Sining Sun
Streaming Decoder-Only Automatic Speech Recognition with Discrete Speech Units: A Pilot Study
Jun 27, 2024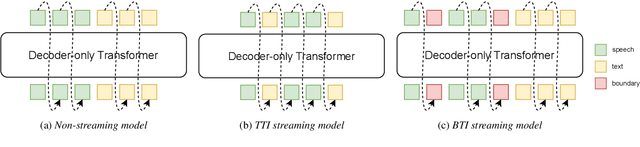
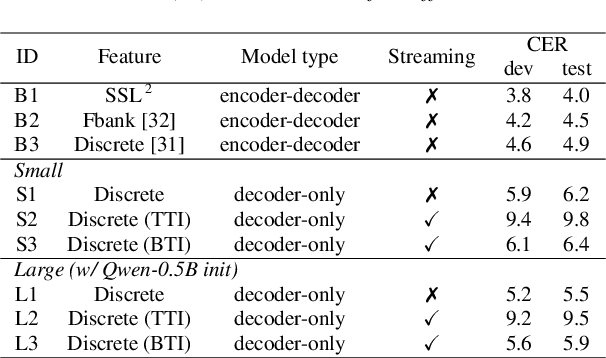
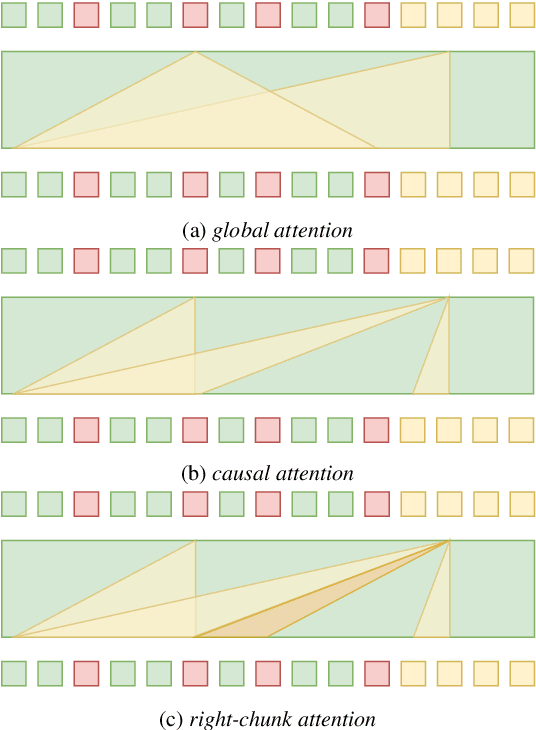
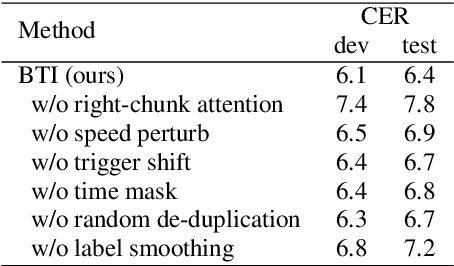
Abstract:Unified speech-text models like SpeechGPT, VioLA, and AudioPaLM have shown impressive performance across various speech-related tasks, especially in Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR). These models typically adopt a unified method to model discrete speech and text tokens, followed by training a decoder-only transformer. However, they are all designed for non-streaming ASR tasks, where the entire speech utterance is needed during decoding. Hence, we introduce a decoder-only model exclusively designed for streaming recognition, incorporating a dedicated boundary token to facilitate streaming recognition and employing causal attention masking during the training phase. Furthermore, we introduce right-chunk attention and various data augmentation techniques to improve the model's contextual modeling abilities. While achieving streaming speech recognition, experiments on the AISHELL-1 and -2 datasets demonstrate the competitive performance of our streaming approach with non-streaming decoder-only counterparts.
Skipformer: A Skip-and-Recover Strategy for Efficient Speech Recognition
Mar 13, 2024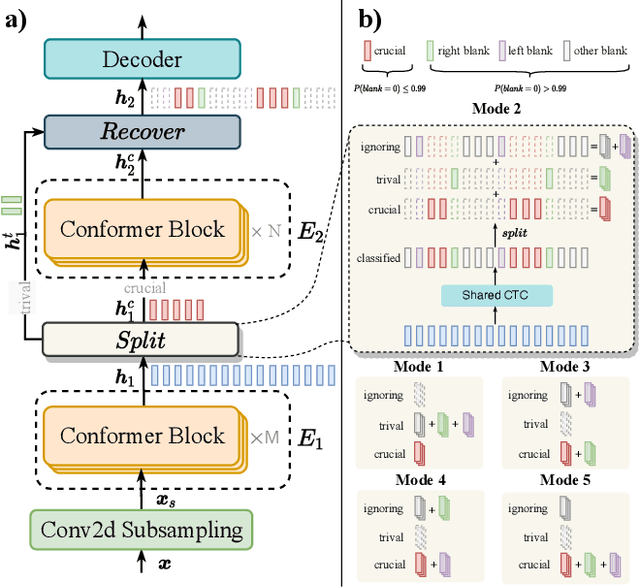
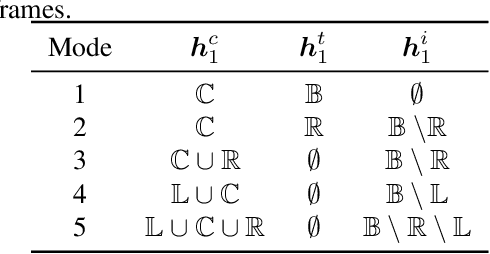
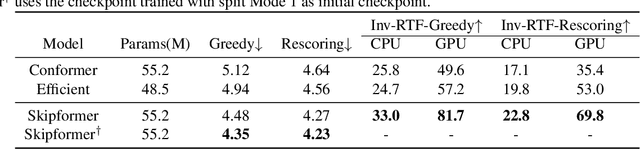
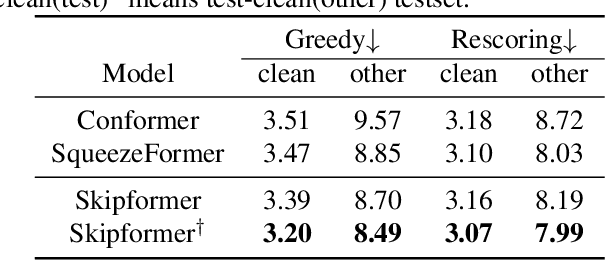
Abstract:Conformer-based attention models have become the de facto backbone model for Automatic Speech Recognition tasks. A blank symbol is usually introduced to align the input and output sequences for CTC or RNN-T models. Unfortunately, the long input length overloads computational budget and memory consumption quadratically by attention mechanism. In this work, we propose a "Skip-and-Recover" Conformer architecture, named Skipformer, to squeeze sequence input length dynamically and inhomogeneously. Skipformer uses an intermediate CTC output as criteria to split frames into three groups: crucial, skipping and ignoring. The crucial group feeds into next conformer blocks and its output joint with skipping group by original temporal order as the final encoder output. Experiments show that our model reduces the input sequence length by 31 times on Aishell-1 and 22 times on Librispeech corpus. Meanwhile, the model can achieve better recognition accuracy and faster inference speed than recent baseline models. Our code is open-sourced and available online.
Self-Supervised Disentangled Representation Learning for Robust Target Speech Extraction
Dec 16, 2023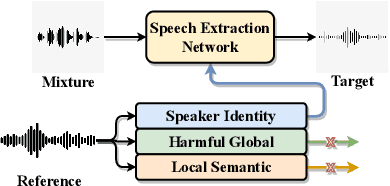
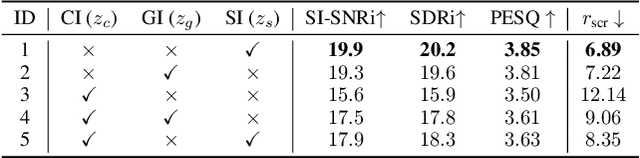
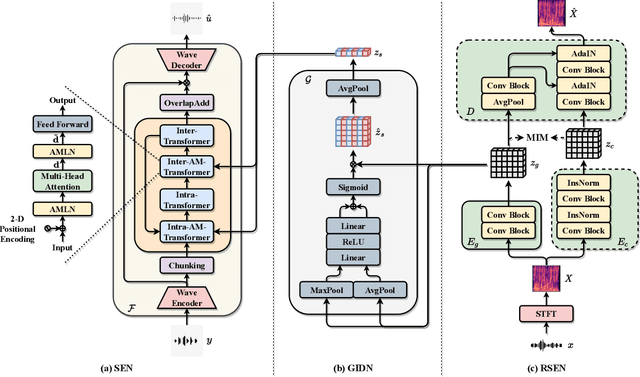
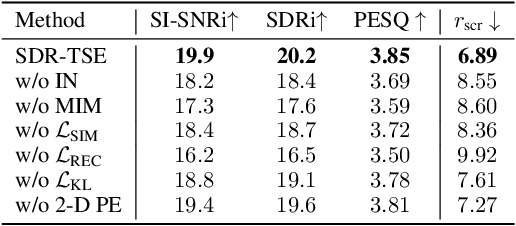
Abstract:Speech signals are inherently complex as they encompass both global acoustic characteristics and local semantic information. However, in the task of target speech extraction, certain elements of global and local semantic information in the reference speech, which are irrelevant to speaker identity, can lead to speaker confusion within the speech extraction network. To overcome this challenge, we propose a self-supervised disentangled representation learning method. Our approach tackles this issue through a two-phase process, utilizing a reference speech encoding network and a global information disentanglement network to gradually disentangle the speaker identity information from other irrelevant factors. We exclusively employ the disentangled speaker identity information to guide the speech extraction network. Moreover, we introduce the adaptive modulation Transformer to ensure that the acoustic representation of the mixed signal remains undisturbed by the speaker embeddings. This component incorporates speaker embeddings as conditional information, facilitating natural and efficient guidance for the speech extraction network. Experimental results substantiate the effectiveness of our meticulously crafted approach, showcasing a substantial reduction in the likelihood of speaker confusion.
Key Frame Mechanism For Efficient Conformer Based End-to-end Speech Recognition
Oct 28, 2023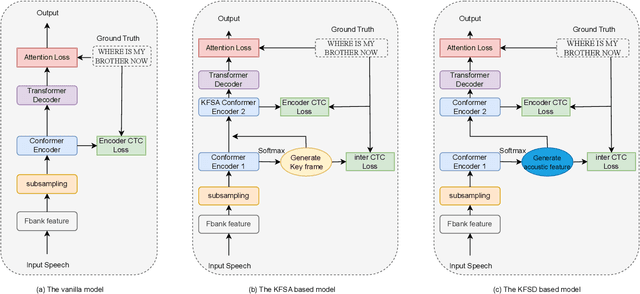
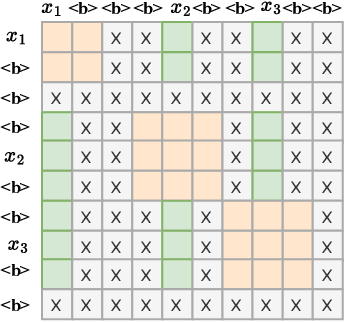
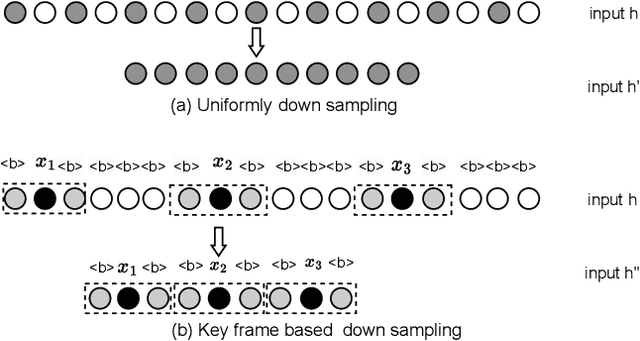
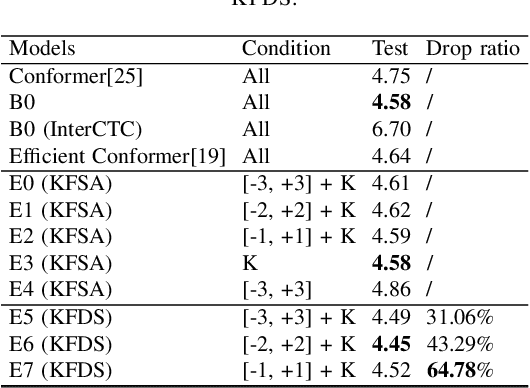
Abstract:Recently, Conformer as a backbone network for end-to-end automatic speech recognition achieved state-of-the-art performance. The Conformer block leverages a self-attention mechanism to capture global information, along with a convolutional neural network to capture local information, resulting in improved performance. However, the Conformer-based model encounters an issue with the self-attention mechanism, as computational complexity grows quadratically with the length of the input sequence. Inspired by previous Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC) guided blank skipping during decoding, we introduce intermediate CTC outputs as guidance into the downsampling procedure of the Conformer encoder. We define the frame with non-blank output as key frame. Specifically, we introduce the key frame-based self-attention (KFSA) mechanism, a novel method to reduce the computation of the self-attention mechanism using key frames. The structure of our proposed approach comprises two encoders. Following the initial encoder, we introduce an intermediate CTC loss function to compute the label frame, enabling us to extract the key frames and blank frames for KFSA. Furthermore, we introduce the key frame-based downsampling (KFDS) mechanism to operate on high-dimensional acoustic features directly and drop the frames corresponding to blank labels, which results in new acoustic feature sequences as input to the second encoder. By using the proposed method, which achieves comparable or higher performance than vanilla Conformer and other similar work such as Efficient Conformer. Meantime, our proposed method can discard more than 60\% useless frames during model training and inference, which will accelerate the inference speed significantly. This work code is available in {https://github.com/scufan1990/Key-Frame-Mechanism-For-Efficient-Conformer}
DCCRN-KWS: an audio bias based model for noise robust small-footprint keyword spotting
May 23, 2023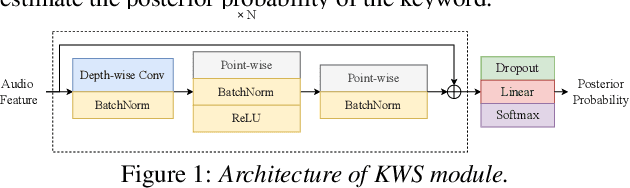
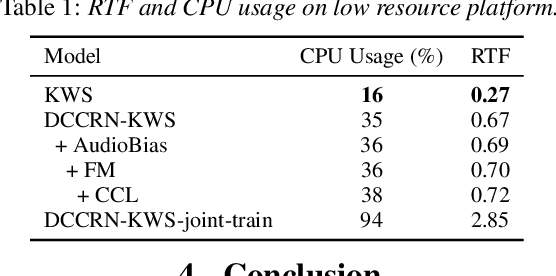
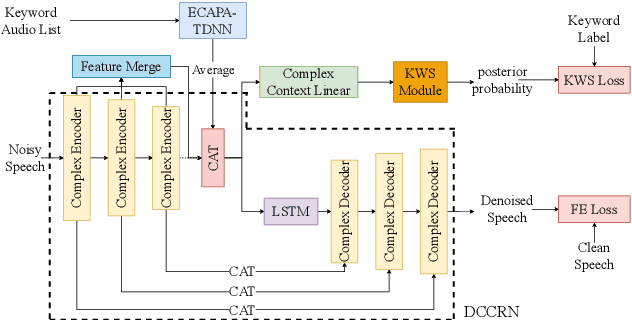
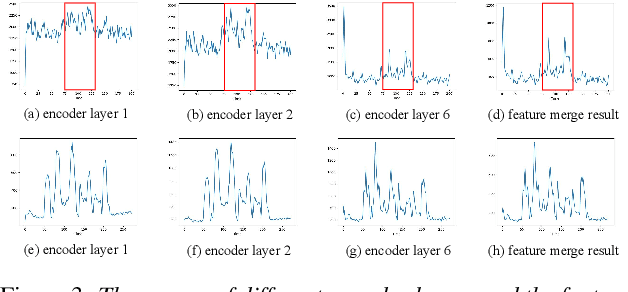
Abstract:Real-world complex acoustic environments especially the ones with a low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) will bring tremendous challenges to a keyword spotting (KWS) system. Inspired by the recent advances of neural speech enhancement and context bias in speech recognition, we propose a robust audio context bias based DCCRN-KWS model to address this challenge. We form the whole architecture as a multi-task learning framework for both denosing and keyword spotting, where the DCCRN encoder is connected with the KWS model. Helped with the denoising task, we further introduce an audio context bias module to leverage the real keyword samples and bias the network to better iscriminate keywords in noisy conditions. Feature merge and complex context linear modules are also introduced to strength such discrimination and to effectively leverage contextual information respectively. Experiments on the internal challenging dataset and the HIMIYA public dataset show that our DCCRN-KWS system is superior in performance, while ablation study demonstrates the good design of the whole model.
Two Stage Contextual Word Filtering for Context bias in Unified Streaming and Non-streaming Transducer
Jan 17, 2023Abstract:It is difficult for an end-to-end (E2E) ASR system to recognize words such as named entities appearing infrequently in the training data. A widely used method to mitigate this issue is feeding contextual information into the acoustic model. A contextual word list is necessary, which lists all possible contextual word candidates. Previous works have proven that the size and quality of the list are crucial. A compact and accurate list can boost the performance significantly. In this paper, we propose an efficient approach to obtain a high quality contextual word list for a unified streaming and non-streaming based Conformer-Transducer (C-T) model. Specifically, we make use of the phone-level streaming output to first filter the predefined contextual word list. During the subsequent non-streaming inference, the words in the filtered list are regarded as contextual information fused into non-casual encoder and decoder to generate the final recognition results. Our approach can take advantage of streaming recognition hypothesis, improve the accuracy of the contextual ASR system and speed up the inference process as well. Experiments on two datasets demonstrates over 20% relative character error rate reduction (CERR) comparing to the baseline system. Meanwile, the RTF of our system can be stabilized within 0.15 when the size of the contextual word list grows over 6,000.
CaTT-KWS: A Multi-stage Customized Keyword Spotting Framework based on Cascaded Transducer-Transformer
Jul 04, 2022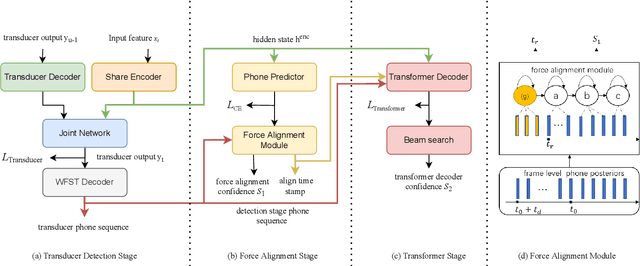
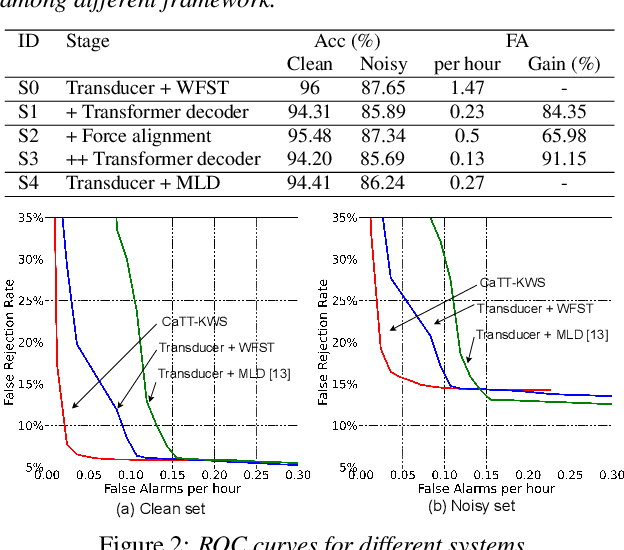
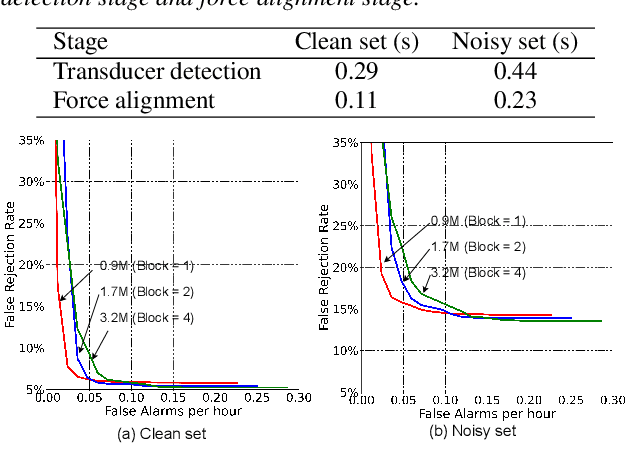
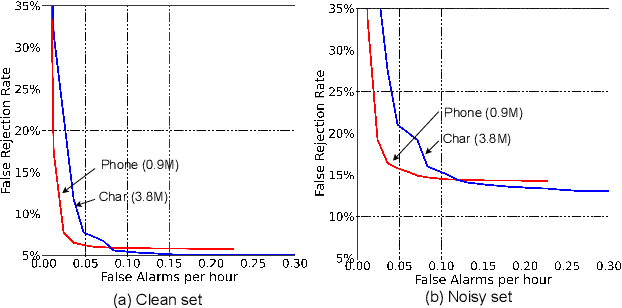
Abstract:Customized keyword spotting (KWS) has great potential to be deployed on edge devices to achieve hands-free user experience. However, in real applications, false alarm (FA) would be a serious problem for spotting dozens or even hundreds of keywords, which drastically affects user experience. To solve this problem, in this paper, we leverage the recent advances in transducer and transformer based acoustic models and propose a new multi-stage customized KWS framework named Cascaded Transducer-Transformer KWS (CaTT-KWS), which includes a transducer based keyword detector, a frame-level phone predictor based force alignment module and a transformer based decoder. Specifically, the streaming transducer module is used to spot keyword candidates in audio stream. Then force alignment is implemented using the phone posteriors predicted by the phone predictor to finish the first stage keyword verification and refine the time boundaries of keyword. Finally, the transformer decoder further verifies the triggered keyword. Our proposed CaTT-KWS framework reduces FA rate effectively without obviously hurting keyword recognition accuracy. Specifically, we can get impressively 0.13 FA per hour on a challenging dataset, with over 90% relative reduction on FA comparing to the transducer based detection model, while keyword recognition accuracy only drops less than 2%.
Leveraging Acoustic Contextual Representation by Audio-textual Cross-modal Learning for Conversational ASR
Jul 03, 2022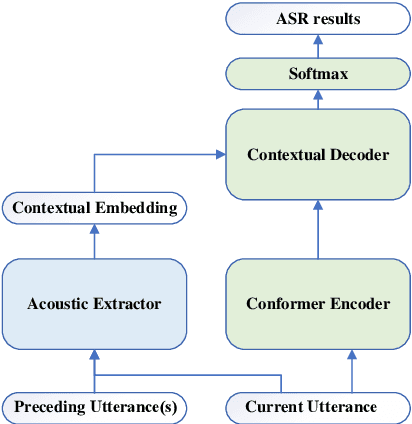
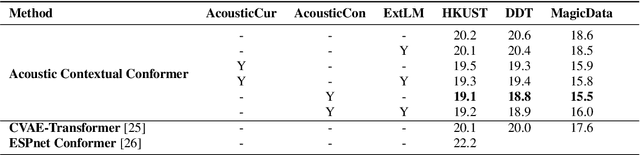
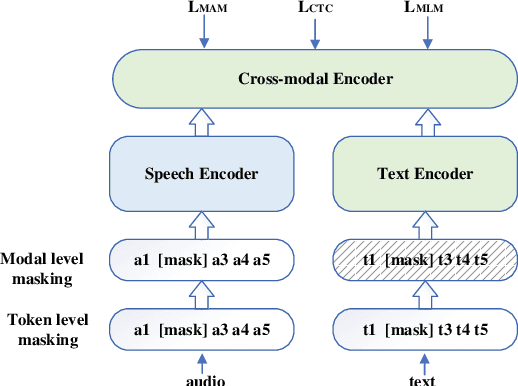

Abstract:Leveraging context information is an intuitive idea to improve performance on conversational automatic speech recognition(ASR). Previous works usually adopt recognized hypotheses of historical utterances as preceding context, which may bias the current recognized hypothesis due to the inevitable historicalrecognition errors. To avoid this problem, we propose an audio-textual cross-modal representation extractor to learn contextual representations directly from preceding speech. Specifically, it consists of two modal-related encoders, extracting high-level latent features from speech and the corresponding text, and a cross-modal encoder, which aims to learn the correlation between speech and text. We randomly mask some input tokens and input sequences of each modality. Then a token-missing or modal-missing prediction with a modal-level CTC loss on the cross-modal encoder is performed. Thus, the model captures not only the bi-directional context dependencies in a specific modality but also relationships between different modalities. Then, during the training of the conversational ASR system, the extractor will be frozen to extract the textual representation of preceding speech, while such representation is used as context fed to the ASR decoder through attention mechanism. The effectiveness of the proposed approach is validated on several Mandarin conversation corpora and the highest character error rate (CER) reduction up to 16% is achieved on the MagicData dataset.
Conversational Speech Recognition By Learning Conversation-level Characteristics
Feb 17, 2022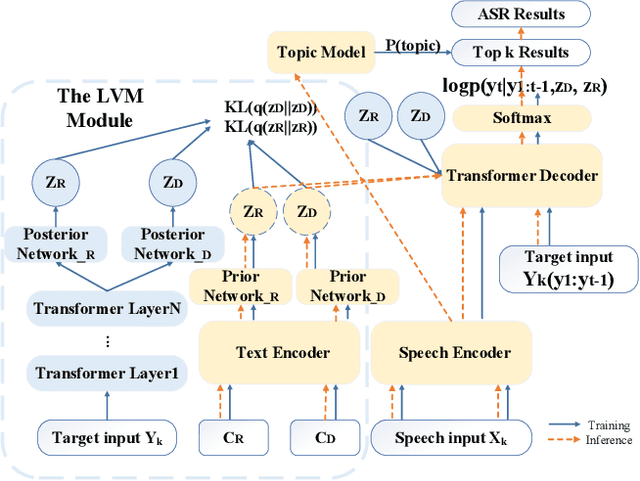
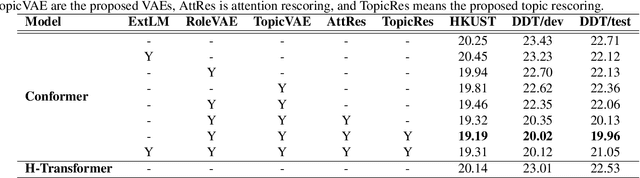
Abstract:Conversational automatic speech recognition (ASR) is a task to recognize conversational speech including multiple speakers. Unlike sentence-level ASR, conversational ASR can naturally take advantages from specific characteristics of conversation, such as role preference and topical coherence. This paper proposes a conversational ASR model which explicitly learns conversation-level characteristics under the prevalent end-to-end neural framework. The highlights of the proposed model are twofold. First, a latent variational module (LVM) is attached to a conformer-based encoder-decoder ASR backbone to learn role preference and topical coherence. Second, a topic model is specifically adopted to bias the outputs of the decoder to words in the predicted topics. Experiments on two Mandarin conversational ASR tasks show that the proposed model achieves a maximum 12% relative character error rate (CER) reduction.
Improving Streaming Transformer Based ASR Under a Framework of Self-supervised Learning
Sep 15, 2021
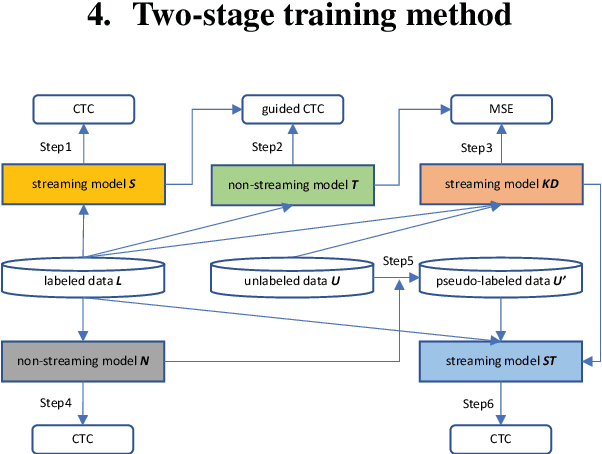
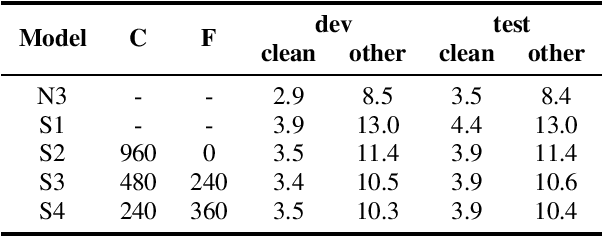
Abstract:Recently self-supervised learning has emerged as an effective approach to improve the performance of automatic speech recognition (ASR). Under such a framework, the neural network is usually pre-trained with massive unlabeled data and then fine-tuned with limited labeled data. However, the non-streaming architecture like bidirectional transformer is usually adopted by the neural network to achieve competitive results, which can not be used in streaming scenarios. In this paper, we mainly focus on improving the performance of streaming transformer under the self-supervised learning framework. Specifically, we propose a novel two-stage training method during fine-tuning, which combines knowledge distilling and self-training. The proposed training method achieves 16.3% relative word error rate (WER) reduction on Librispeech noisy test set. Finally, by only using the 100h clean subset of Librispeech as the labeled data and the rest (860h) as the unlabeled data, our streaming transformer based model obtains competitive WERs 3.5/8.7 on Librispeech clean/noisy test sets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge