Simon Wang
Breaking Down Video LLM Benchmarks: Knowledge, Spatial Perception, or True Temporal Understanding?
May 20, 2025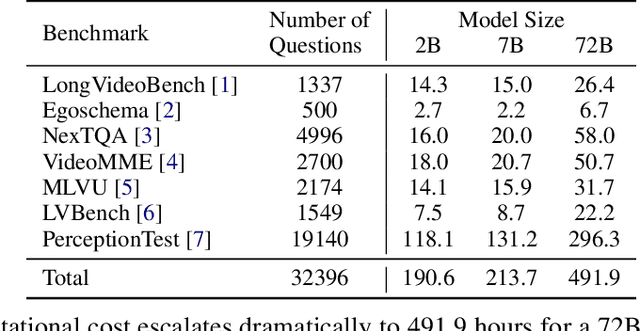
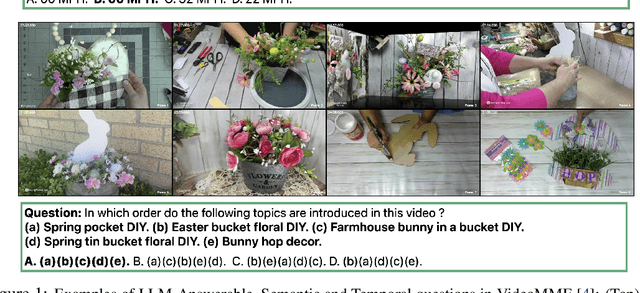
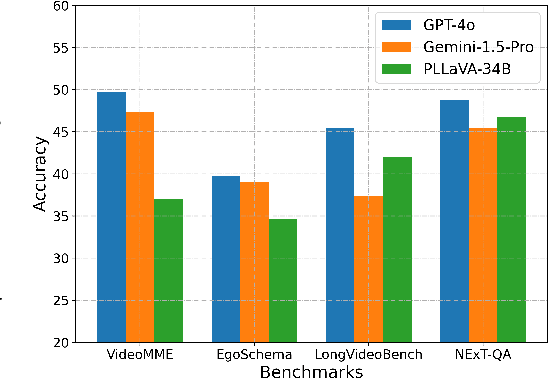
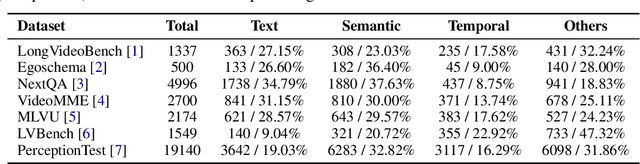
Abstract:Existing video understanding benchmarks often conflate knowledge-based and purely image-based questions, rather than clearly isolating a model's temporal reasoning ability, which is the key aspect that distinguishes video understanding from other modalities. We identify two major limitations that obscure whether higher scores truly indicate stronger understanding of the dynamic content in videos: (1) strong language priors, where models can answer questions without watching the video; and (2) shuffling invariance, where models maintain similar performance on certain questions even when video frames are temporally shuffled. To alleviate these issues, we propose VBenchComp, an automated pipeline that categorizes questions into different domains: LLM-Answerable, Semantic, and Temporal. Specifically, LLM-Answerable questions can be answered without viewing the video; Semantic questions remain answerable even when the video frames are shuffled; and Temporal questions require understanding the correct temporal order of frames. The rest of the questions are labeled as Others. This can enable fine-grained evaluation of different capabilities of a video LLM. Our analysis reveals nuanced model weaknesses that are hidden by traditional overall scores, and we offer insights and recommendations for designing future benchmarks that more accurately assess video LLMs.
MR. Judge: Multimodal Reasoner as a Judge
May 19, 2025Abstract:The paradigm of using Large Language Models (LLMs) and Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) as evaluative judges has emerged as an effective approach in RLHF and inference-time scaling. In this work, we propose Multimodal Reasoner as a Judge (MR. Judge), a paradigm for empowering general-purpose MLLMs judges with strong reasoning capabilities. Instead of directly assigning scores for each response, we formulate the judgement process as a reasoning-inspired multiple-choice problem. Specifically, the judge model first conducts deliberate reasoning covering different aspects of the responses and eventually selects the best response from them. This reasoning process not only improves the interpretibility of the judgement, but also greatly enhances the performance of MLLM judges. To cope with the lack of questions with scored responses, we propose the following strategy to achieve automatic annotation: 1) Reverse Response Candidates Synthesis: starting from a supervised fine-tuning (SFT) dataset, we treat the original response as the best candidate and prompt the MLLM to generate plausible but flawed negative candidates. 2) Text-based reasoning extraction: we carefully design a data synthesis pipeline for distilling the reasoning capability from a text-based reasoning model, which is adopted to enable the MLLM judges to regain complex reasoning ability via warm up supervised fine-tuning. Experiments demonstrate that our MR. Judge is effective across a wide range of tasks. Specifically, our MR. Judge-7B surpasses GPT-4o by 9.9% on VL-RewardBench, and improves performance on MM-Vet during inference-time scaling by up to 7.7%.
Mutual Reinforcement of LLM Dialogue Synthesis and Summarization Capabilities for Few-Shot Dialogue Summarization
Feb 24, 2025Abstract:In this work, we propose Mutual Reinforcing Data Synthesis (MRDS) within LLMs to improve few-shot dialogue summarization task. Unlike prior methods that require external knowledge, we mutually reinforce the LLM\'s dialogue synthesis and summarization capabilities, allowing them to complement each other during training and enhance overall performances. The dialogue synthesis capability is enhanced by directed preference optimization with preference scoring from summarization capability. The summarization capability is enhanced by the additional high quality dialogue-summary paired data produced by the dialogue synthesis capability. By leveraging the proposed MRDS mechanism, we elicit the internal knowledge of LLM in the format of synthetic data, and use it to augment the few-shot real training dataset. Empirical results demonstrate that our method improves dialogue summarization, achieving a 1.5% increase in ROUGE scores and a 0.3% improvement in BERT scores in few-shot settings. Furthermore, our method attains the highest average scores in human evaluations, surpassing both the pre-trained models and the baselines fine-tuned solely for summarization tasks.
TIS-DPO: Token-level Importance Sampling for Direct Preference Optimization With Estimated Weights
Oct 06, 2024

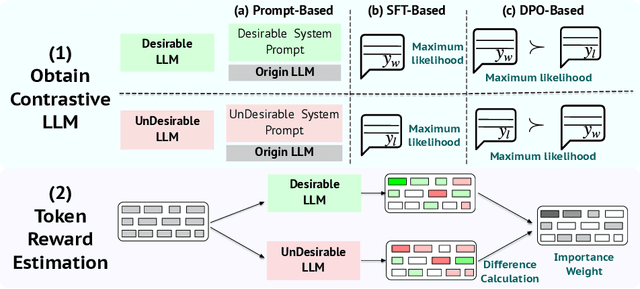
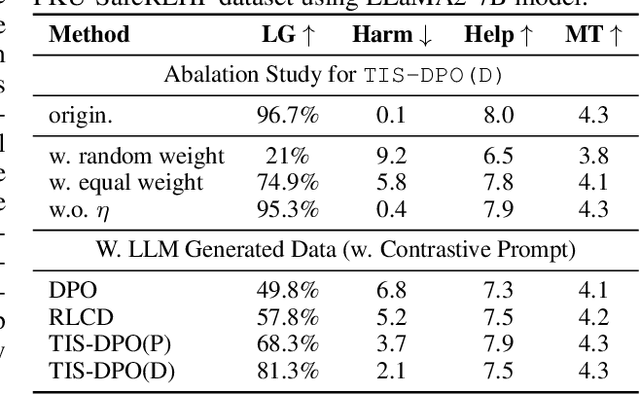
Abstract:Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) has been widely adopted for preference alignment of Large Language Models (LLMs) due to its simplicity and effectiveness. However, DPO is derived as a bandit problem in which the whole response is treated as a single arm, ignoring the importance differences between tokens, which may affect optimization efficiency and make it difficult to achieve optimal results. In this work, we propose that the optimal data for DPO has equal expected rewards for each token in winning and losing responses, as there is no difference in token importance. However, since the optimal dataset is unavailable in practice, we propose using the original dataset for importance sampling to achieve unbiased optimization. Accordingly, we propose a token-level importance sampling DPO objective named TIS-DPO that assigns importance weights to each token based on its reward. Inspired by previous works, we estimate the token importance weights using the difference in prediction probabilities from a pair of contrastive LLMs. We explore three methods to construct these contrastive LLMs: (1) guiding the original LLM with contrastive prompts, (2) training two separate LLMs using winning and losing responses, and (3) performing forward and reverse DPO training with winning and losing responses. Experiments show that TIS-DPO significantly outperforms various baseline methods on harmlessness and helpfulness alignment and summarization tasks. We also visualize the estimated weights, demonstrating their ability to identify key token positions.
Imagen 3
Aug 13, 2024Abstract:We introduce Imagen 3, a latent diffusion model that generates high quality images from text prompts. We describe our quality and responsibility evaluations. Imagen 3 is preferred over other state-of-the-art (SOTA) models at the time of evaluation. In addition, we discuss issues around safety and representation, as well as methods we used to minimize the potential harm of our models.
Apple Intelligence Foundation Language Models
Jul 29, 2024
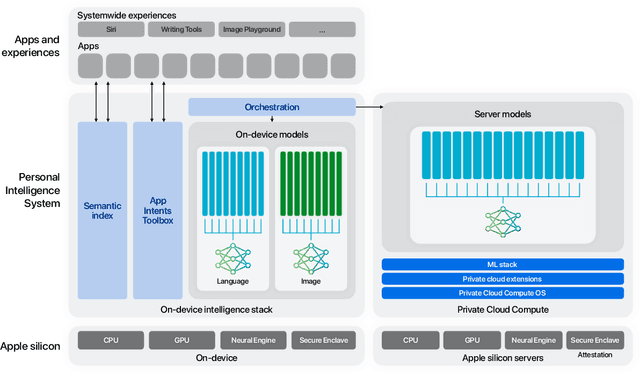


Abstract:We present foundation language models developed to power Apple Intelligence features, including a ~3 billion parameter model designed to run efficiently on devices and a large server-based language model designed for Private Cloud Compute. These models are designed to perform a wide range of tasks efficiently, accurately, and responsibly. This report describes the model architecture, the data used to train the model, the training process, how the models are optimized for inference, and the evaluation results. We highlight our focus on Responsible AI and how the principles are applied throughout the model development.
Direct Large Language Model Alignment Through Self-Rewarding Contrastive Prompt Distillation
Feb 19, 2024



Abstract:Aligning large language models (LLMs) with human expectations without human-annotated preference data is an important problem. In this paper, we propose a method to evaluate the response preference by using the output probabilities of response pairs under contrastive prompt pairs, which could achieve better performance on LLaMA2-7B and LLaMA2-13B compared to RLAIF. Based on this, we propose an automatic alignment method, Direct Large Model Alignment (DLMA). First, we use contrastive prompt pairs to automatically generate preference data. Then, we continue to evaluate the generated preference data using contrastive prompt pairs and calculate a self-rewarding score. Finally, we use the DPO algorithm to effectively align LLMs by combining this self-rewarding score. In the experimental stage, our DLMA method could surpass the \texttt{RLHF} method without relying on human-annotated preference data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge