Aerial Vehicle (MAV) and hand-held VIO datasets. The results demonstrate the effectiveness of the fusion strategies, which offer better performances compared to direct fusion, particularly in presence of corrupted data. In addition, we study the interpretability of the fusion networks by visualising the masking layers in different scenarios and with varying data corruption, revealing interesting correlations between the fusion networks and imperfect sensory input data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge