Can We Generate Shellcodes via Natural Language? An Empirical Study
Paper and Code
Feb 08, 2022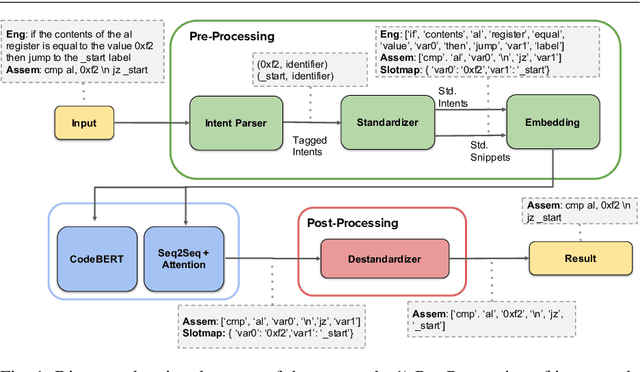
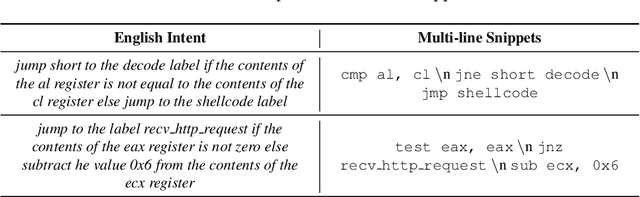

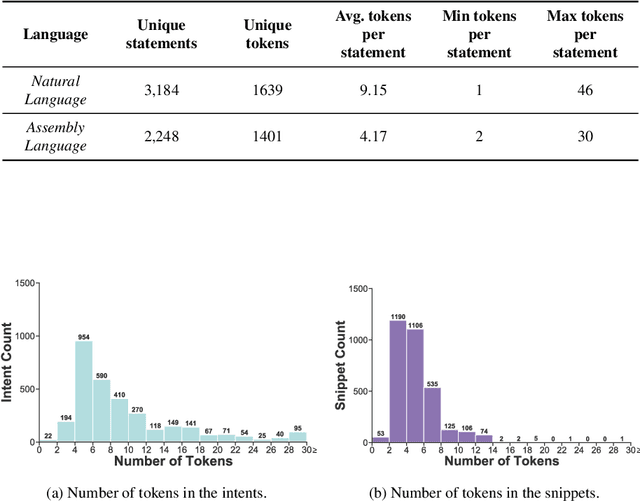
Writing software exploits is an important practice for offensive security analysts to investigate and prevent attacks. In particular, shellcodes are especially time-consuming and a technical challenge, as they are written in assembly language. In this work, we address the task of automatically generating shellcodes, starting purely from descriptions in natural language, by proposing an approach based on Neural Machine Translation (NMT). We then present an empirical study using a novel dataset (Shellcode_IA32), which consists of 3,200 assembly code snippets of real Linux/x86 shellcodes from public databases, annotated using natural language. Moreover, we propose novel metrics to evaluate the accuracy of NMT at generating shellcodes. The empirical analysis shows that NMT can generate assembly code snippets from the natural language with high accuracy and that in many cases can generate entire shellcodes with no errors.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge