Samira Shaikh
Report from the NSF Future Directions Workshop on Automatic Evaluation of Dialog: Research Directions and Challenges
Mar 18, 2022

Abstract:This is a report on the NSF Future Directions Workshop on Automatic Evaluation of Dialog. The workshop explored the current state of the art along with its limitations and suggested promising directions for future work in this important and very rapidly changing area of research.
A Survey on Artificial Intelligence for Source Code: A Dialogue Systems Perspective
Feb 10, 2022Abstract:In this survey paper, we overview major deep learning methods used in Natural Language Processing (NLP) and source code over the last 35 years. Next, we present a survey of the applications of Artificial Intelligence (AI) for source code, also known as Code Intelligence (CI) and Programming Language Processing (PLP). We survey over 287 publications and present a software-engineering centered taxonomy for CI placing each of the works into one category describing how it best assists the software development cycle. Then, we overview the field of conversational assistants and their applications in software engineering and education. Lastly, we highlight research opportunities at the intersection of AI for code and conversational assistants and provide future directions for researching conversational assistants with CI capabilities.
Can We Generate Shellcodes via Natural Language? An Empirical Study
Feb 08, 2022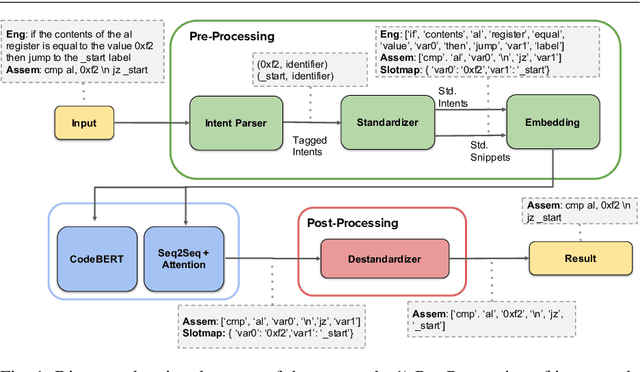
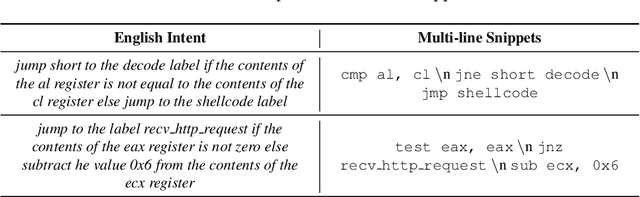

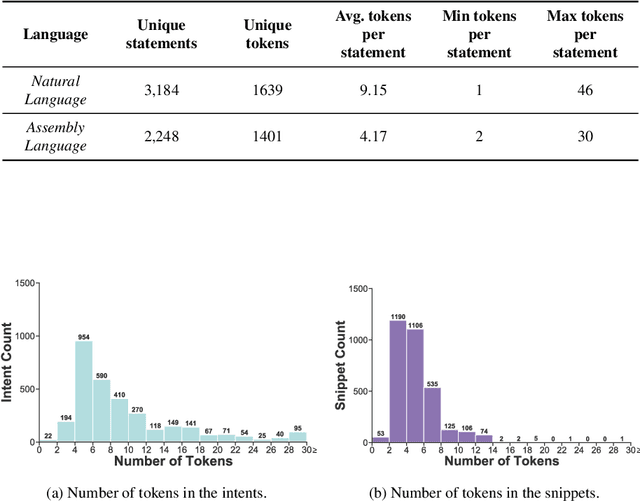
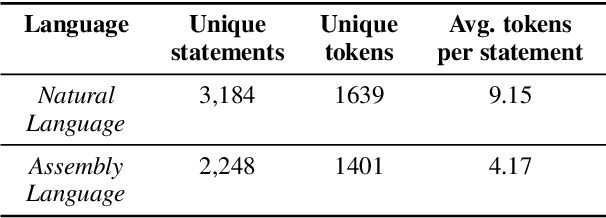
Abstract:Writing software exploits is an important practice for offensive security analysts to investigate and prevent attacks. In particular, shellcodes are especially time-consuming and a technical challenge, as they are written in assembly language. In this work, we address the task of automatically generating shellcodes, starting purely from descriptions in natural language, by proposing an approach based on Neural Machine Translation (NMT). We then present an empirical study using a novel dataset (Shellcode_IA32), which consists of 3,200 assembly code snippets of real Linux/x86 shellcodes from public databases, annotated using natural language. Moreover, we propose novel metrics to evaluate the accuracy of NMT at generating shellcodes. The empirical analysis shows that NMT can generate assembly code snippets from the natural language with high accuracy and that in many cases can generate entire shellcodes with no errors.
Shellcode_IA32: A Dataset for Automatic Shellcode Generation
Apr 27, 2021


Abstract:We take the first step to address the task of automatically generating shellcodes, i.e., small pieces of code used as a payload in the exploitation of a software vulnerability, starting from natural language comments. We assemble and release a novel dataset (Shellcode_IA32), consisting of challenging but common assembly instructions with their natural language descriptions. We experiment with standard methods in neural machine translation (NMT) to establish baseline performance levels on this task.
The GEM Benchmark: Natural Language Generation, its Evaluation and Metrics
Feb 03, 2021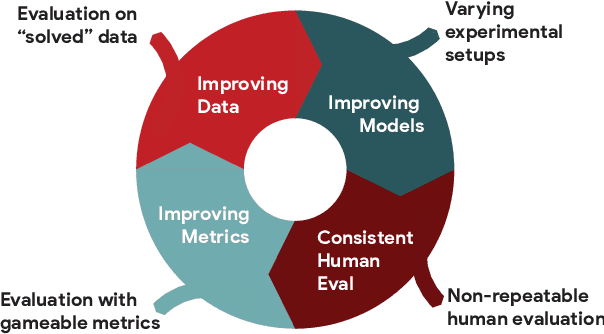
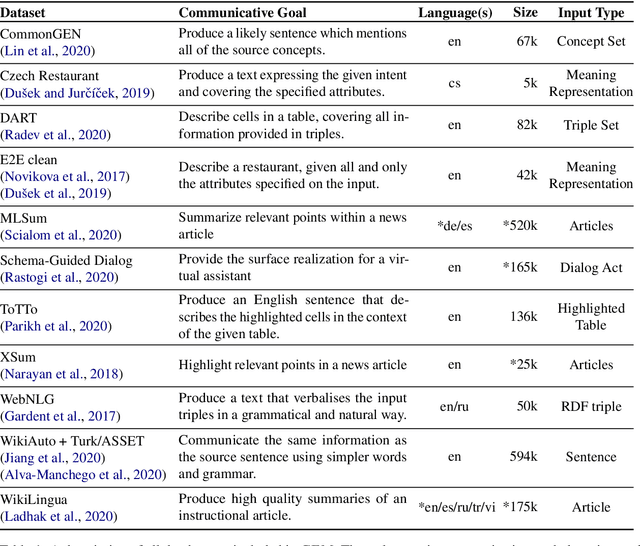
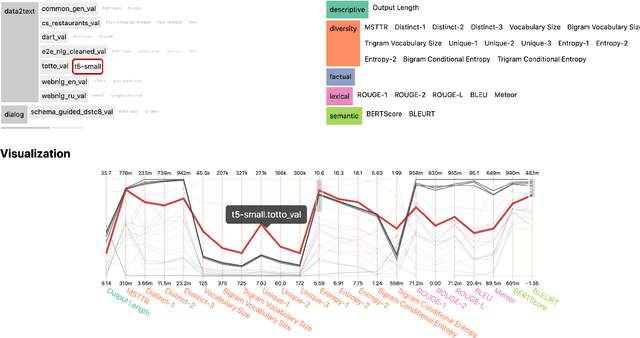
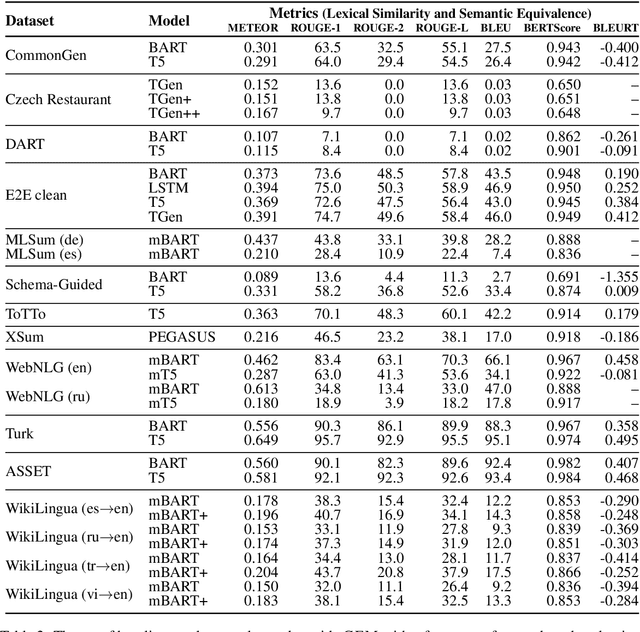
Abstract:We introduce GEM, a living benchmark for natural language Generation (NLG), its Evaluation, and Metrics. Measuring progress in NLG relies on a constantly evolving ecosystem of automated metrics, datasets, and human evaluation standards. However, due to this moving target, new models often still evaluate on divergent anglo-centric corpora with well-established, but flawed, metrics. This disconnect makes it challenging to identify the limitations of current models and opportunities for progress. Addressing this limitation, GEM provides an environment in which models can easily be applied to a wide set of corpora and evaluation strategies can be tested. Regular updates to the benchmark will help NLG research become more multilingual and evolve the challenge alongside models. This paper serves as the description of the initial release for which we are organizing a shared task at our ACL 2021 Workshop and to which we invite the entire NLG community to participate.
Learning to Plan and Realize Separately for Open-Ended Dialogue Systems
Oct 04, 2020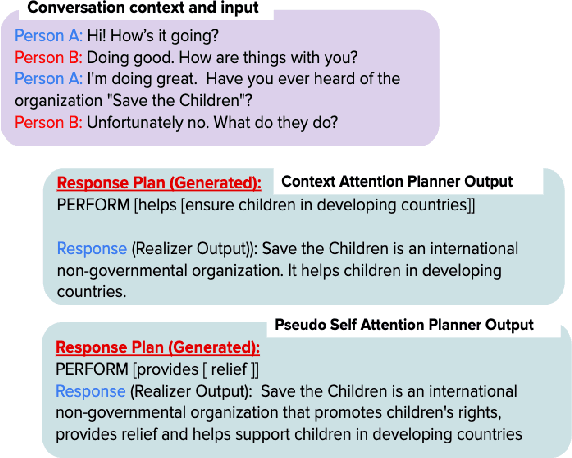
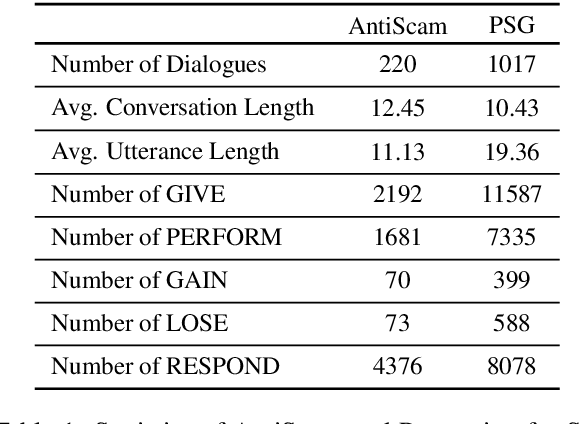
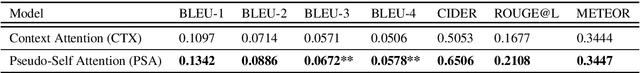
Abstract:Achieving true human-like ability to conduct a conversation remains an elusive goal for open-ended dialogue systems. We posit this is because extant approaches towards natural language generation (NLG) are typically construed as end-to-end architectures that do not adequately model human generation processes. To investigate, we decouple generation into two separate phases: planning and realization. In the planning phase, we train two planners to generate plans for response utterances. The realization phase uses response plans to produce an appropriate response. Through rigorous evaluations, both automated and human, we demonstrate that decoupling the process into planning and realization performs better than an end-to-end approach.
The Panacea Threat Intelligence and Active Defense Platform
Apr 20, 2020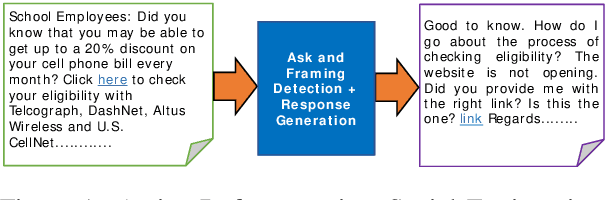
Abstract:We describe Panacea, a system that supports natural language processing (NLP) components for active defenses against social engineering attacks. We deploy a pipeline of human language technology, including Ask and Framing Detection, Named Entity Recognition, Dialogue Engineering, and Stylometry. Panacea processes modern message formats through a plug-in architecture to accommodate innovative approaches for message analysis, knowledge representation and dialogue generation. The novelty of the Panacea system is that uses NLP for cyber defense and engages the attacker using bots to elicit evidence to attribute to the attacker and to waste the attacker's time and resources.
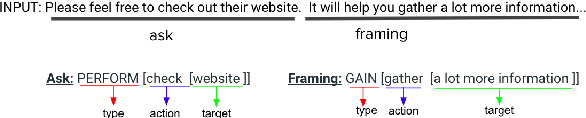
Adaptation of a Lexical Organization for Social Engineering Detection and Response Generation
Apr 20, 2020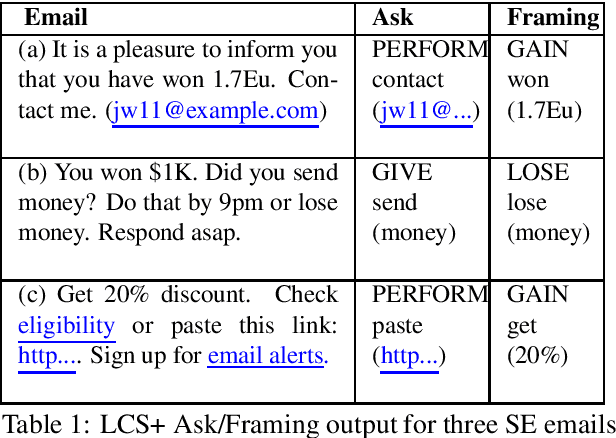

Abstract:We present a paradigm for extensible lexicon development based on Lexical Conceptual Structure to support social engineering detection and response generation. We leverage the central notions of ask (elicitation of behaviors such as providing access to money) and framing (risk/reward implied by the ask). We demonstrate improvements in ask/framing detection through refinements to our lexical organization and show that response generation qualitatively improves as ask/framing detection performance improves. The paradigm presents a systematic and efficient approach to resource adaptation for improved task-specific performance.
Studying the Effects of Cognitive Biases in Evaluation of Conversational Agents
Feb 26, 2020



Abstract:Humans quite frequently interact with conversational agents. The rapid advancement in generative language modeling through neural networks has helped advance the creation of intelligent conversational agents. Researchers typically evaluate the output of their models through crowdsourced judgments, but there are no established best practices for conducting such studies. Moreover, it is unclear if cognitive biases in decision-making are affecting crowdsourced workers' judgments when they undertake these tasks. To investigate, we conducted a between-subjects study with 77 crowdsourced workers to understand the role of cognitive biases, specifically anchoring bias, when humans are asked to evaluate the output of conversational agents. Our results provide insight into how best to evaluate conversational agents. We find increased consistency in ratings across two experimental conditions may be a result of anchoring bias. We also determine that external factors such as time and prior experience in similar tasks have effects on inter-rater consistency.
Detecting Asks in SE attacks: Impact of Linguistic and Structural Knowledge
Feb 25, 2020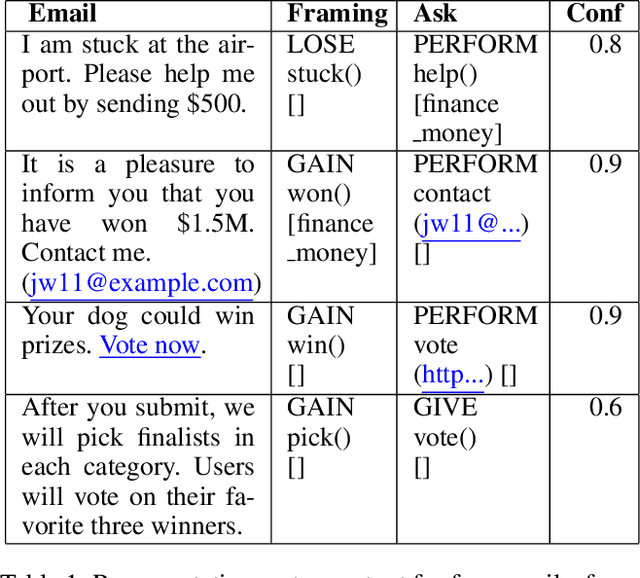
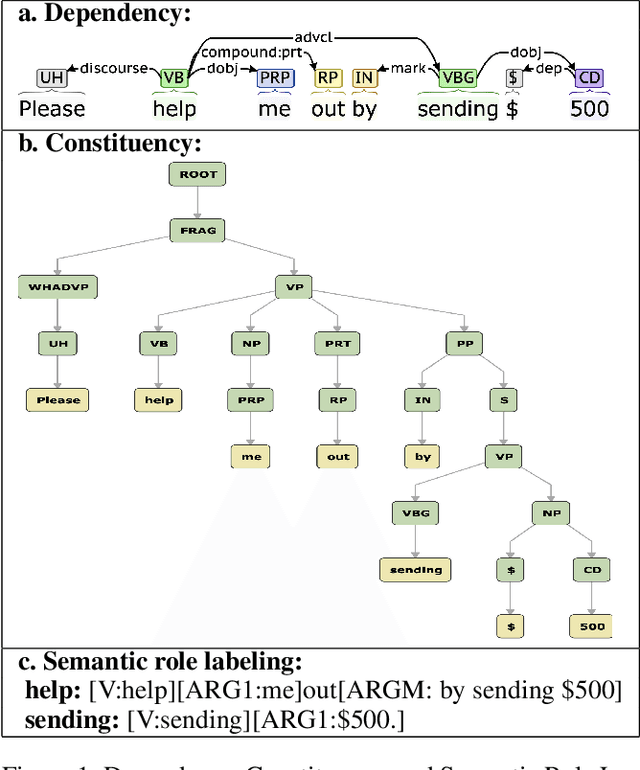
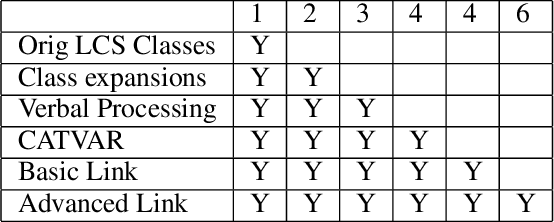
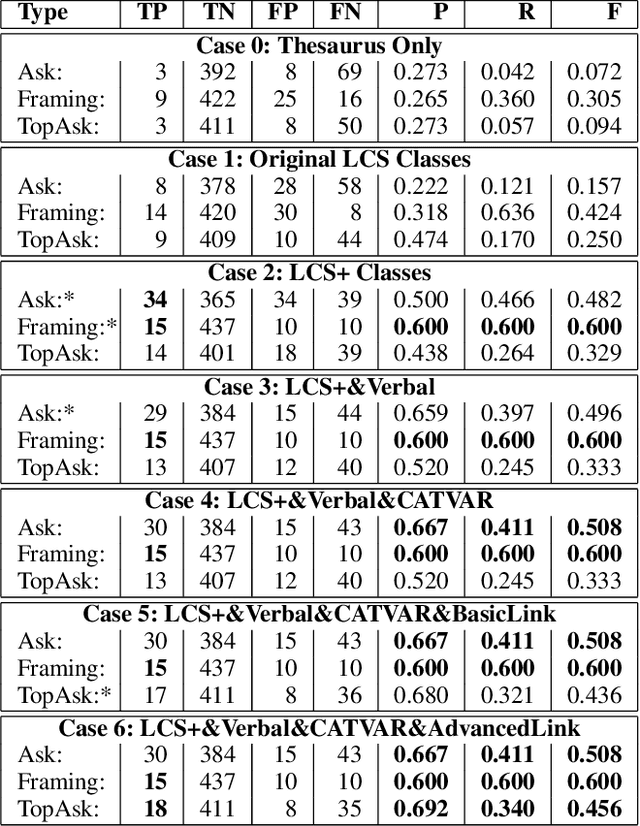
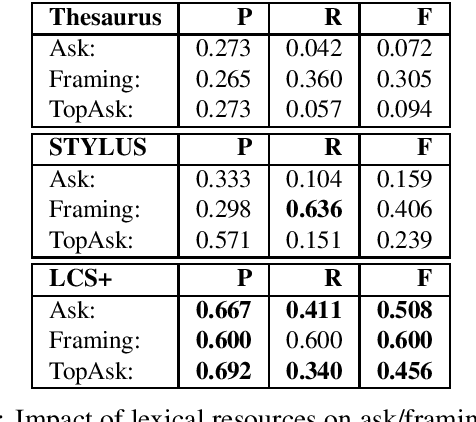
Abstract:Social engineers attempt to manipulate users into undertaking actions such as downloading malware by clicking links or providing access to money or sensitive information. Natural language processing, computational sociolinguistics, and media-specific structural clues provide a means for detecting both the ask (e.g., buy gift card) and the risk/reward implied by the ask, which we call framing (e.g., lose your job, get a raise). We apply linguistic resources such as Lexical Conceptual Structure to tackle ask detection and also leverage structural clues such as links and their proximity to identified asks to improve confidence in our results. Our experiments indicate that the performance of ask detection, framing detection, and identification of the top ask is improved by linguistically motivated classes coupled with structural clues such as links. Our approach is implemented in a system that informs users about social engineering risk situations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge