Anton Jeran Ratnarajah
ProSE: Diffusion Priors for Speech Enhancement
Mar 09, 2025
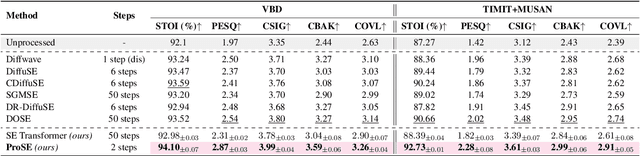
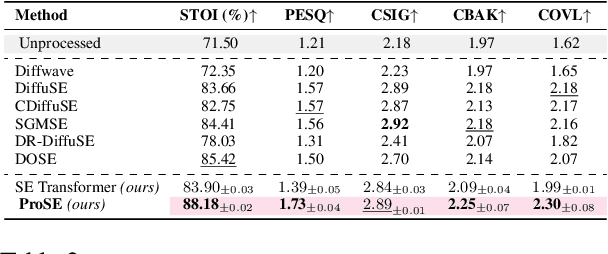
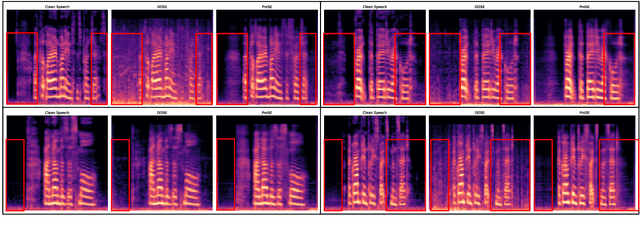
Abstract:Speech enhancement (SE) is the foundational task of enhancing the clarity and quality of speech in the presence of non-stationary additive noise. While deterministic deep learning models have been commonly employed for SE, recent research indicates that generative models, such as denoising diffusion probabilistic models (DDPMs), have shown promise. However, unlike speech generation, SE has a strong constraint in generating results in accordance with the underlying ground-truth signal. Additionally, for a wide variety of applications, SE systems need to be employed in real-time, and traditional diffusion models (DMs) requiring many iterations of a large model during inference are inefficient. To address these issues, we propose ProSE (diffusion-based Priors for SE), a novel methodology based on an alternative framework for applying diffusion models to SE. Specifically, we first apply DDPMs to generate priors in a latent space due to their powerful distribution mapping capabilities. The priors are then integrated into a transformer-based regression model for SE. The priors guide the regression model in the enhancement process. Since the diffusion process is applied to a compact latent space, the diffusion model takes fewer iterations than the traditional DM to obtain accurate estimations. Additionally, using a regression model for SE avoids the distortion issue caused by misaligned details generated by DMs. Our experiments show that ProSE achieves state-of-the-art performance on benchmark datasets with fewer computational costs.
Scene2BIR: Material-aware learning-based binaural impulse response generator for reconstructed real-world 3D scenes
Feb 02, 2023Abstract:We present an end-to-end binaural impulse response generator (BIR) to generate plausible sounds in real-time for real-world models. Our approach uses a novel neural-network-based BIR generator (Scene2BIR) for the reconstructed 3D model. We propose a graph neural network that uses both the material and the topology information of the 3D scenes and generates a scene latent vector. Moreover, we use a conditional generative adversarial network (CGAN) to generate BIRs from the scene latent vector. Our network is able to handle holes or other artifacts in the reconstructed 3D mesh model. We present an efficient cost function to the generator network to incorporate spatial audio effects. Given the source and the listener position, our approach can generate a BIR in 0.1 milliseconds on an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2080 Ti GPU and can easily handle multiple sources. We have evaluated the accuracy of our approach with real-world captured BIRs and an interactive geometric sound propagation algorithm.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge