Ramani Duraiswami
SPUR: A Plug-and-Play Framework for Integrating Spatial Audio Understanding and Reasoning into Large Audio-Language Models
Nov 13, 2025



Abstract:Spatial perception is central to auditory intelligence, enabling accurate understanding of real-world acoustic scenes and advancing human-level perception of the world around us. While recent large audio-language models (LALMs) show strong reasoning over complex audios, most operate on monaural inputs and lack the ability to capture spatial cues such as direction, elevation, and distance. We introduce SPUR, a lightweight, plug-in approach that equips LALMs with spatial perception through minimal architectural changes. SPUR consists of: (i) a First-Order Ambisonics (FOA) encoder that maps (W, X, Y, Z) channels to rotation-aware, listener-centric spatial features, integrated into target LALMs via a multimodal adapter; and (ii) SPUR-Set, a spatial QA dataset combining open-source FOA recordings with controlled simulations, emphasizing relative direction, elevation, distance, and overlap for supervised spatial reasoning. Fine-tuning our model on the SPUR-Set consistently improves spatial QA and multi-speaker attribution while preserving general audio understanding. SPUR provides a simple recipe that transforms monaural LALMs into spatially aware models. Extensive ablations validate the effectiveness of our approach.
Music Flamingo: Scaling Music Understanding in Audio Language Models
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:We introduce Music Flamingo, a novel large audio-language model designed to advance music (including song) understanding in foundational audio models. While audio-language research has progressed rapidly, music remains challenging due to its dynamic, layered, and information-dense nature. Progress has been further limited by the difficulty of scaling open audio understanding models, primarily because of the scarcity of high-quality music data and annotations. As a result, prior models are restricted to producing short, high-level captions, answering only surface-level questions, and showing limited generalization across diverse musical cultures. To address these challenges, we curate MF-Skills, a large-scale dataset labeled through a multi-stage pipeline that yields rich captions and question-answer pairs covering harmony, structure, timbre, lyrics, and cultural context. We fine-tune an enhanced Audio Flamingo 3 backbone on MF-Skills and further strengthen multiple skills relevant to music understanding. To improve the model's reasoning abilities, we introduce a post-training recipe: we first cold-start with MF-Think, a novel chain-of-thought dataset grounded in music theory, followed by GRPO-based reinforcement learning with custom rewards. Music Flamingo achieves state-of-the-art results across 10+ benchmarks for music understanding and reasoning, establishing itself as a generalist and musically intelligent audio-language model. Beyond strong empirical results, Music Flamingo sets a new standard for advanced music understanding by demonstrating how models can move from surface-level recognition toward layered, human-like perception of songs. We believe this work provides both a benchmark and a foundation for the community to build the next generation of models that engage with music as meaningfully as humans do.
AURA: A Fine-Grained Benchmark and Decomposed Metric for Audio-Visual Reasoning
Aug 10, 2025Abstract:Current audio-visual (AV) benchmarks focus on final answer accuracy, overlooking the underlying reasoning process. This makes it difficult to distinguish genuine comprehension from correct answers derived through flawed reasoning or hallucinations. To address this, we introduce AURA (Audio-visual Understanding and Reasoning Assessment), a benchmark for evaluating the cross-modal reasoning capabilities of Audio-Visual Large Language Models (AV-LLMs) and Omni-modal Language Models (OLMs). AURA includes questions across six challenging cognitive domains, such as causality, timbre and pitch, tempo and AV synchronization, unanswerability, implicit distractions, and skill profiling, explicitly designed to be unanswerable from a single modality. This forces models to construct a valid logical path grounded in both audio and video, setting AURA apart from AV datasets that allow uni-modal shortcuts. To assess reasoning traces, we propose a novel metric, AuraScore, which addresses the lack of robust tools for evaluating reasoning fidelity. It decomposes reasoning into two aspects: (i) Factual Consistency - whether reasoning is grounded in perceptual evidence, and (ii) Core Inference - the logical validity of each reasoning step. Evaluations of SOTA models on AURA reveal a critical reasoning gap: although models achieve high accuracy (up to 92% on some tasks), their Factual Consistency and Core Inference scores fall below 45%. This discrepancy highlights that models often arrive at correct answers through flawed logic, underscoring the need for our benchmark and paving the way for more robust multimodal evaluation.
Multi-Domain Audio Question Answering Toward Acoustic Content Reasoning in The DCASE 2025 Challenge
May 12, 2025Abstract:We present Task 5 of the DCASE 2025 Challenge: an Audio Question Answering (AQA) benchmark spanning multiple domains of sound understanding. This task defines three QA subsets (Bioacoustics, Temporal Soundscapes, and Complex QA) to test audio-language models on interactive question-answering over diverse acoustic scenes. We describe the dataset composition (from marine mammal calls to soundscapes and complex real-world clips), the evaluation protocol (top-1 accuracy with answer-shuffling robustness), and baseline systems (Qwen2-Audio-7B, AudioFlamingo 2, Gemini-2-Flash). Preliminary results on the development set are compared, showing strong variation across models and subsets. This challenge aims to advance the audio understanding and reasoning capabilities of audio-language models toward human-level acuity, which are crucial for enabling AI agents to perceive and interact about the world effectively.
ProSE: Diffusion Priors for Speech Enhancement
Mar 09, 2025
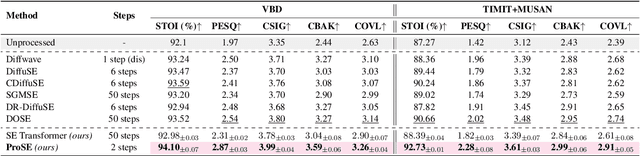
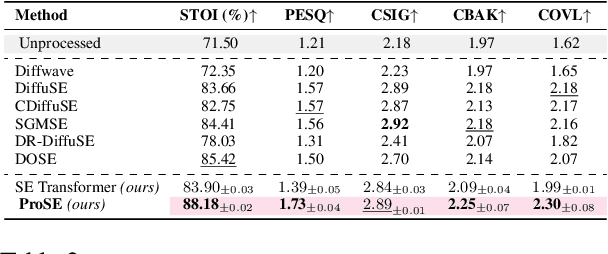
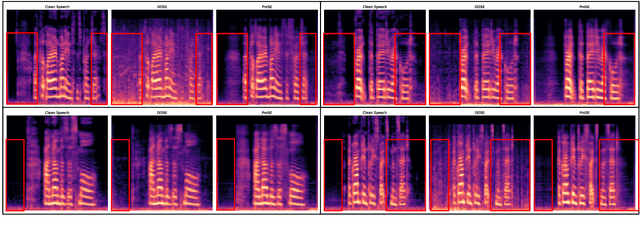
Abstract:Speech enhancement (SE) is the foundational task of enhancing the clarity and quality of speech in the presence of non-stationary additive noise. While deterministic deep learning models have been commonly employed for SE, recent research indicates that generative models, such as denoising diffusion probabilistic models (DDPMs), have shown promise. However, unlike speech generation, SE has a strong constraint in generating results in accordance with the underlying ground-truth signal. Additionally, for a wide variety of applications, SE systems need to be employed in real-time, and traditional diffusion models (DMs) requiring many iterations of a large model during inference are inefficient. To address these issues, we propose ProSE (diffusion-based Priors for SE), a novel methodology based on an alternative framework for applying diffusion models to SE. Specifically, we first apply DDPMs to generate priors in a latent space due to their powerful distribution mapping capabilities. The priors are then integrated into a transformer-based regression model for SE. The priors guide the regression model in the enhancement process. Since the diffusion process is applied to a compact latent space, the diffusion model takes fewer iterations than the traditional DM to obtain accurate estimations. Additionally, using a regression model for SE avoids the distortion issue caused by misaligned details generated by DMs. Our experiments show that ProSE achieves state-of-the-art performance on benchmark datasets with fewer computational costs.
Exploiting Sparsity for Long Context Inference: Million Token Contexts on Commodity GPUs
Feb 10, 2025



Abstract:There is growing demand for performing inference with hundreds of thousands of input tokens on trained transformer models. Inference at this extreme scale demands significant computational resources, hindering the application of transformers at long contexts on commodity (i.e not data center scale) hardware. To address the inference time costs associated with running self-attention based transformer language models on long contexts and enable their adoption on widely available hardware, we propose a tunable mechanism that reduces the cost of the forward pass by attending to only the most relevant tokens at every generation step using a top-k selection mechanism. We showcase the efficiency gains afforded by our method by performing inference on context windows up to 1M tokens using approximately 16GB of GPU RAM. Our experiments reveal that models are capable of handling the sparsity induced by the reduced number of keys and values. By attending to less than 2% of input tokens, we achieve over 95% of model performance on common long context benchmarks (LM-Eval, AlpacaEval, and RULER).
3D Gaussian Splatting with Normal Information for Mesh Extraction and Improved Rendering
Jan 14, 2025



Abstract:Differentiable 3D Gaussian splatting has emerged as an efficient and flexible rendering technique for representing complex scenes from a collection of 2D views and enabling high-quality real-time novel-view synthesis. However, its reliance on photometric losses can lead to imprecisely reconstructed geometry and extracted meshes, especially in regions with high curvature or fine detail. We propose a novel regularization method using the gradients of a signed distance function estimated from the Gaussians, to improve the quality of rendering while also extracting a surface mesh. The regularizing normal supervision facilitates better rendering and mesh reconstruction, which is crucial for downstream applications in video generation, animation, AR-VR and gaming. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach on datasets such as Mip-NeRF360, Tanks and Temples, and Deep-Blending. Our method scores higher on photorealism metrics compared to other mesh extracting rendering methods without compromising mesh quality.
TSPE: Task-Specific Prompt Ensemble for Improved Zero-Shot Audio Classification
Dec 31, 2024Abstract:Audio-language models (ALMs) excel in zero-shot audio classification, a task where models classify previously unseen audio clips at test time by leveraging descriptive natural language prompts. We introduce TSPE (Task-Specific Prompt Ensemble), a simple, training-free hard prompting method that boosts ALEs' zero-shot performance by customizing prompts for diverse audio classification tasks. Rather than using generic template-based prompts like "Sound of a car" we generate context-rich prompts, such as "Sound of a car coming from a tunnel". Specifically, we leverage label information to identify suitable sound attributes, such as "loud" and "feeble", and appropriate sound sources, such as "tunnel" and "street" and incorporate this information into the prompts used by Audio-Language Models (ALMs) for audio classification. Further, to enhance audio-text alignment, we perform prompt ensemble across TSPE-generated task-specific prompts. When evaluated on 12 diverse audio classification datasets, TSPE improves performance across ALMs by showing an absolute improvement of 1.23-16.36% over vanilla zero-shot evaluation.
Applying Automatic Differentiation to Optimize Differential Microphone Array Designs
Dec 06, 2024Abstract:This paper introduces a novel methodology leveraging differentiable programming to design efficient, constrained adaptive non-uniform Linear Differential Microphone Arrays (LDMAs) with reduced implementation costs. Utilizing an automatic differentiation framework, we propose a differentiable convex approach that enables the adaptive design of a filter with a distortionless constraint in the desired sound direction, while also imposing constraints on microphone positioning to ensure consistent performance. This approach achieves the desired Directivity Factor (DF) over a wide frequency range and facilitates effective recovery of wide-band speech signals at lower implementation costs.
MMAU: A Massive Multi-Task Audio Understanding and Reasoning Benchmark
Oct 24, 2024



Abstract:The ability to comprehend audio--which includes speech, non-speech sounds, and music--is crucial for AI agents to interact effectively with the world. We present MMAU, a novel benchmark designed to evaluate multimodal audio understanding models on tasks requiring expert-level knowledge and complex reasoning. MMAU comprises 10k carefully curated audio clips paired with human-annotated natural language questions and answers spanning speech, environmental sounds, and music. It includes information extraction and reasoning questions, requiring models to demonstrate 27 distinct skills across unique and challenging tasks. Unlike existing benchmarks, MMAU emphasizes advanced perception and reasoning with domain-specific knowledge, challenging models to tackle tasks akin to those faced by experts. We assess 18 open-source and proprietary (Large) Audio-Language Models, demonstrating the significant challenges posed by MMAU. Notably, even the most advanced Gemini Pro v1.5 achieves only 52.97% accuracy, and the state-of-the-art open-source Qwen2-Audio achieves only 52.50%, highlighting considerable room for improvement. We believe MMAU will drive the audio and multimodal research community to develop more advanced audio understanding models capable of solving complex audio tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge