Sotiris Papatheodorou
FindAnything: Open-Vocabulary and Object-Centric Mapping for Robot Exploration in Any Environment
Apr 11, 2025Abstract:Geometrically accurate and semantically expressive map representations have proven invaluable to facilitate robust and safe mobile robot navigation and task planning. Nevertheless, real-time, open-vocabulary semantic understanding of large-scale unknown environments is still an open problem. In this paper we present FindAnything, an open-world mapping and exploration framework that incorporates vision-language information into dense volumetric submaps. Thanks to the use of vision-language features, FindAnything bridges the gap between pure geometric and open-vocabulary semantic information for a higher level of understanding while allowing to explore any environment without the help of any external source of ground-truth pose information. We represent the environment as a series of volumetric occupancy submaps, resulting in a robust and accurate map representation that deforms upon pose updates when the underlying SLAM system corrects its drift, allowing for a locally consistent representation between submaps. Pixel-wise vision-language features are aggregated from efficient SAM (eSAM)-generated segments, which are in turn integrated into object-centric volumetric submaps, providing a mapping from open-vocabulary queries to 3D geometry that is scalable also in terms of memory usage. The open-vocabulary map representation of FindAnything achieves state-of-the-art semantic accuracy in closed-set evaluations on the Replica dataset. This level of scene understanding allows a robot to explore environments based on objects or areas of interest selected via natural language queries. Our system is the first of its kind to be deployed on resource-constrained devices, such as MAVs, leveraging vision-language information for real-world robotic tasks.
Efficient Submap-based Autonomous MAV Exploration using Visual-Inertial SLAM Configurable for LiDARs or Depth Cameras
Sep 25, 2024



Abstract:Autonomous exploration of unknown space is an essential component for the deployment of mobile robots in the real world. Safe navigation is crucial for all robotics applications and requires accurate and consistent maps of the robot's surroundings. To achieve full autonomy and allow deployment in a wide variety of environments, the robot must rely on on-board state estimation which is prone to drift over time. We propose a Micro Aerial Vehicle (MAV) exploration framework based on local submaps to allow retaining global consistency by applying loop-closure corrections to the relative submap poses. To enable large-scale exploration we efficiently compute global, environment-wide frontiers from the local submap frontiers and use a sampling-based next-best-view exploration planner. Our method seamlessly supports using either a LiDAR sensor or a depth camera, making it suitable for different kinds of MAV platforms. We perform comparative evaluations in simulation against a state-of-the-art submap-based exploration framework to showcase the efficiency and reconstruction quality of our approach. Finally, we demonstrate the applicability of our method to real-world MAVs, one equipped with a LiDAR and the other with a depth camera. Video available at https://youtu.be/Uf5fwmYcuq4 .
Scalable Autonomous Drone Flight in the Forest with Visual-Inertial SLAM and Dense Submaps Built without LiDAR
Mar 14, 2024



Abstract:Forestry constitutes a key element for a sustainable future, while it is supremely challenging to introduce digital processes to improve efficiency. The main limitation is the difficulty of obtaining accurate maps at high temporal and spatial resolution as a basis for informed forestry decision-making, due to the vast area forests extend over and the sheer number of trees. To address this challenge, we present an autonomous Micro Aerial Vehicle (MAV) system which purely relies on cost-effective and light-weight passive visual and inertial sensors to perform under-canopy autonomous navigation. We leverage visual-inertial simultaneous localization and mapping (VI-SLAM) for accurate MAV state estimates and couple it with a volumetric occupancy submapping system to achieve a scalable mapping framework which can be directly used for path planning. As opposed to a monolithic map, submaps inherently deal with inevitable drift and corrections from VI-SLAM, since they move with pose estimates as they are updated. To ensure the safety of the MAV during navigation, we also propose a novel reference trajectory anchoring scheme that moves and deforms the reference trajectory the MAV is tracking upon state updates from the VI-SLAM system in a consistent way, even upon large changes in state estimates due to loop-closures. We thoroughly validate our system in both real and simulated forest environments with high tree densities in excess of 400 trees per hectare and at speeds up to 3 m/s - while not encountering a single collision or system failure. To the best of our knowledge this is the first system which achieves this level of performance in such unstructured environment using low-cost passive visual sensors and fully on-board computation including VI-SLAM.
Control-Barrier-Aided Teleoperation with Visual-Inertial SLAM for Safe MAV Navigation in Complex Environments
Mar 07, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we consider a Micro Aerial Vehicle (MAV) system teleoperated by a non-expert and introduce a perceptive safety filter that leverages Control Barrier Functions (CBFs) in conjunction with Visual-Inertial Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (VI-SLAM) and dense 3D occupancy mapping to guarantee safe navigation in complex and unstructured environments. Our system relies solely on onboard IMU measurements, stereo infrared images, and depth images and autonomously corrects teleoperated inputs when they are deemed unsafe. We define a point in 3D space as unsafe if it satisfies either of two conditions: (i) it is occupied by an obstacle, or (ii) it remains unmapped. At each time step, an occupancy map of the environment is updated by the VI-SLAM by fusing the onboard measurements, and a CBF is constructed to parameterize the (un)safe region in the 3D space. Given the CBF and state feedback from the VI-SLAM module, a safety filter computes a certified reference that best matches the teleoperation input while satisfying the safety constraint encoded by the CBF. In contrast to existing perception-based safe control frameworks, we directly close the perception-action loop and demonstrate the full capability of safe control in combination with real-time VI-SLAM without any external infrastructure or prior knowledge of the environment. We verify the efficacy of the perceptive safety filter in real-time MAV experiments using exclusively onboard sensing and computation and show that the teleoperated MAV is able to safely navigate through unknown environments despite arbitrary inputs sent by the teleoperator.
Finding Things in the Unknown: Semantic Object-Centric Exploration with an MAV
Mar 03, 2023



Abstract:Exploration of unknown space with an autonomous mobile robot is a well-studied problem. In this work we broaden the scope of exploration, moving beyond the pure geometric goal of uncovering as much free space as possible. We believe that for many practical applications, exploration should be contextualised with semantic and object-level understanding of the environment for task-specific exploration. Here, we study the task of both finding specific objects in unknown space as well as reconstructing them to a target level of detail. We therefore extend our environment reconstruction to not only consist of a background map, but also object-level and semantically fused submaps. Importantly, we adapt our previous objective function of uncovering as much free space as possible in as little time as possible with two additional elements: first, we require a maximum observation distance of background surfaces to ensure target objects are not missed by image-based detectors because they are too small to be detected. Second, we require an even smaller maximum distance to the found objects in order to reconstruct them with the desired accuracy. We further created a Micro Aerial Vehicle (MAV) semantic exploration simulator based on Habitat in order to quantitatively demonstrate how our framework can be used to efficiently find specific objects as part of exploration. Finally, we showcase this capability can be deployed in real-world scenes involving our drone equipped with an Intel RealSense D455 RGB-D camera.
Efficient Volumetric Mapping Using Depth Completion With Uncertainty for Robotic Navigation
Dec 05, 2020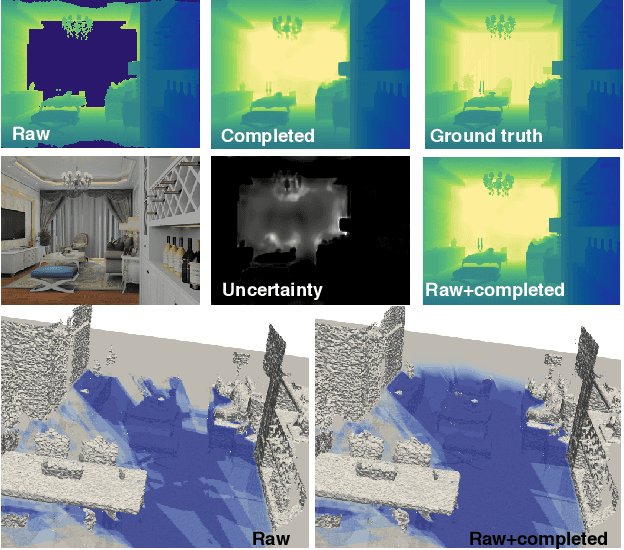
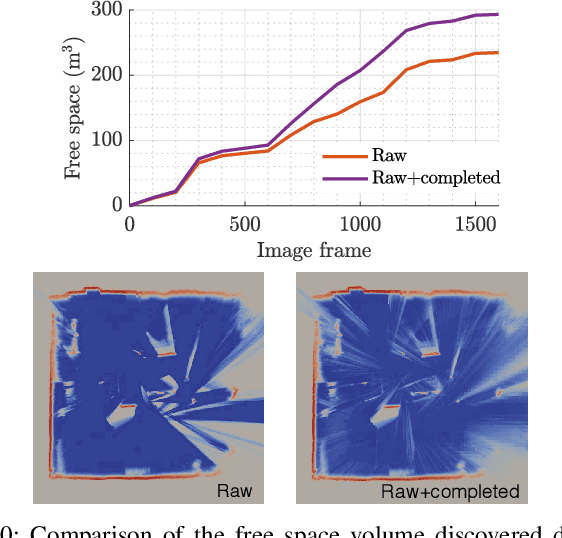
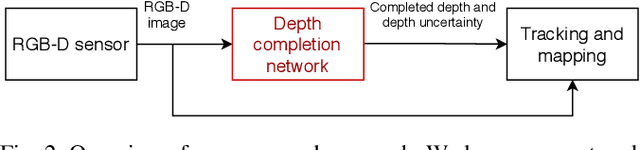
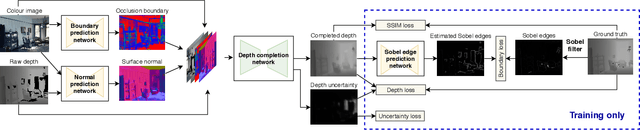
Abstract:In robotic applications, a key requirement for safe and efficient motion planning is the ability to map obstacle-free space in unknown, cluttered 3D environments. However, commodity-grade RGB-D cameras commonly used for sensing fail to register valid depth values on shiny, glossy, bright, or distant surfaces, leading to missing data in the map. To address this issue, we propose a framework leveraging probabilistic depth completion as an additional input for spatial mapping. We introduce a deep learning architecture providing uncertainty estimates for the depth completion of RGB-D images. Our pipeline exploits the inferred missing depth values and depth uncertainty to complement raw depth images and improve the speed and quality of free space mapping. Evaluations on synthetic data show that our approach maps significantly more correct free space with relatively low error when compared against using raw data alone in different indoor environments; thereby producing more complete maps that can be directly used for robotic navigation tasks. The performance of our framework is validated using real-world data.
Multi-Resolution 3D Mapping with Explicit Free Space Representation for Fast and Accurate Mobile Robot Motion Planning
Oct 19, 2020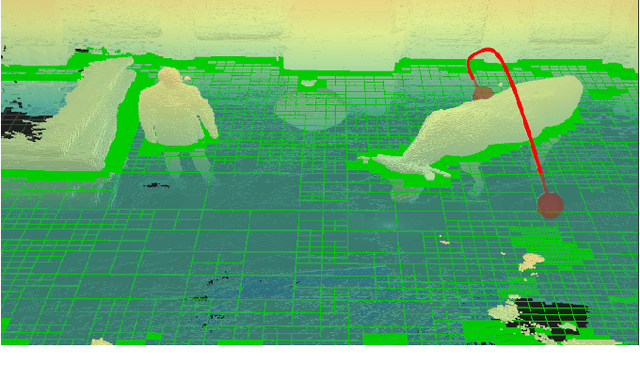
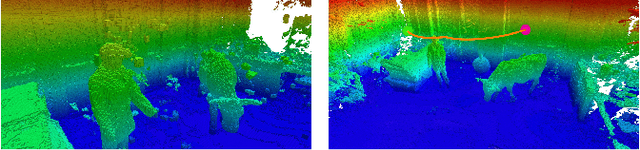
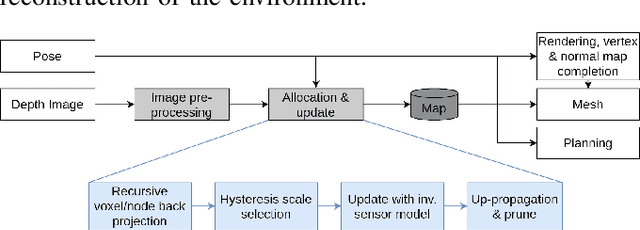
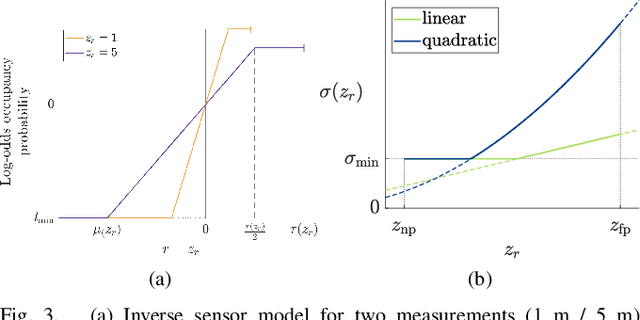
Abstract:With the aim of bridging the gap between high quality reconstruction and mobile robot motion planning, we propose an efficient system that leverages the concept of adaptive-resolution volumetric mapping, which naturally integrates with the hierarchical decomposition of space in an octree data structure. Instead of a Truncated Signed Distance Function (TSDF), we adopt mapping of occupancy probabilities in log-odds representation, which allows to represent both surfaces, as well as the entire free, i.e. observed space, as opposed to unobserved space. We introduce a method for choosing resolution -- on the fly -- in real-time by means of a multi-scale max-min pooling of the input depth image. The notion of explicit free space mapping paired with the spatial hierarchy in the data structure, as well as map resolution, allows for collision queries, as needed for robot motion planning, at unprecedented speed. We quantitatively evaluate mapping accuracy, memory, runtime performance, and planning performance showing improvements over the state of the art, particularly in cases requiring high resolution maps.
Elastic and Efficient LiDAR Reconstruction for Large-Scale Exploration Tasks
Oct 19, 2020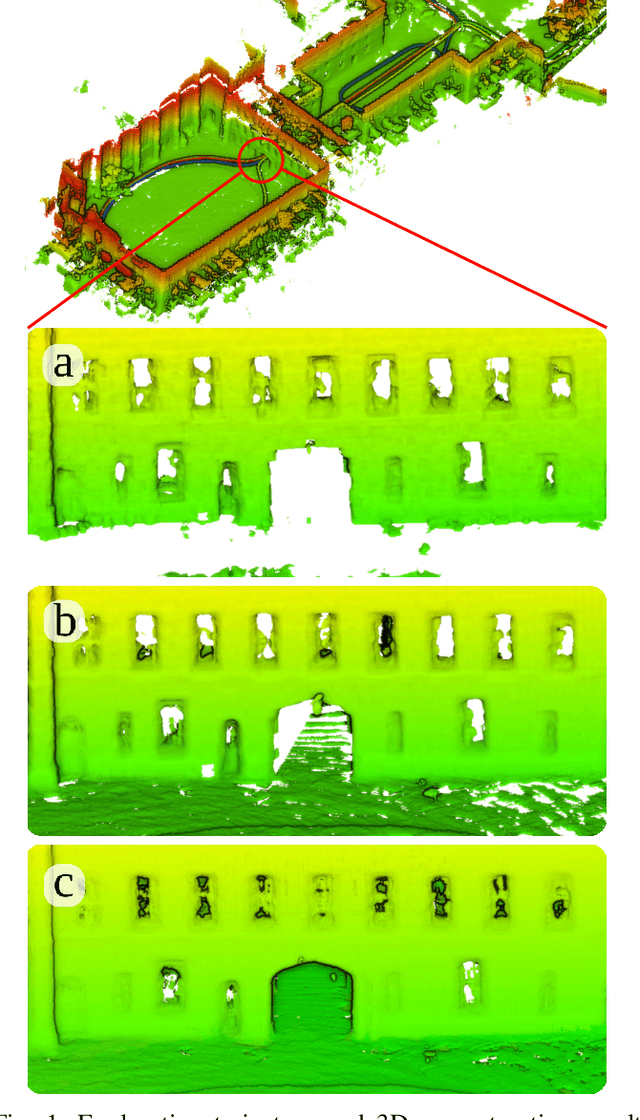
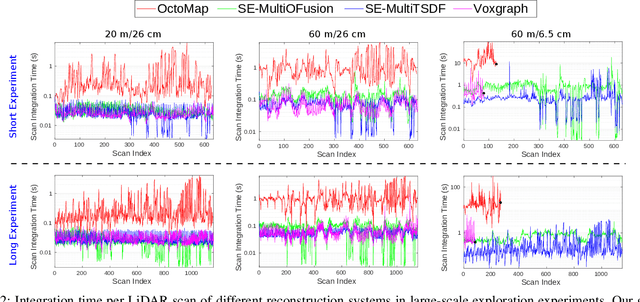
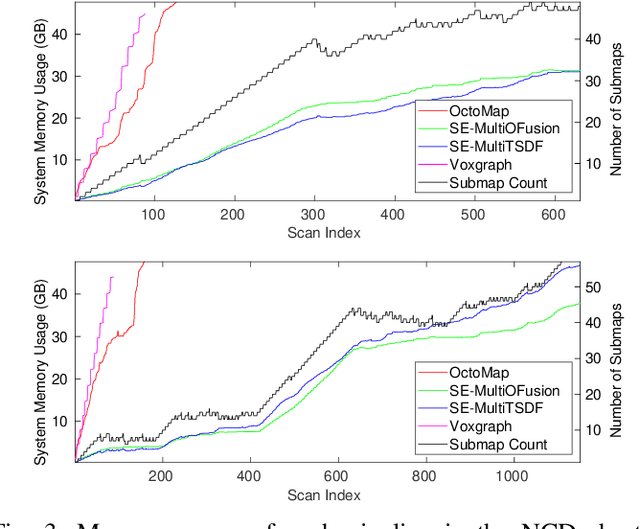
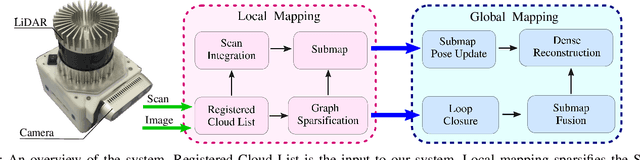
Abstract:We present an efficient, elastic 3D LiDAR reconstruction framework which can reconstruct up to maximum LiDAR ranges (60 m) at multiple frames per second, thus enabling robot exploration in large-scale environments. Our approach only requires a CPU. We focus on three main challenges of large-scale reconstruction: integration of long-range LiDAR scans at high frequency, the capacity to deform the reconstruction after loop closures are detected, and scalability for long-duration exploration. Our system extends upon a state-of-the-art efficient RGB-D volumetric reconstruction technique, called supereight, to support LiDAR scans and a newly developed submapping technique to allow for dynamic correction of the 3D reconstruction. We then introduce a novel pose graph sparsification and submap fusion feature to make our system more scalable for large environments. We evaluate the performance using a published dataset captured by a handheld mapping device scanning a set of buildings, and with a mobile robot exploring an underground room network. Experimental results demonstrate that our system can reconstruct at 3 Hz with 60 m sensor range and ~5 cm resolution, while state-of-the-art approaches can only reconstruct to 25 cm resolution or 20 m range at the same frequency.
Fast Frontier-based Information-driven Autonomous Exploration with an MAV
Feb 13, 2020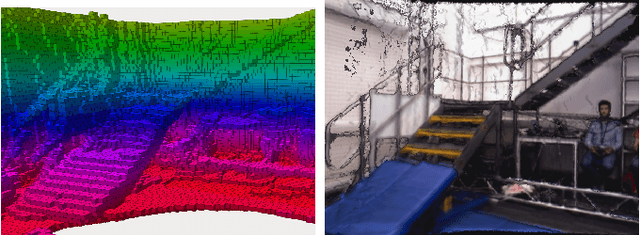
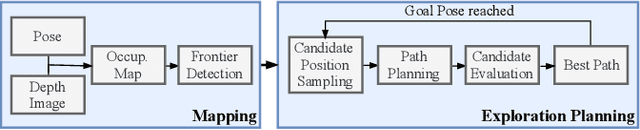
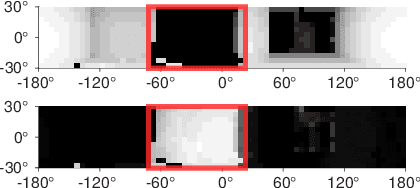
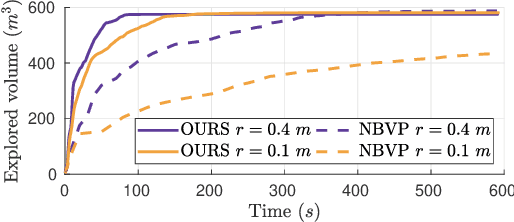
Abstract:Exploration and collision-free navigation through an unknown environment is a fundamental task for autonomous robots. In this paper, a novel exploration strategy for Micro Aerial Vehicles (MAVs) is presented. The goal of the exploration strategy is the reduction of map entropy regarding occupancy probabilities, which is reflected in a utility function to be maximised. We achieve fast and efficient exploration performance with tight integration between our octree-based occupancy mapping approach, frontier extraction, and motion planning-as a hybrid between frontier-based and sampling-based exploration methods. The computationally expensive frontier clustering employed in classic frontier-based exploration is avoided by exploiting the implicit grouping of frontier voxels in the underlying octree map representation. Candidate next-views are sampled from the map frontiers and are evaluated using a utility function combining map entropy and travel time, where the former is computed efficiently using sparse raycasting. These optimisations along with the targeted exploration of frontier-based methods result in a fast and computationally efficient exploration planner. The proposed method is evaluated using both simulated and real-world experiments, demonstrating clear advantages over state-of-the-art approaches.
Distributed area coverage control with imprecise robot localization: Simulation and experimental studies
Dec 14, 2016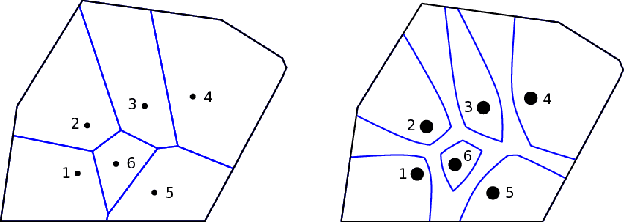
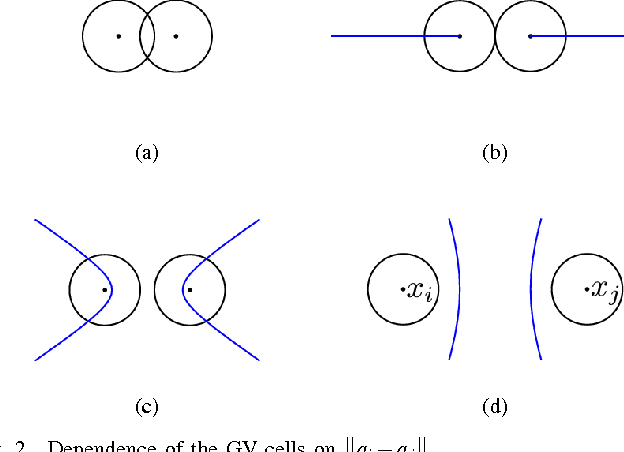
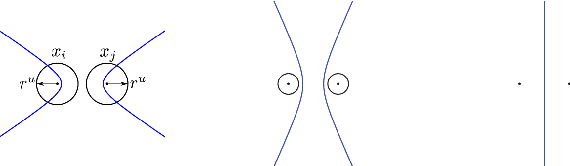
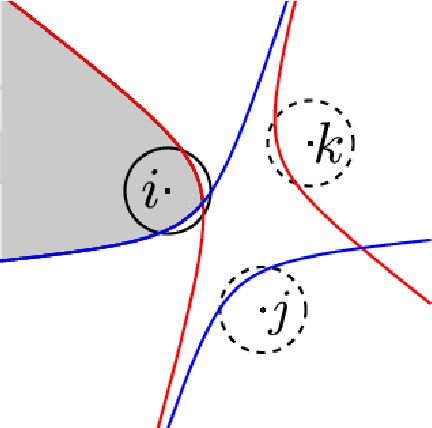
Abstract:This article examines the area coverage problem for a network of mobile robots with imprecise agents' localization. Each robot has uniform radial sensing ability, governed by first order kinodynamics. The convex-space is partitioned based on the Guaranteed Voronoi (GV) principle and each robot's area of responsibility corresponds to its GV-cell, bounded by hyperbolic arcs. The proposed control law is distributed, demanding the positioning information about its GV-Delaunay neighbors. Simulation and experimental studies are offered to highlight the efficiency of the proposed control law.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge