Bonnie J. Dorr
DETQUS: Decomposition-Enhanced Transformers for QUery-focused Summarization
Mar 07, 2025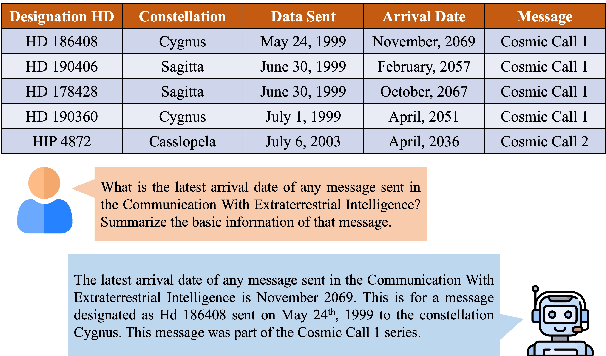
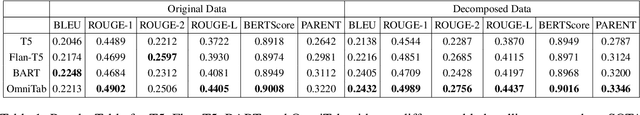
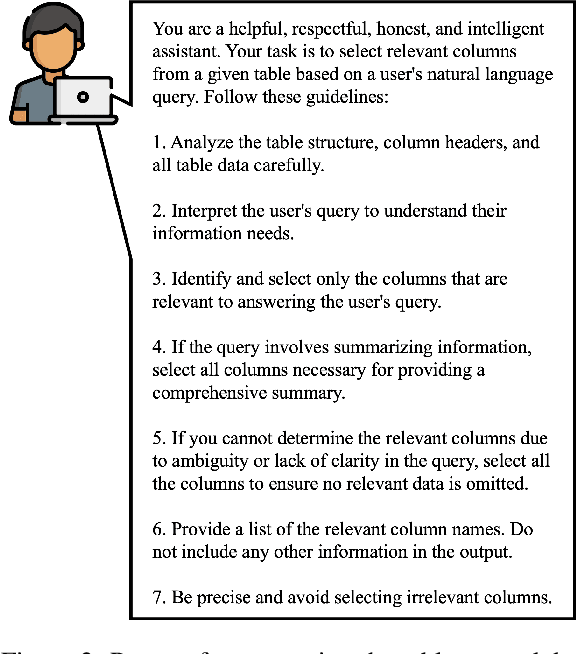
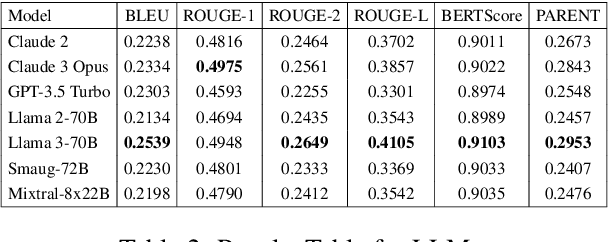
Abstract:Query-focused tabular summarization is an emerging task in table-to-text generation that synthesizes a summary response from tabular data based on user queries. Traditional transformer-based approaches face challenges due to token limitations and the complexity of reasoning over large tables. To address these challenges, we introduce DETQUS (Decomposition-Enhanced Transformers for QUery-focused Summarization), a system designed to improve summarization accuracy by leveraging tabular decomposition alongside a fine-tuned encoder-decoder model. DETQUS employs a large language model to selectively reduce table size, retaining only query-relevant columns while preserving essential information. This strategy enables more efficient processing of large tables and enhances summary quality. Our approach, equipped with table-based QA model Omnitab, achieves a ROUGE-L score of 0.4437, outperforming the previous state-of-the-art REFACTOR model (ROUGE-L: 0.422). These results highlight DETQUS as a scalable and effective solution for query-focused tabular summarization, offering a structured alternative to more complex architectures.
Balancing Transparency and Accuracy: A Comparative Analysis of Rule-Based and Deep Learning Models in Political Bias Classification
Nov 07, 2024



Abstract:The unchecked spread of digital information, combined with increasing political polarization and the tendency of individuals to isolate themselves from opposing political viewpoints, has driven researchers to develop systems for automatically detecting political bias in media. This trend has been further fueled by discussions on social media. We explore methods for categorizing bias in US news articles, comparing rule-based and deep learning approaches. The study highlights the sensitivity of modern self-learning systems to unconstrained data ingestion, while reconsidering the strengths of traditional rule-based systems. Applying both models to left-leaning (CNN) and right-leaning (FOX) news articles, we assess their effectiveness on data beyond the original training and test sets.This analysis highlights each model's accuracy, offers a framework for exploring deep-learning explainability, and sheds light on political bias in US news media. We contrast the opaque architecture of a deep learning model with the transparency of a linguistically informed rule-based model, showing that the rule-based model performs consistently across different data conditions and offers greater transparency, whereas the deep learning model is dependent on the training set and struggles with unseen data.
Making Task-Oriented Dialogue Datasets More Natural by Synthetically Generating Indirect User Requests
Jun 16, 2024
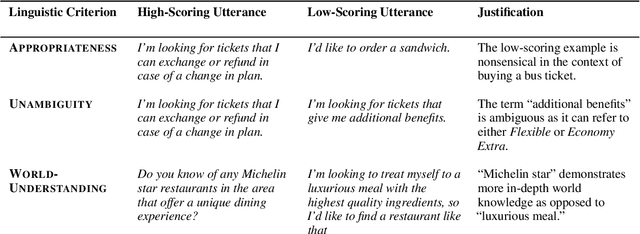

Abstract:Indirect User Requests (IURs), such as "It's cold in here" instead of "Could you please increase the temperature?" are common in human-human task-oriented dialogue and require world knowledge and pragmatic reasoning from the listener. While large language models (LLMs) can handle these requests effectively, smaller models deployed on virtual assistants often struggle due to resource constraints. Moreover, existing task-oriented dialogue benchmarks lack sufficient examples of complex discourse phenomena such as indirectness. To address this, we propose a set of linguistic criteria along with an LLM-based pipeline for generating realistic IURs to test natural language understanding (NLU) and dialogue state tracking (DST) models before deployment in a new domain. We also release IndirectRequests, a dataset of IURs based on the Schema Guided Dialog (SGD) corpus, as a comparative testbed for evaluating the performance of smaller models in handling indirect requests.
IndirectRequests: Making Task-Oriented Dialogue Datasets More Natural by Synthetically Generating Indirect User Requests
Jun 12, 2024



Abstract:Existing benchmark corpora of task-oriented dialogue are collected either using a "machines talking to machines" approach or by giving template-based goal descriptions to crowdworkers. These methods, however, often produce utterances that are markedly different from natural human conversations in which people often convey their preferences in indirect ways, such as through small talk. We term such utterances as Indirect User Requests (IURs). Understanding such utterances demands considerable world knowledge and reasoning capabilities on the listener's part. Our study introduces an LLM-based pipeline to automatically generate realistic, high-quality IURs for a given domain, with the ultimate goal of supporting research in natural language understanding (NLU) and dialogue state tracking (DST) for task-oriented dialogue systems. Our findings show that while large LLMs such as GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 generate high-quality IURs, achieving similar quality with smaller models is more challenging. We release IndirectRequests, a dataset of IURs that advances beyond the initial Schema-Guided Dialog (SGD) dataset in that it provides a challenging testbed for testing the "in the wild" performance of NLU and DST models.
The Effect of Data Partitioning Strategy on Model Generalizability: A Case Study of Morphological Segmentation
Apr 14, 2024



Abstract:Recent work to enhance data partitioning strategies for more realistic model evaluation face challenges in providing a clear optimal choice. This study addresses these challenges, focusing on morphological segmentation and synthesizing limitations related to language diversity, adoption of multiple datasets and splits, and detailed model comparisons. Our study leverages data from 19 languages, including ten indigenous or endangered languages across 10 language families with diverse morphological systems (polysynthetic, fusional, and agglutinative) and different degrees of data availability. We conduct large-scale experimentation with varying sized combinations of training and evaluation sets as well as new test data. Our results show that, when faced with new test data: (1) models trained from random splits are able to achieve higher numerical scores; (2) model rankings derived from random splits tend to generalize more consistently.
Can Similarity-Based Domain-Ordering Reduce Catastrophic Forgetting for Intent Recognition?
Feb 21, 2024Abstract:Task-oriented dialogue systems are expected to handle a constantly expanding set of intents and domains even after they have been deployed to support more and more functionalities. To live up to this expectation, it becomes critical to mitigate the catastrophic forgetting problem (CF) that occurs in continual learning (CL) settings for a task such as intent recognition. While existing dialogue systems research has explored replay-based and regularization-based methods to this end, the effect of domain ordering on the CL performance of intent recognition models remains unexplored. If understood well, domain ordering has the potential to be an orthogonal technique that can be leveraged alongside existing techniques such as experience replay. Our work fills this gap by comparing the impact of three domain-ordering strategies (min-sum path, max-sum path, random) on the CL performance of a generative intent recognition model. Our findings reveal that the min-sum path strategy outperforms the others in reducing catastrophic forgetting when training on the 220M T5-Base model. However, this advantage diminishes with the larger 770M T5-Large model. These results underscores the potential of domain ordering as a complementary strategy for mitigating catastrophic forgetting in continually learning intent recognition models, particularly in resource-constrained scenarios.
SPLAIN: Augmenting CybersecurityWarnings with Reasons and Data
Nov 19, 2023Abstract:Effective cyber threat recognition and prevention demand comprehensible forecasting systems, as prior approaches commonly offer limited and, ultimately, unconvincing information. We introduce Simplified Plaintext Language (SPLAIN), a natural language generator that converts warning data into user-friendly cyber threat explanations. SPLAIN is designed to generate clear, actionable outputs, incorporating hierarchically organized explanatory details about input data and system functionality. Given the inputs of individual sensor-induced forecasting signals and an overall warning from a fusion module, SPLAIN queries each signal for information on contributing sensors and data signals. This collected data is processed into a coherent English explanation, encompassing forecasting, sensing, and data elements for user review. SPLAIN's template-based approach ensures consistent warning structure and vocabulary. SPLAIN's hierarchical output structure allows each threat and its components to be expanded to reveal underlying explanations on demand. Our conclusions emphasize the need for designers to specify the "how" and "why" behind cyber warnings, advocate for simple structured templates in generating consistent explanations, and recognize that direct causal links in Machine Learning approaches may not always be identifiable, requiring some explanations to focus on general methodologies, such as model and training data.
* Presented at FLAIRS-2019 as poster (see ancillary files)
Agreement Tracking for Multi-Issue Negotiation Dialogues
Jul 13, 2023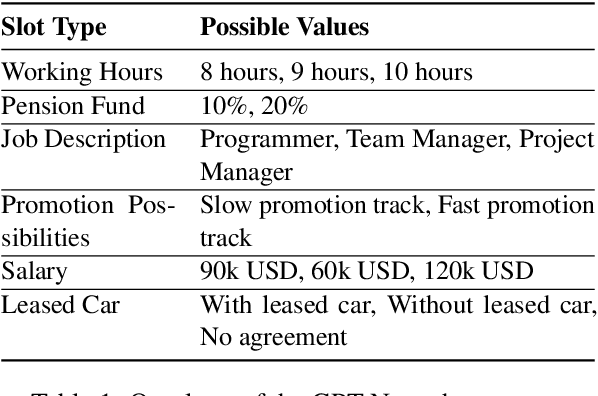


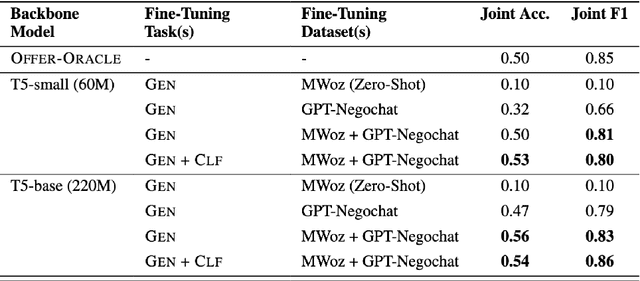
Abstract:Automated negotiation support systems aim to help human negotiators reach more favorable outcomes in multi-issue negotiations (e.g., an employer and a candidate negotiating over issues such as salary, hours, and promotions before a job offer). To be successful, these systems must accurately track agreements reached by participants in real-time. Existing approaches either focus on task-oriented dialogues or produce unstructured outputs, rendering them unsuitable for this objective. Our work introduces the novel task of agreement tracking for two-party multi-issue negotiations, which requires continuous monitoring of agreements within a structured state space. To address the scarcity of annotated corpora with realistic multi-issue negotiation dialogues, we use GPT-3 to build GPT-Negochat, a synthesized dataset that we make publicly available. We present a strong initial baseline for our task by transfer-learning a T5 model trained on the MultiWOZ 2.4 corpus. Pre-training T5-small and T5-base on MultiWOZ 2.4's DST task enhances results by 21% and 9% respectively over training solely on GPT-Negochat. We validate our method's sample-efficiency via smaller training subset experiments. By releasing GPT-Negochat and our baseline models, we aim to encourage further research in multi-issue negotiation dialogue agreement tracking.
LonXplain: Lonesomeness as a Consequence of Mental Disturbance in Reddit Posts
May 30, 2023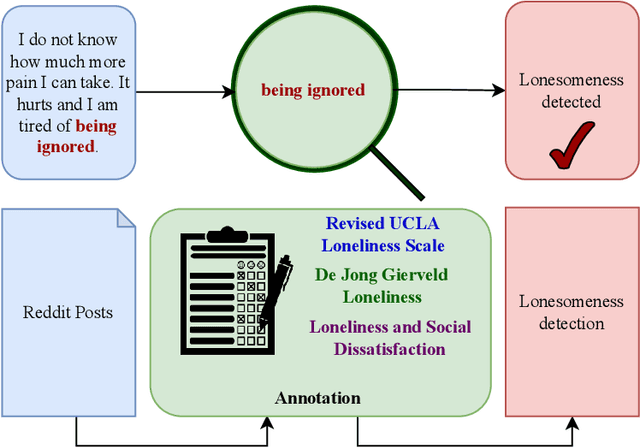


Abstract:Social media is a potential source of information that infers latent mental states through Natural Language Processing (NLP). While narrating real-life experiences, social media users convey their feeling of loneliness or isolated lifestyle, impacting their mental well-being. Existing literature on psychological theories points to loneliness as the major consequence of interpersonal risk factors, propounding the need to investigate loneliness as a major aspect of mental disturbance. We formulate lonesomeness detection in social media posts as an explainable binary classification problem, discovering the users at-risk, suggesting the need of resilience for early control. To the best of our knowledge, there is no existing explainable dataset, i.e., one with human-readable, annotated text spans, to facilitate further research and development in loneliness detection causing mental disturbance. In this work, three experts: a senior clinical psychologist, a rehabilitation counselor, and a social NLP researcher define annotation schemes and perplexity guidelines to mark the presence or absence of lonesomeness, along with the marking of text-spans in original posts as explanation, in 3,521 Reddit posts. We expect the public release of our dataset, LonXplain, and traditional classifiers as baselines via GitHub.
Exploiting Explainability to Design Adversarial Attacks and Evaluate Attack Resilience in Hate-Speech Detection Models
May 29, 2023Abstract:The advent of social media has given rise to numerous ethical challenges, with hate speech among the most significant concerns. Researchers are attempting to tackle this problem by leveraging hate-speech detection and employing language models to automatically moderate content and promote civil discourse. Unfortunately, recent studies have revealed that hate-speech detection systems can be misled by adversarial attacks, raising concerns about their resilience. While previous research has separately addressed the robustness of these models under adversarial attacks and their interpretability, there has been no comprehensive study exploring their intersection. The novelty of our work lies in combining these two critical aspects, leveraging interpretability to identify potential vulnerabilities and enabling the design of targeted adversarial attacks. We present a comprehensive and comparative analysis of adversarial robustness exhibited by various hate-speech detection models. Our study evaluates the resilience of these models against adversarial attacks using explainability techniques. To gain insights into the models' decision-making processes, we employ the Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations (LIME) framework. Based on the explainability results obtained by LIME, we devise and execute targeted attacks on the text by leveraging the TextAttack tool. Our findings enhance the understanding of the vulnerabilities and strengths exhibited by state-of-the-art hate-speech detection models. This work underscores the importance of incorporating explainability in the development and evaluation of such models to enhance their resilience against adversarial attacks. Ultimately, this work paves the way for creating more robust and reliable hate-speech detection systems, fostering safer online environments and promoting ethical discourse on social media platforms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge