Shijia Yang
AV-Odyssey Bench: Can Your Multimodal LLMs Really Understand Audio-Visual Information?
Dec 03, 2024



Abstract:Recently, multimodal large language models (MLLMs), such as GPT-4o, Gemini 1.5 Pro, and Reka Core, have expanded their capabilities to include vision and audio modalities. While these models demonstrate impressive performance across a wide range of audio-visual applications, our proposed DeafTest reveals that MLLMs often struggle with simple tasks humans find trivial: 1) determining which of two sounds is louder, and 2) determining which of two sounds has a higher pitch. Motivated by these observations, we introduce AV-Odyssey Bench, a comprehensive audio-visual benchmark designed to assess whether those MLLMs can truly understand the audio-visual information. This benchmark encompasses 4,555 carefully crafted problems, each incorporating text, visual, and audio components. To successfully infer answers, models must effectively leverage clues from both visual and audio inputs. To ensure precise and objective evaluation of MLLM responses, we have structured the questions as multiple-choice, eliminating the need for human evaluation or LLM-assisted assessment. We benchmark a series of closed-source and open-source models and summarize the observations. By revealing the limitations of current models, we aim to provide useful insight for future dataset collection and model development.
Law of Vision Representation in MLLMs
Aug 29, 2024



Abstract:We present the "Law of Vision Representation" in multimodal large language models (MLLMs). It reveals a strong correlation between the combination of cross-modal alignment, correspondence in vision representation, and MLLM performance. We quantify the two factors using the cross-modal Alignment and Correspondence score (AC score). Through extensive experiments involving thirteen different vision representation settings and evaluations across eight benchmarks, we find that the AC score is linearly correlated to model performance. By leveraging this relationship, we are able to identify and train the optimal vision representation only, which does not require finetuning the language model every time, resulting in a 99.7% reduction in computational cost.
HallE-Switch: Rethinking and Controlling Object Existence Hallucinations in Large Vision Language Models for Detailed Caption
Oct 03, 2023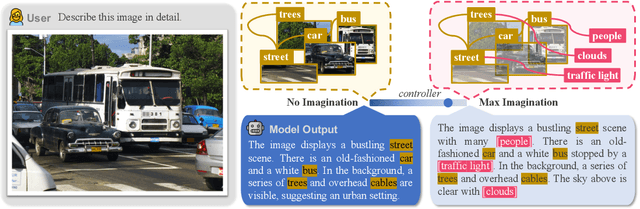
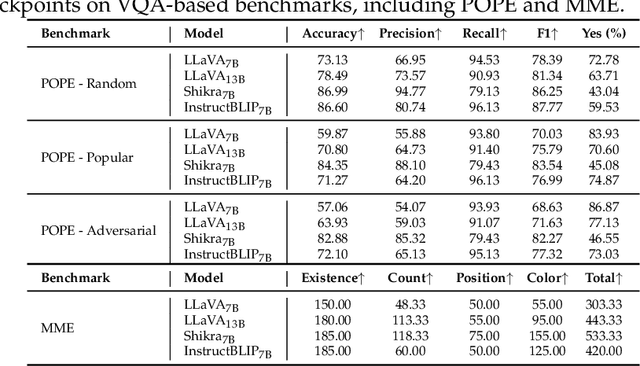

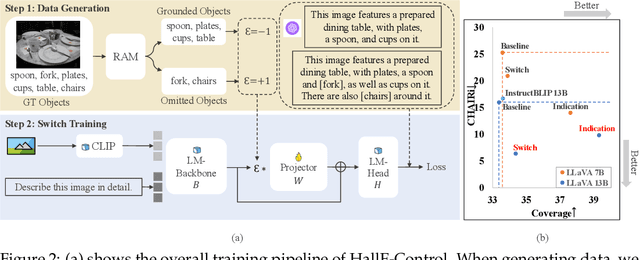
Abstract:Current large vision-language models (LVLMs) achieve remarkable progress, yet there remains significant uncertainty regarding their ability to accurately apprehend visual details, that is, in performing detailed captioning. To address this, we introduce \textit{CCEval}, a GPT-4 assisted evaluation method tailored for detailed captioning. Interestingly, while LVLMs demonstrate minimal object existence hallucination in existing VQA benchmarks, our proposed evaluation reveals continued susceptibility to such hallucinations. In this paper, we make the first attempt to investigate and attribute such hallucinations, including image resolution, the language decoder size, and instruction data amount, quality, granularity. Our findings underscore the unwarranted inference when the language description includes details at a finer object granularity than what the vision module can ground or verify, thus inducing hallucination. To control such hallucinations, we further attribute the reliability of captioning to contextual knowledge (involving only contextually grounded objects) and parametric knowledge (containing inferred objects by the model). Thus, we introduce $\textit{HallE-Switch}$, a controllable LVLM in terms of $\textbf{Hall}$ucination in object $\textbf{E}$xistence. HallE-Switch can condition the captioning to shift between (i) exclusively depicting contextual knowledge for grounded objects and (ii) blending it with parametric knowledge to imagine inferred objects. Our method reduces hallucination by 44% compared to LLaVA$_{7B}$ and maintains the same object coverage.
Multitask Vision-Language Prompt Tuning
Dec 05, 2022



Abstract:Prompt Tuning, conditioning on task-specific learned prompt vectors, has emerged as a data-efficient and parameter-efficient method for adapting large pretrained vision-language models to multiple downstream tasks. However, existing approaches usually consider learning prompt vectors for each task independently from scratch, thereby failing to exploit the rich shareable knowledge across different vision-language tasks. In this paper, we propose multitask vision-language prompt tuning (MVLPT), which incorporates cross-task knowledge into prompt tuning for vision-language models. Specifically, (i) we demonstrate the effectiveness of learning a single transferable prompt from multiple source tasks to initialize the prompt for each target task; (ii) we show many target tasks can benefit each other from sharing prompt vectors and thus can be jointly learned via multitask prompt tuning. We benchmark the proposed MVLPT using three representative prompt tuning methods, namely text prompt tuning, visual prompt tuning, and the unified vision-language prompt tuning. Results in 20 vision tasks demonstrate that the proposed approach outperforms all single-task baseline prompt tuning methods, setting the new state-of-the-art on the few-shot ELEVATER benchmarks and cross-task generalization benchmarks. To understand where the cross-task knowledge is most effective, we also conduct a large-scale study on task transferability with 20 vision tasks in 400 combinations for each prompt tuning method. It shows that the most performant MVLPT for each prompt tuning method prefers different task combinations and many tasks can benefit each other, depending on their visual similarity and label similarity. Code is available at https://github.com/sIncerass/MVLPT.
Time Will Tell: New Outlooks and A Baseline for Temporal Multi-View 3D Object Detection
Oct 05, 2022



Abstract:While recent camera-only 3D detection methods leverage multiple timesteps, the limited history they use significantly hampers the extent to which temporal fusion can improve object perception. Observing that existing works' fusion of multi-frame images are instances of temporal stereo matching, we find that performance is hindered by the interplay between 1) the low granularity of matching resolution and 2) the sub-optimal multi-view setup produced by limited history usage. Our theoretical and empirical analysis demonstrates that the optimal temporal difference between views varies significantly for different pixels and depths, making it necessary to fuse many timesteps over long-term history. Building on our investigation, we propose to generate a cost volume from a long history of image observations, compensating for the coarse but efficient matching resolution with a more optimal multi-view matching setup. Further, we augment the per-frame monocular depth predictions used for long-term, coarse matching with short-term, fine-grained matching and find that long and short term temporal fusion are highly complementary. While maintaining high efficiency, our framework sets new state-of-the-art on nuScenes, achieving first place on the test set and outperforming previous best art by 5.2% mAP and 3.7% NDS on the validation set. Code will be released $\href{https://github.com/Divadi/SOLOFusion}{here.}$
Image2Point: 3D Point-Cloud Understanding with Pretrained 2D ConvNets
Jun 08, 2021



Abstract:3D point-clouds and 2D images are different visual representations of the physical world. While human vision can understand both representations, computer vision models designed for 2D image and 3D point-cloud understanding are quite different. Our paper investigates the potential for transferability between these two representations by empirically investigating whether this approach works, what factors affect the transfer performance, and how to make it work even better. We discovered that we can indeed use the same neural net model architectures to understand both images and point-clouds. Moreover, we can transfer pretrained weights from image models to point-cloud models with minimal effort. Specifically, based on a 2D ConvNet pretrained on an image dataset, we can transfer the image model to a point-cloud model by \textit{inflating} 2D convolutional filters to 3D then finetuning its input, output, and optionally normalization layers. The transferred model can achieve competitive performance on 3D point-cloud classification, indoor and driving scene segmentation, even beating a wide range of point-cloud models that adopt task-specific architectures and use a variety of tricks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge