Nishit Anand
Why Stop at Words? Unveiling the Bigger Picture through Line-Level OCR
Aug 29, 2025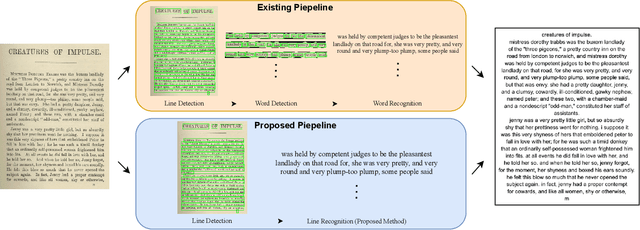
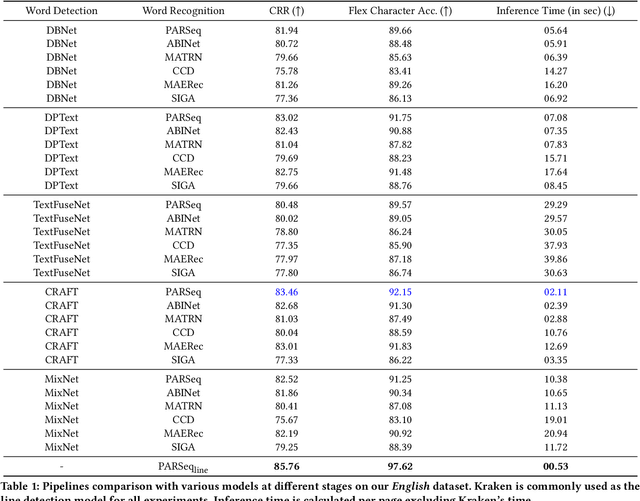

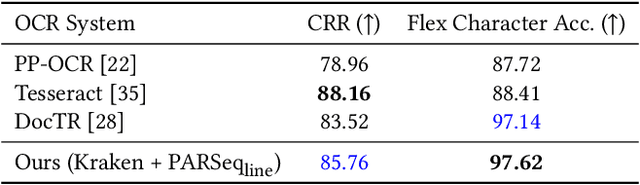
Abstract:Conventional optical character recognition (OCR) techniques segmented each character and then recognized. This made them prone to error in character segmentation, and devoid of context to exploit language models. Advances in sequence to sequence translation in last decade led to modern techniques first detecting words and then inputting one word at a time to a model to directly output full words as sequence of characters. This allowed better utilization of language models and bypass error-prone character segmentation step. We observe that the above transition in style has moved the bottleneck in accuracy to word segmentation. Hence, in this paper, we propose a natural and logical progression from word level OCR to line-level OCR. The proposal allows to bypass errors in word detection, and provides larger sentence context for better utilization of language models. We show that the proposed technique not only improves the accuracy but also efficiency of OCR. Despite our thorough literature survey, we did not find any public dataset to train and benchmark such shift from word to line-level OCR. Hence, we also contribute a meticulously curated dataset of 251 English page images with line-level annotations. Our experimentation revealed a notable end-to-end accuracy improvement of 5.4%, underscoring the potential benefits of transitioning towards line-level OCR, especially for document images. We also report a 4 times improvement in efficiency compared to word-based pipelines. With continuous improvements in large language models, our methodology also holds potential to exploit such advances. Project Website: https://nishitanand.github.io/line-level-ocr-website
Aurelia: Test-time Reasoning Distillation in Audio-Visual LLMs
Mar 29, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in reasoning optimization have greatly enhanced the performance of large language models (LLMs). However, existing work fails to address the complexities of audio-visual scenarios, underscoring the need for further research. In this paper, we introduce AURELIA, a novel actor-critic based audio-visual (AV) reasoning framework that distills structured, step-by-step reasoning into AVLLMs at test time, improving their ability to process complex multi-modal inputs without additional training or fine-tuning. To further advance AVLLM reasoning skills, we present AVReasonBench, a challenging benchmark comprising 4500 audio-visual questions, each paired with detailed step-by-step reasoning. Our benchmark spans six distinct tasks, including AV-GeoIQ, which evaluates AV reasoning combined with geographical and cultural knowledge. Evaluating 18 AVLLMs on AVReasonBench reveals significant limitations in their multi-modal reasoning capabilities. Using AURELIA, we achieve up to a 100% relative improvement, demonstrating its effectiveness. This performance gain highlights the potential of reasoning-enhanced data generation for advancing AVLLMs in real-world applications. Our code and data will be publicly released at: https: //github.com/schowdhury671/aurelia.
Mitigating Memorization in LLMs using Activation Steering
Mar 08, 2025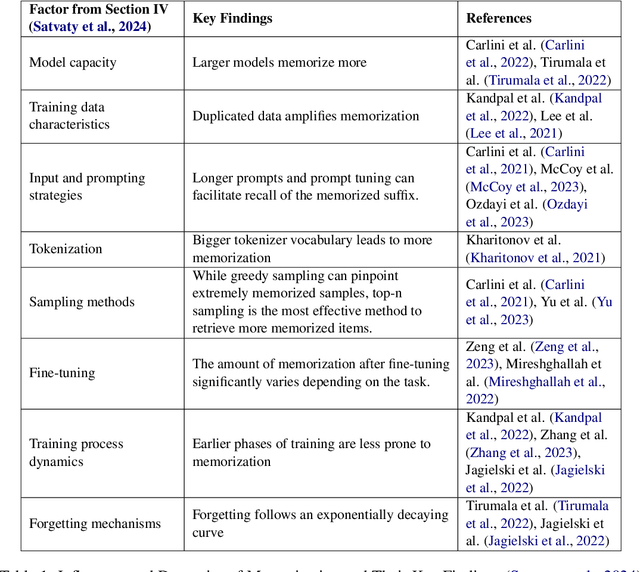
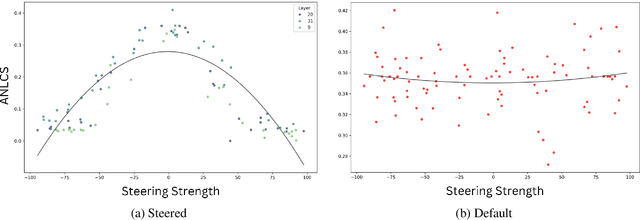
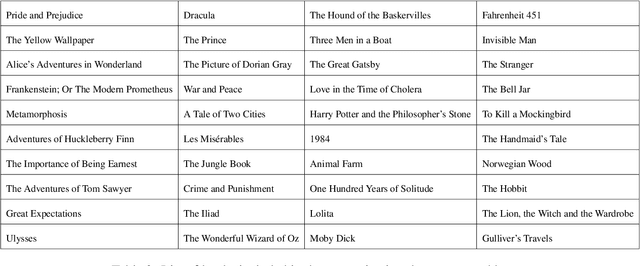
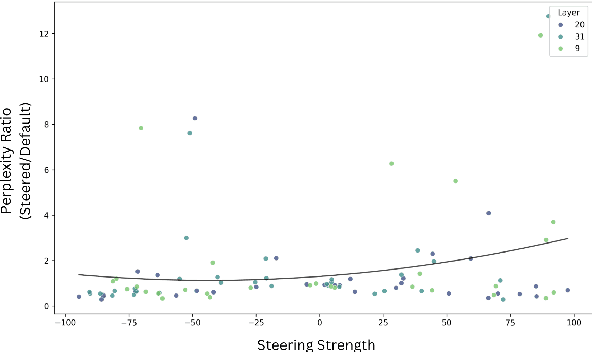
Abstract:The memorization of training data by Large Language Models (LLMs) poses significant risks, including privacy leaks and the regurgitation of copyrighted content. Activation steering, a technique that directly intervenes in model activations, has emerged as a promising approach for manipulating LLMs. In this work, we explore the effectiveness of activation steering in reducing memorization while preserving generalization capabilities. We conduct empirical evaluations using a controlled memorization benchmark of literary material and demonstrate that our method successfully suppresses memorized content with minimal degradation in model performance in Gemma. Additionally, we analyze the trade-offs between suppression effectiveness and linguistic fluency, highlighting the advantages and limitations of activation-based interventions. Our findings contribute to ongoing efforts in developing safer and more privacy-preserving LLMs by providing a practical and efficient mechanism to mitigate unintended memorization.
TSPE: Task-Specific Prompt Ensemble for Improved Zero-Shot Audio Classification
Dec 31, 2024Abstract:Audio-language models (ALMs) excel in zero-shot audio classification, a task where models classify previously unseen audio clips at test time by leveraging descriptive natural language prompts. We introduce TSPE (Task-Specific Prompt Ensemble), a simple, training-free hard prompting method that boosts ALEs' zero-shot performance by customizing prompts for diverse audio classification tasks. Rather than using generic template-based prompts like "Sound of a car" we generate context-rich prompts, such as "Sound of a car coming from a tunnel". Specifically, we leverage label information to identify suitable sound attributes, such as "loud" and "feeble", and appropriate sound sources, such as "tunnel" and "street" and incorporate this information into the prompts used by Audio-Language Models (ALMs) for audio classification. Further, to enhance audio-text alignment, we perform prompt ensemble across TSPE-generated task-specific prompts. When evaluated on 12 diverse audio classification datasets, TSPE improves performance across ALMs by showing an absolute improvement of 1.23-16.36% over vanilla zero-shot evaluation.
Do Audio-Language Models Understand Linguistic Variations?
Oct 21, 2024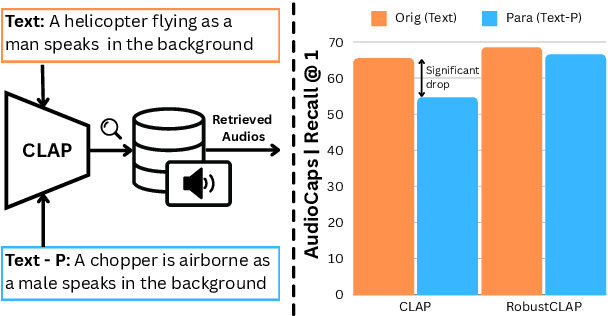
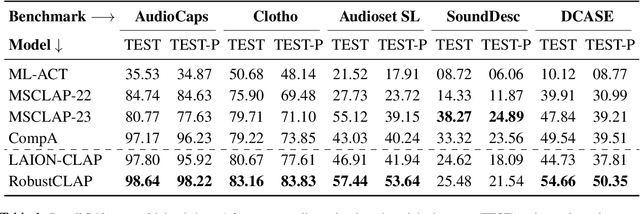
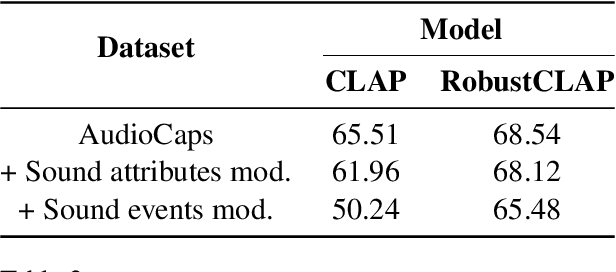
Abstract:Open-vocabulary audio language models (ALMs), like Contrastive Language Audio Pretraining (CLAP), represent a promising new paradigm for audio-text retrieval using natural language queries. In this paper, for the first time, we perform controlled experiments on various benchmarks to show that existing ALMs struggle to generalize to linguistic variations in textual queries. To address this issue, we propose RobustCLAP, a novel and compute-efficient technique to learn audio-language representations agnostic to linguistic variations. Specifically, we reformulate the contrastive loss used in CLAP architectures by introducing a multi-view contrastive learning objective, where paraphrases are treated as different views of the same audio scene and use this for training. Our proposed approach improves the text-to-audio retrieval performance of CLAP by 0.8%-13% across benchmarks and enhances robustness to linguistic variation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge