Sai Praneeth Karimireddy
Sparks of Rationality: Do Reasoning LLMs Align with Human Judgment and Choice?
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly positioned as decision engines for hiring, healthcare, and economic judgment, yet real-world human judgment reflects a balance between rational deliberation and emotion-driven bias. If LLMs are to participate in high-stakes decisions or serve as models of human behavior, it is critical to assess whether they exhibit analogous patterns of (ir)rationalities and biases. To this end, we evaluate multiple LLM families on (i) benchmarks testing core axioms of rational choice and (ii) classic decision domains from behavioral economics and social norms where emotions are known to shape judgment and choice. Across settings, we show that deliberate "thinking" reliably improves rationality and pushes models toward expected-value maximization. To probe human-like affective distortions and their interaction with reasoning, we use two emotion-steering methods: in-context priming (ICP) and representation-level steering (RLS). ICP induces strong directional shifts that are often extreme and difficult to calibrate, whereas RLS produces more psychologically plausible patterns but with lower reliability. Our results suggest that the same mechanisms that improve rationality also amplify sensitivity to affective interventions, and that different steering methods trade off controllability against human-aligned behavior. Overall, this points to a tension between reasoning and affective steering, with implications for both human simulation and the safe deployment of LLM-based decision systems.
Hair-Trigger Alignment: Black-Box Evaluation Cannot Guarantee Post-Update Alignment
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are rarely static and are frequently updated in practice. A growing body of alignment research has shown that models initially deemed "aligned" can exhibit misaligned behavior after fine-tuning, such as forgetting jailbreak safety features or re-surfacing knowledge that was intended to be forgotten. These works typically assume that the initial model is aligned based on static black-box evaluation, i.e., the absence of undesired responses to a fixed set of queries. In contrast, we formalize model alignment in both the static and post-update settings and uncover a fundamental limitation of black-box evaluation. We theoretically show that, due to overparameterization, static alignment provides no guarantee of post-update alignment for any update dataset. Moreover, we prove that static black-box probing cannot distinguish a model that is genuinely post-update robust from one that conceals an arbitrary amount of adversarial behavior which can be activated by even a single benign gradient update. We further validate these findings empirically in LLMs across three core alignment domains: privacy, jailbreak safety, and behavioral honesty. We demonstrate the existence of LLMs that pass all standard black-box alignment tests, yet become severely misaligned after a single benign update. Finally, we show that the capacity to hide such latent adversarial behavior increases with model scale, confirming our theoretical prediction that post-update misalignment grows with the number of parameters. Together, our results highlight the inadequacy of static evaluation protocols and emphasize the urgent need for post-update-robust alignment evaluation.
ContextLeak: Auditing Leakage in Private In-Context Learning Methods
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:In-Context Learning (ICL) has become a standard technique for adapting Large Language Models (LLMs) to specialized tasks by supplying task-specific exemplars within the prompt. However, when these exemplars contain sensitive information, reliable privacy-preserving mechanisms are essential to prevent unintended leakage through model outputs. Many privacy-preserving methods are proposed to protect the information leakage in the context, but there are less efforts on how to audit those methods. We introduce ContextLeak, the first framework to empirically measure the worst-case information leakage in ICL. ContextLeak uses canary insertion, embedding uniquely identifiable tokens in exemplars and crafting targeted queries to detect their presence. We apply ContextLeak across a range of private ICL techniques, both heuristic such as prompt-based defenses and those with theoretical guarantees such as Embedding Space Aggregation and Report Noisy Max. We find that ContextLeak tightly correlates with the theoretical privacy budget ($ε$) and reliably detects leakage. Our results further reveal that existing methods often strike poor privacy-utility trade-offs, either leaking sensitive information or severely degrading performance.
A Closer Look at Personalized Fine-Tuning in Heterogeneous Federated Learning
Nov 16, 2025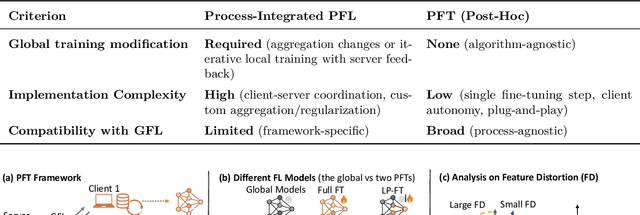
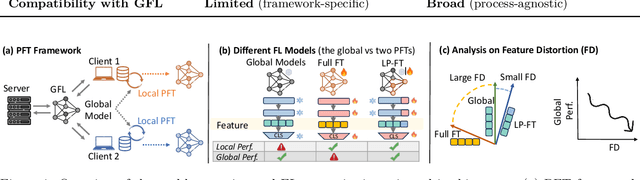
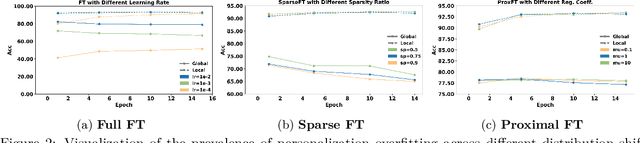
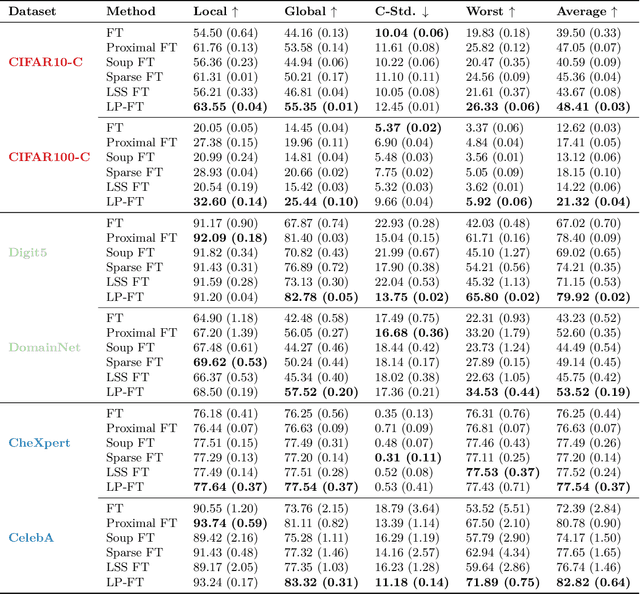
Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) enables decentralized, privacy-preserving model training but struggles to balance global generalization and local personalization due to non-identical data distributions across clients. Personalized Fine-Tuning (PFT), a popular post-hoc solution, fine-tunes the final global model locally but often overfits to skewed client distributions or fails under domain shifts. We propose adapting Linear Probing followed by full Fine-Tuning (LP-FT), a principled centralized strategy for alleviating feature distortion (Kumar et al., 2022), to the FL setting. Through systematic evaluation across seven datasets and six PFT variants, we demonstrate LP-FT's superiority in balancing personalization and generalization. Our analysis uncovers federated feature distortion, a phenomenon where local fine-tuning destabilizes globally learned features, and theoretically characterizes how LP-FT mitigates this via phased parameter updates. We further establish conditions (e.g., partial feature overlap, covariate-concept shift) under which LP-FT outperforms standard fine-tuning, offering actionable guidelines for deploying robust personalization in FL.
Psychological Steering in LLMs: An Evaluation of Effectiveness and Trustworthiness
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:The ability to control LLMs' emulated emotional states and personality traits is essential for enabling rich, human-centered interactions in socially interactive settings. We introduce PsySET, a Psychologically-informed benchmark to evaluate LLM Steering Effectiveness and Trustworthiness across the emotion and personality domains. Our study spans four models from different LLM families paired with various steering strategies, including prompting, fine-tuning, and representation engineering. Our results indicate that prompting is consistently effective but limited in intensity control, whereas vector injections achieve finer controllability while slightly reducing output quality. Moreover, we explore the trustworthiness of steered LLMs by assessing safety, truthfulness, fairness, and ethics, highlighting potential side effects and behavioral shifts. Notably, we observe idiosyncratic effects; for instance, even a positive emotion like joy can degrade robustness to adversarial factuality, lower privacy awareness, and increase preferential bias. Meanwhile, anger predictably elevates toxicity yet strengthens leakage resistance. Our framework establishes the first holistic evaluation of emotion and personality steering, offering insights into its interpretability and reliability for socially interactive applications.
Conformal Prediction Adaptive to Unknown Subpopulation Shifts
Jun 05, 2025Abstract:Conformal prediction is widely used to equip black-box machine learning models with uncertainty quantification enjoying formal coverage guarantees. However, these guarantees typically break down in the presence of distribution shifts, where the data distribution at test time differs from the training (or calibration-time) distribution. In this work, we address subpopulation shifts, where the test environment exhibits an unknown and differing mixture of subpopulations compared to the calibration data. We propose new methods that provably adapt conformal prediction to such shifts, ensuring valid coverage without requiring explicit knowledge of subpopulation structure. Our algorithms scale to high-dimensional settings and perform effectively in realistic machine learning tasks. Extensive experiments on vision (with vision transformers) and language (with large language models) benchmarks demonstrate that our methods reliably maintain coverage and controls risk in scenarios where standard conformal prediction fails.
A Systematic Analysis of Base Model Choice for Reward Modeling
May 16, 2025Abstract:Reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF) and, at its core, reward modeling have become a crucial part of training powerful large language models (LLMs). One commonly overlooked factor in training high-quality reward models (RMs) is the effect of the base model, which is becoming more challenging to choose given the rapidly growing pool of LLMs. In this work, we present a systematic analysis of the effect of base model selection on reward modeling performance. Our results show that the performance can be improved by up to 14% compared to the most common (i.e., default) choice. Moreover, we showcase the strong statistical relation between some existing benchmarks and downstream performances. We also demonstrate that the results from a small set of benchmarks could be combined to boost the model selection ($+$18% on average in the top 5-10). Lastly, we illustrate the impact of different post-training steps on the final performance and explore using estimated data distributions to reduce performance prediction error.
From Fairness to Truthfulness: Rethinking Data Valuation Design
Apr 07, 2025Abstract:As large language models increasingly rely on external data sources, fairly compensating data contributors has become a central concern. In this paper, we revisit the design of data markets through a game-theoretic lens, where data owners face private, heterogeneous costs for data sharing. We show that commonly used valuation methods--such as Leave-One-Out and Data Shapley--fail to ensure truthful reporting of these costs, leading to inefficient market outcomes. To address this, we adapt well-established payment rules from mechanism design, namely Myerson and Vickrey-Clarke-Groves (VCG), to the data market setting. We demonstrate that the Myerson payment is the minimal truthful payment mechanism, optimal from the buyer's perspective, and that VCG and Myerson payments coincide in unconstrained allocation settings. Our findings highlight the importance of incorporating incentive compatibility into data valuation, paving the way for more robust and efficient data markets.
A Differentially Private Kaplan-Meier Estimator for Privacy-Preserving Survival Analysis
Dec 06, 2024
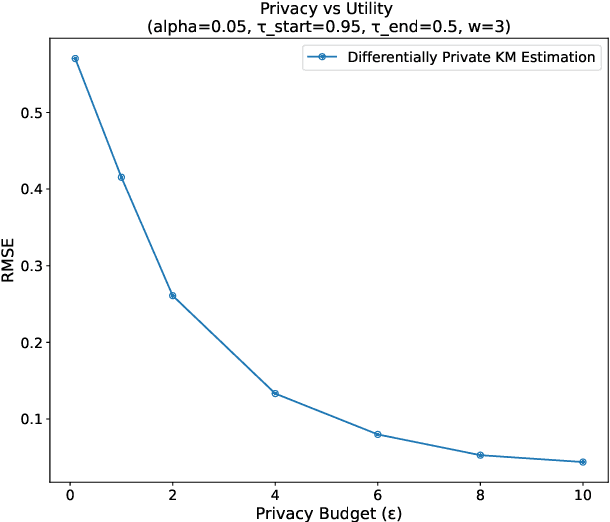
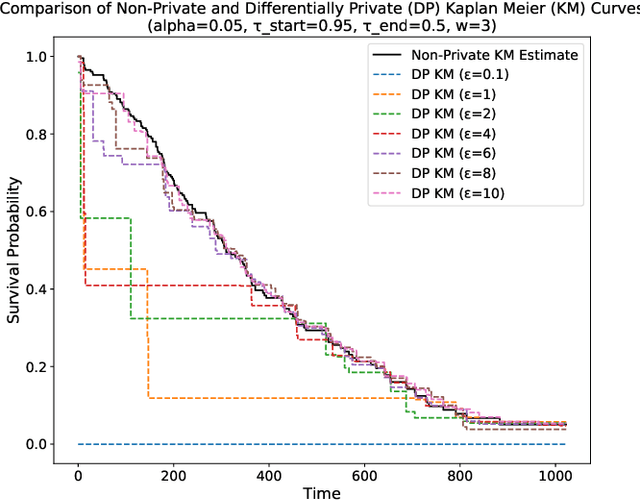
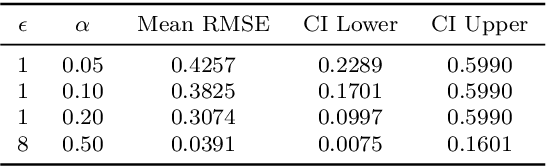
Abstract:This paper presents a differentially private approach to Kaplan-Meier estimation that achieves accurate survival probability estimates while safeguarding individual privacy. The Kaplan-Meier estimator is widely used in survival analysis to estimate survival functions over time, yet applying it to sensitive datasets, such as clinical records, risks revealing private information. To address this, we introduce a novel algorithm that applies time-indexed Laplace noise, dynamic clipping, and smoothing to produce a privacy-preserving survival curve while maintaining the cumulative structure of the Kaplan-Meier estimator. By scaling noise over time, the algorithm accounts for decreasing sensitivity as fewer individuals remain at risk, while dynamic clipping and smoothing prevent extreme values and reduce fluctuations, preserving the natural shape of the survival curve. Our results, evaluated on the NCCTG lung cancer dataset, show that the proposed method effectively lowers root mean squared error (RMSE) and enhances accuracy across privacy budgets ($\epsilon$). At $\epsilon = 10$, the algorithm achieves an RMSE as low as 0.04, closely approximating non-private estimates. Additionally, membership inference attacks reveal that higher $\epsilon$ values (e.g., $\epsilon \geq 6$) significantly reduce influential points, particularly at higher thresholds, lowering susceptibility to inference attacks. These findings confirm that our approach balances privacy and utility, advancing privacy-preserving survival analysis.
Defection-Free Collaboration between Competitors in a Learning System
Jun 22, 2024



Abstract:We study collaborative learning systems in which the participants are competitors who will defect from the system if they lose revenue by collaborating. As such, we frame the system as a duopoly of competitive firms who are each engaged in training machine-learning models and selling their predictions to a market of consumers. We first examine a fully collaborative scheme in which both firms share their models with each other and show that this leads to a market collapse with the revenues of both firms going to zero. We next show that one-sided collaboration in which only the firm with the lower-quality model shares improves the revenue of both firms. Finally, we propose a more equitable, *defection-free* scheme in which both firms share with each other while losing no revenue, and we show that our algorithm converges to the Nash bargaining solution.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge