Saachi Jain
Tony
OpenAI GPT-5 System Card
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:This is the system card published alongside the OpenAI GPT-5 launch, August 2025. GPT-5 is a unified system with a smart and fast model that answers most questions, a deeper reasoning model for harder problems, and a real-time router that quickly decides which model to use based on conversation type, complexity, tool needs, and explicit intent (for example, if you say 'think hard about this' in the prompt). The router is continuously trained on real signals, including when users switch models, preference rates for responses, and measured correctness, improving over time. Once usage limits are reached, a mini version of each model handles remaining queries. This system card focuses primarily on gpt-5-thinking and gpt-5-main, while evaluations for other models are available in the appendix. The GPT-5 system not only outperforms previous models on benchmarks and answers questions more quickly, but -- more importantly -- is more useful for real-world queries. We've made significant advances in reducing hallucinations, improving instruction following, and minimizing sycophancy, and have leveled up GPT-5's performance in three of ChatGPT's most common uses: writing, coding, and health. All of the GPT-5 models additionally feature safe-completions, our latest approach to safety training to prevent disallowed content. Similarly to ChatGPT agent, we have decided to treat gpt-5-thinking as High capability in the Biological and Chemical domain under our Preparedness Framework, activating the associated safeguards. While we do not have definitive evidence that this model could meaningfully help a novice to create severe biological harm -- our defined threshold for High capability -- we have chosen to take a precautionary approach.
OpenAI o1 System Card
Dec 21, 2024



Abstract:The o1 model series is trained with large-scale reinforcement learning to reason using chain of thought. These advanced reasoning capabilities provide new avenues for improving the safety and robustness of our models. In particular, our models can reason about our safety policies in context when responding to potentially unsafe prompts, through deliberative alignment. This leads to state-of-the-art performance on certain benchmarks for risks such as generating illicit advice, choosing stereotyped responses, and succumbing to known jailbreaks. Training models to incorporate a chain of thought before answering has the potential to unlock substantial benefits, while also increasing potential risks that stem from heightened intelligence. Our results underscore the need for building robust alignment methods, extensively stress-testing their efficacy, and maintaining meticulous risk management protocols. This report outlines the safety work carried out for the OpenAI o1 and OpenAI o1-mini models, including safety evaluations, external red teaming, and Preparedness Framework evaluations.
Deliberative Alignment: Reasoning Enables Safer Language Models
Dec 20, 2024Abstract:As large-scale language models increasingly impact safety-critical domains, ensuring their reliable adherence to well-defined principles remains a fundamental challenge. We introduce Deliberative Alignment, a new paradigm that directly teaches the model safety specifications and trains it to explicitly recall and accurately reason over the specifications before answering. We used this approach to align OpenAI's o-series models, and achieved highly precise adherence to OpenAI's safety policies, without requiring human-written chain-of-thoughts or answers. Deliberative Alignment pushes the Pareto frontier by simultaneously increasing robustness to jailbreaks while decreasing overrefusal rates, and also improves out-of-distribution generalization. We demonstrate that reasoning over explicitly specified policies enables more scalable, trustworthy, and interpretable alignment.
GPT-4o System Card
Oct 25, 2024Abstract:GPT-4o is an autoregressive omni model that accepts as input any combination of text, audio, image, and video, and generates any combination of text, audio, and image outputs. It's trained end-to-end across text, vision, and audio, meaning all inputs and outputs are processed by the same neural network. GPT-4o can respond to audio inputs in as little as 232 milliseconds, with an average of 320 milliseconds, which is similar to human response time in conversation. It matches GPT-4 Turbo performance on text in English and code, with significant improvement on text in non-English languages, while also being much faster and 50\% cheaper in the API. GPT-4o is especially better at vision and audio understanding compared to existing models. In line with our commitment to building AI safely and consistent with our voluntary commitments to the White House, we are sharing the GPT-4o System Card, which includes our Preparedness Framework evaluations. In this System Card, we provide a detailed look at GPT-4o's capabilities, limitations, and safety evaluations across multiple categories, focusing on speech-to-speech while also evaluating text and image capabilities, and measures we've implemented to ensure the model is safe and aligned. We also include third-party assessments on dangerous capabilities, as well as discussion of potential societal impacts of GPT-4o's text and vision capabilities.
Data Debiasing with Datamodels (D3M): Improving Subgroup Robustness via Data Selection
Jun 24, 2024Abstract:Machine learning models can fail on subgroups that are underrepresented during training. While techniques such as dataset balancing can improve performance on underperforming groups, they require access to training group annotations and can end up removing large portions of the dataset. In this paper, we introduce Data Debiasing with Datamodels (D3M), a debiasing approach which isolates and removes specific training examples that drive the model's failures on minority groups. Our approach enables us to efficiently train debiased classifiers while removing only a small number of examples, and does not require training group annotations or additional hyperparameter tuning.
Dataset Interfaces: Diagnosing Model Failures Using Controllable Counterfactual Generation
Feb 15, 2023Abstract:Distribution shifts are a major source of failure of deployed machine learning models. However, evaluating a model's reliability under distribution shifts can be challenging, especially since it may be difficult to acquire counterfactual examples that exhibit a specified shift. In this work, we introduce dataset interfaces: a framework which allows users to scalably synthesize such counterfactual examples from a given dataset. Specifically, we represent each class from the input dataset as a custom token within the text space of a text-to-image diffusion model. By incorporating these tokens into natural language prompts, we can then generate instantiations of objects in that dataset under desired distribution shifts. We demonstrate how applying our framework to the ImageNet dataset enables us to study model behavior across a diverse array of shifts, including variations in background, lighting, and attributes of the objects themselves. Code available at https://github.com/MadryLab/dataset-interfaces.
A Data-Based Perspective on Transfer Learning
Jul 12, 2022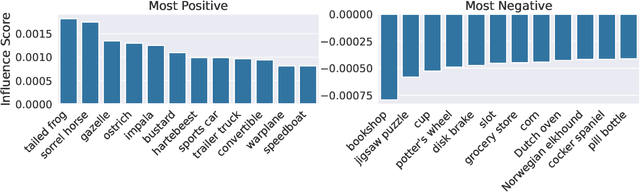
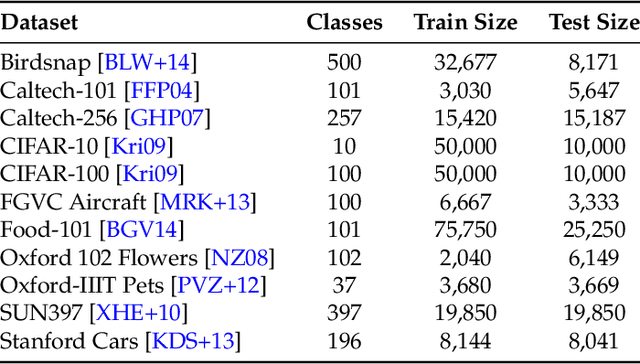
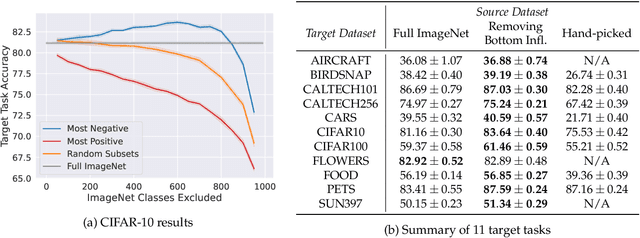
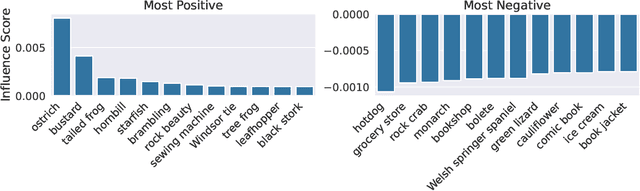
Abstract:It is commonly believed that in transfer learning including more pre-training data translates into better performance. However, recent evidence suggests that removing data from the source dataset can actually help too. In this work, we take a closer look at the role of the source dataset's composition in transfer learning and present a framework for probing its impact on downstream performance. Our framework gives rise to new capabilities such as pinpointing transfer learning brittleness as well as detecting pathologies such as data-leakage and the presence of misleading examples in the source dataset. In particular, we demonstrate that removing detrimental datapoints identified by our framework improves transfer learning performance from ImageNet on a variety of target tasks. Code is available at https://github.com/MadryLab/data-transfer
When does Bias Transfer in Transfer Learning?
Jul 06, 2022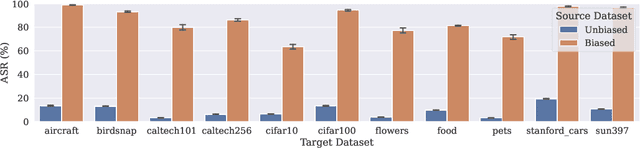
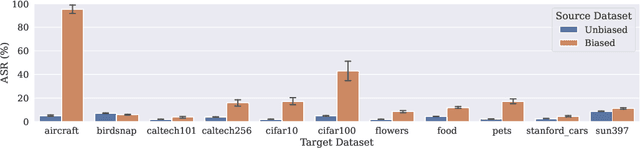

Abstract:Using transfer learning to adapt a pre-trained "source model" to a downstream "target task" can dramatically increase performance with seemingly no downside. In this work, we demonstrate that there can exist a downside after all: bias transfer, or the tendency for biases of the source model to persist even after adapting the model to the target class. Through a combination of synthetic and natural experiments, we show that bias transfer both (a) arises in realistic settings (such as when pre-training on ImageNet or other standard datasets) and (b) can occur even when the target dataset is explicitly de-biased. As transfer-learned models are increasingly deployed in the real world, our work highlights the importance of understanding the limitations of pre-trained source models. Code is available at https://github.com/MadryLab/bias-transfer
Distilling Model Failures as Directions in Latent Space
Jun 29, 2022



Abstract:Existing methods for isolating hard subpopulations and spurious correlations in datasets often require human intervention. This can make these methods labor-intensive and dataset-specific. To address these shortcomings, we present a scalable method for automatically distilling a model's failure modes. Specifically, we harness linear classifiers to identify consistent error patterns, and, in turn, induce a natural representation of these failure modes as directions within the feature space. We demonstrate that this framework allows us to discover and automatically caption challenging subpopulations within the training dataset, and intervene to improve the model's performance on these subpopulations. Code available at https://github.com/MadryLab/failure-directions
Missingness Bias in Model Debugging
Apr 19, 2022



Abstract:Missingness, or the absence of features from an input, is a concept fundamental to many model debugging tools. However, in computer vision, pixels cannot simply be removed from an image. One thus tends to resort to heuristics such as blacking out pixels, which may in turn introduce bias into the debugging process. We study such biases and, in particular, show how transformer-based architectures can enable a more natural implementation of missingness, which side-steps these issues and improves the reliability of model debugging in practice. Our code is available at https://github.com/madrylab/missingness
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge