Songxuan Lai
OCR-Reasoning Benchmark: Unveiling the True Capabilities of MLLMs in Complex Text-Rich Image Reasoning
May 22, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in multimodal slow-thinking systems have demonstrated remarkable performance across diverse visual reasoning tasks. However, their capabilities in text-rich image reasoning tasks remain understudied due to the lack of a systematic benchmark. To address this gap, we propose OCR-Reasoning, a comprehensive benchmark designed to systematically assess Multimodal Large Language Models on text-rich image reasoning tasks. The benchmark comprises 1,069 human-annotated examples spanning 6 core reasoning abilities and 18 practical reasoning tasks in text-rich visual scenarios. Furthermore, unlike other text-rich image understanding benchmarks that only annotate the final answers, OCR-Reasoning also annotates the reasoning process simultaneously. With the annotated reasoning process and the final answers, OCR-Reasoning evaluates not only the final answers generated by models but also their reasoning processes, enabling a holistic analysis of their problem-solving abilities. Leveraging this benchmark, we conducted a comprehensive evaluation of state-of-the-art MLLMs. Our results demonstrate the limitations of existing methodologies. Notably, even state-of-the-art MLLMs exhibit substantial difficulties, with none achieving accuracy surpassing 50\% across OCR-Reasoning, indicating that the challenges of text-rich image reasoning are an urgent issue to be addressed. The benchmark and evaluation scripts are available at https://github.com/SCUT-DLVCLab/OCR-Reasoning.
Privacy-Preserving Biometric Verification with Handwritten Random Digit String
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:Handwriting verification has stood as a steadfast identity authentication method for decades. However, this technique risks potential privacy breaches due to the inclusion of personal information in handwritten biometrics such as signatures. To address this concern, we propose using the Random Digit String (RDS) for privacy-preserving handwriting verification. This approach allows users to authenticate themselves by writing an arbitrary digit sequence, effectively ensuring privacy protection. To evaluate the effectiveness of RDS, we construct a new HRDS4BV dataset composed of online naturally handwritten RDS. Unlike conventional handwriting, RDS encompasses unconstrained and variable content, posing significant challenges for modeling consistent personal writing style. To surmount this, we propose the Pattern Attentive VErification Network (PAVENet), along with a Discriminative Pattern Mining (DPM) module. DPM adaptively enhances the recognition of consistent and discriminative writing patterns, thus refining handwriting style representation. Through comprehensive evaluations, we scrutinize the applicability of online RDS verification and showcase a pronounced outperformance of our model over existing methods. Furthermore, we discover a noteworthy forgery phenomenon that deviates from prior findings and discuss its positive impact in countering malicious impostor attacks. Substantially, our work underscores the feasibility of privacy-preserving biometric verification and propels the prospects of its broader acceptance and application.
DocKylin: A Large Multimodal Model for Visual Document Understanding with Efficient Visual Slimming
Jun 27, 2024



Abstract:Current multimodal large language models (MLLMs) face significant challenges in visual document understanding (VDU) tasks due to the high resolution, dense text, and complex layouts typical of document images. These characteristics demand a high level of detail perception ability from MLLMs. While increasing input resolution improves detail perception, it also leads to longer sequences of visual tokens, increasing computational costs and straining the models' ability to handle long contexts. To address these challenges, we introduce DocKylin, a document-centric MLLM that performs visual content slimming at both the pixel and token levels, thereby reducing token sequence length in VDU scenarios. DocKylin utilizes an Adaptive Pixel Slimming (APS) preprocessing module to perform pixel-level slimming, increasing the proportion of informative pixels. Moreover, DocKylin incorporates a novel Dynamic Token Slimming (DTS) module to conduct token-level slimming, filtering essential tokens and removing others to create a compressed, adaptive visual sequence. Experiments demonstrate DocKylin's promising performance across various VDU benchmarks. Notably, both the proposed APS and DTS are parameter-free, facilitating easy integration into existing MLLMs, and our experiments indicate their potential for broader applications.
PageNet: Towards End-to-End Weakly Supervised Page-Level Handwritten Chinese Text Recognition
Jul 29, 2022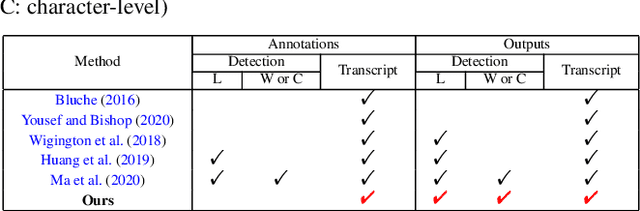
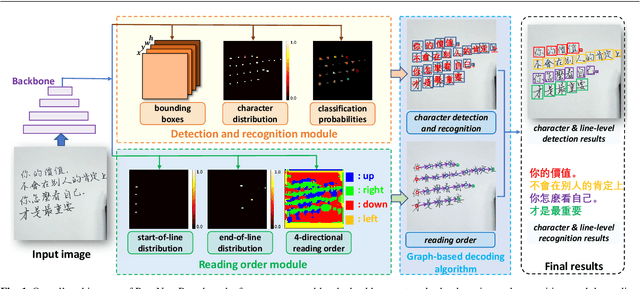
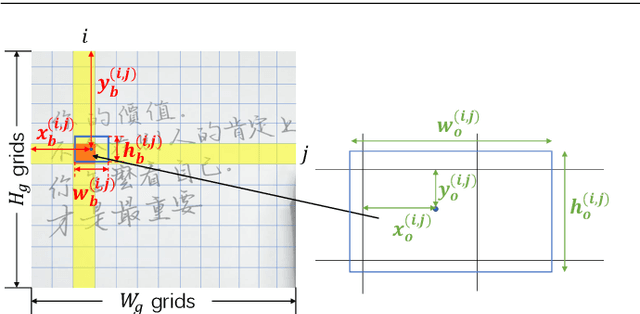
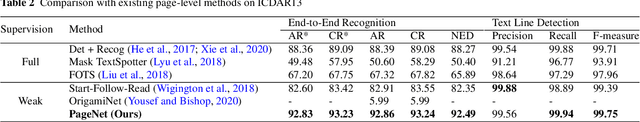
Abstract:Handwritten Chinese text recognition (HCTR) has been an active research topic for decades. However, most previous studies solely focus on the recognition of cropped text line images, ignoring the error caused by text line detection in real-world applications. Although some approaches aimed at page-level text recognition have been proposed in recent years, they either are limited to simple layouts or require very detailed annotations including expensive line-level and even character-level bounding boxes. To this end, we propose PageNet for end-to-end weakly supervised page-level HCTR. PageNet detects and recognizes characters and predicts the reading order between them, which is more robust and flexible when dealing with complex layouts including multi-directional and curved text lines. Utilizing the proposed weakly supervised learning framework, PageNet requires only transcripts to be annotated for real data; however, it can still output detection and recognition results at both the character and line levels, avoiding the labor and cost of labeling bounding boxes of characters and text lines. Extensive experiments conducted on five datasets demonstrate the superiority of PageNet over existing weakly supervised and fully supervised page-level methods. These experimental results may spark further research beyond the realms of existing methods based on connectionist temporal classification or attention. The source code is available at https://github.com/shannanyinxiang/PageNet.
SPTS: Single-Point Text Spotting
Dec 15, 2021
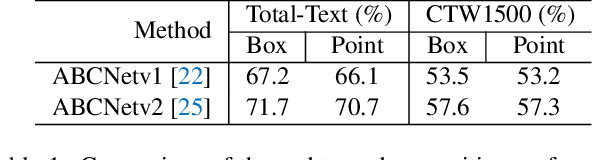

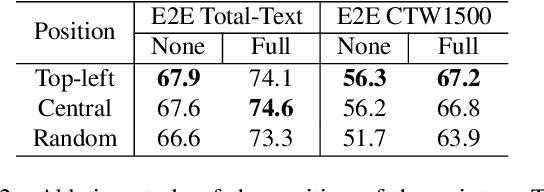
Abstract:Almost all scene text spotting (detection and recognition) methods rely on costly box annotation (e.g., text-line box, word-level box, and character-level box). For the first time, we demonstrate that training scene text spotting models can be achieved with an extremely low-cost annotation of a single-point for each instance. We propose an end-to-end scene text spotting method that tackles scene text spotting as a sequence prediction task, like language modeling. Given an image as input, we formulate the desired detection and recognition results as a sequence of discrete tokens and use an auto-regressive transformer to predict the sequence. We achieve promising results on several horizontal, multi-oriented, and arbitrarily shaped scene text benchmarks. Most significantly, we show that the performance is not very sensitive to the positions of the point annotation, meaning that it can be much easier to be annotated and automatically generated than the bounding box that requires precise positions. We believe that such a pioneer attempt indicates a significant opportunity for scene text spotting applications of a much larger scale than previously possible.
SVC-onGoing: Signature Verification Competition
Aug 13, 2021



Abstract:This article presents SVC-onGoing, an on-going competition for on-line signature verification where researchers can easily benchmark their systems against the state of the art in an open common platform using large-scale public databases, such as DeepSignDB and SVC2021_EvalDB, and standard experimental protocols. SVC-onGoing is based on the ICDAR 2021 Competition on On-Line Signature Verification (SVC 2021), which has been extended to allow participants anytime. The goal of SVC-onGoing is to evaluate the limits of on-line signature verification systems on popular scenarios (office/mobile) and writing inputs (stylus/finger) through large-scale public databases. Three different tasks are considered in the competition, simulating realistic scenarios as both random and skilled forgeries are simultaneously considered on each task. The results obtained in SVC-onGoing prove the high potential of deep learning methods in comparison with traditional methods. In particular, the best signature verification system has obtained Equal Error Rate (EER) values of 3.33% (Task 1), 7.41% (Task 2), and 6.04% (Task 3). Future studies in the field should be oriented to improve the performance of signature verification systems on the challenging mobile scenarios of SVC-onGoing in which several mobile devices and the finger are used during the signature acquisition.
ICDAR 2021 Competition on On-Line Signature Verification
Jun 01, 2021

Abstract:This paper describes the experimental framework and results of the ICDAR 2021 Competition on On-Line Signature Verification (SVC 2021). The goal of SVC 2021 is to evaluate the limits of on-line signature verification systems on popular scenarios (office/mobile) and writing inputs (stylus/finger) through large-scale public databases. Three different tasks are considered in the competition, simulating realistic scenarios as both random and skilled forgeries are simultaneously considered on each task. The results obtained in SVC 2021 prove the high potential of deep learning methods. In particular, the best on-line signature verification system of SVC 2021 obtained Equal Error Rate (EER) values of 3.33% (Task 1), 7.41% (Task 2), and 6.04% (Task 3). SVC 2021 will be established as an on-going competition, where researchers can easily benchmark their systems against the state of the art in an open common platform using large-scale public databases such as DeepSignDB and SVC2021_EvalDB, and standard experimental protocols.
Improving Attention-Based Handwritten Mathematical Expression Recognition with Scale Augmentation and Drop Attention
Jul 20, 2020



Abstract:Handwritten mathematical expression recognition (HMER) is an important research direction in handwriting recognition. The performance of HMER suffers from the two-dimensional structure of mathematical expressions (MEs). To address this issue, in this paper, we propose a high-performance HMER model with scale augmentation and drop attention. Specifically, tackling ME with unstable scale in both horizontal and vertical directions, scale augmentation improves the performance of the model on MEs of various scales. An attention-based encoder-decoder network is used for extracting features and generating predictions. In addition, drop attention is proposed to further improve performance when the attention distribution of the decoder is not precise. Compared with previous methods, our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on two public datasets of CROHME 2014 and CROHME 2016.
SynSig2Vec: Learning Representations from Synthetic Dynamic Signatures for Real-world Verification
Nov 14, 2019



Abstract:An open research problem in automatic signature verification is the skilled forgery attacks. However, the skilled forgeries are very difficult to acquire for representation learning. To tackle this issue, this paper proposes to learn dynamic signature representations through ranking synthesized signatures. First, a neuromotor inspired signature synthesis method is proposed to synthesize signatures with different distortion levels for any template signature. Then, given the templates, we construct a lightweight one-dimensional convolutional network to learn to rank the synthesized samples, and directly optimize the average precision of the ranking to exploit relative and fine-grained signature similarities. Finally, after training, fixed-length representations can be extracted from dynamic signatures of variable lengths for verification. One highlight of our method is that it requires neither skilled nor random forgeries for training, yet it surpasses the state-of-the-art by a large margin on two public benchmarks.
Offline Writer Identification based on the Path Signature Feature
May 03, 2019



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel set of features for offline writer identification based on the path signature approach, which provides a principled way to express information contained in a path. By extracting local pathlets from handwriting contours, the path signature can also characterize the offline handwriting style. A codebook method based on the log path signature---a more compact way to express the path signature---is used in this work and shows competitive results on several benchmark offline writer identification datasets, namely the IAM, Firemaker, CVL and ICDAR2013 writer identification contest dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge