Parthasarathy Suryanarayanan
MAMMAL -- Molecular Aligned Multi-Modal Architecture and Language
Oct 28, 2024Abstract:Drug discovery typically consists of multiple steps, including identifying a target protein key to a disease's etiology, validating that interacting with this target could prevent symptoms or cure the disease, discovering a small molecule or biologic therapeutic to interact with it, and optimizing the candidate molecule through a complex landscape of required properties. Drug discovery related tasks often involve prediction and generation while considering multiple entities that potentially interact, which poses a challenge for typical AI models. For this purpose we present MAMMAL - Molecular Aligned Multi-Modal Architecture and Language - a method that we applied to create a versatile multi-task foundation model ibm/biomed.omics.bl.sm.ma-ted-458m that learns from large-scale biological datasets (2 billion samples) across diverse modalities, including proteins, small molecules, and genes. We introduce a prompt syntax that supports a wide range of classification, regression, and generation tasks. It allows combining different modalities and entity types as inputs and/or outputs. Our model handles combinations of tokens and scalars and enables the generation of small molecules and proteins, property prediction, and transcriptomic lab test predictions. We evaluated the model on 11 diverse downstream tasks spanning different steps within a typical drug discovery pipeline, where it reaches new SOTA in 9 tasks and is comparable to SOTA in 2 tasks. This performance is achieved while using a unified architecture serving all tasks, in contrast to the original SOTA performance achieved using tailored architectures. The model code and pretrained weights are publicly available at https://github.com/BiomedSciAI/biomed-multi-alignment and https://huggingface.co/ibm/biomed.omics.bl.sm.ma-ted-458m.
Multi-view biomedical foundation models for molecule-target and property prediction
Oct 25, 2024


Abstract:Foundation models applied to bio-molecular space hold promise to accelerate drug discovery. Molecular representation is key to building such models. Previous works have typically focused on a single representation or view of the molecules. Here, we develop a multi-view foundation model approach, that integrates molecular views of graph, image and text. Single-view foundation models are each pre-trained on a dataset of up to 200M molecules and then aggregated into combined representations. Our multi-view model is validated on a diverse set of 18 tasks, encompassing ligand-protein binding, molecular solubility, metabolism and toxicity. We show that the multi-view models perform robustly and are able to balance the strengths and weaknesses of specific views. We then apply this model to screen compounds against a large (>100 targets) set of G Protein-Coupled receptors (GPCRs). From this library of targets, we identify 33 that are related to Alzheimer's disease. On this subset, we employ our model to identify strong binders, which are validated through structure-based modeling and identification of key binding motifs.
Disease Progression Modeling Workbench 360
Jun 24, 2021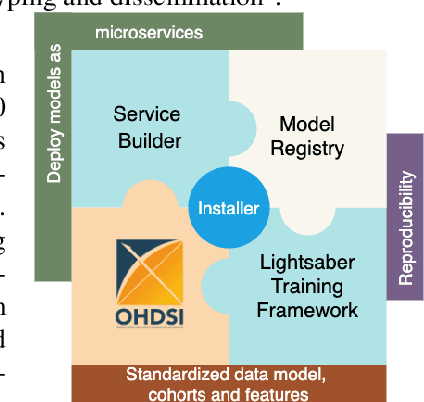
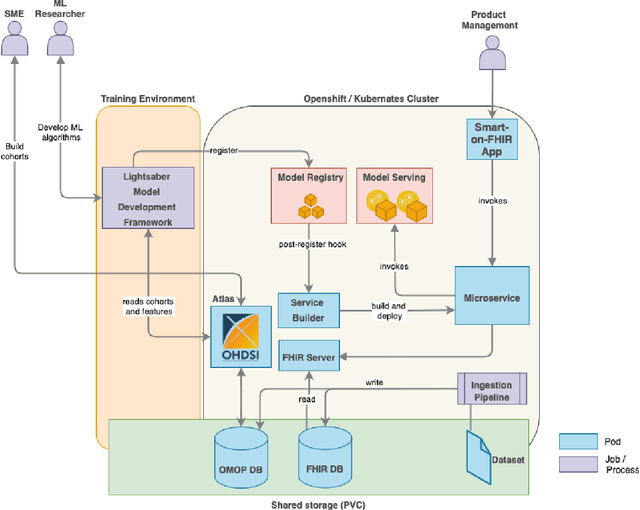
Abstract:In this work we introduce Disease Progression Modeling workbench 360 (DPM360) opensource clinical informatics framework for collaborative research and delivery of healthcare AI. DPM360, when fully developed, will manage the entire modeling life cycle, from data analysis (e.g., cohort identification) to machine learning algorithm development and prototyping. DPM360 augments the advantages of data model standardization and tooling (OMOP-CDM, Athena, ATLAS) provided by the widely-adopted OHDSI initiative with a powerful machine learning training framework, and a mechanism for rapid prototyping through automatic deployment of models as containerized services to a cloud environment.
A Novel Methodology For Crowdsourcing AI Models in an Enterprise
Mar 22, 2021
Abstract:The evolution of AI is advancing rapidly, creating both challenges and opportunities for industry-community collaboration. In this work, we present a novel methodology aiming to facilitate this collaboration through crowdsourcing of AI models. Concretely, we have implemented a system and a process that any organization can easily adopt to host AI competitions. The system allows them to automatically harvest and evaluate the submitted models against in-house proprietary data and also to incorporate them as reusable services in a product.
WNTRAC: Artificial Intelligence Assisted Tracking of Non-pharmaceutical Interventions Implemented Worldwide for COVID-19
Sep 16, 2020



Abstract:The Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) global pandemic has transformed almost every facet of human society throughout the world. Against an emerging, highly transmissible disease with no definitive treatment or vaccine, governments worldwide have implemented non-pharmaceutical intervention (NPI) to slow the spread of the virus. Examples of such interventions include community actions (e.g. school closures, restrictions on mass gatherings), individual actions (e.g. mask wearing, self-quarantine), and environmental actions (e.g. public facility cleaning). We present the Worldwide Non-pharmaceutical Interventions Tracker for COVID-19 (WNTRAC), a comprehensive dataset consisting of over 6,000 NPIs implemented worldwide since the start of the pandemic. WNTRAC covers NPIs implemented across 261 countries and territories, and classifies NPI measures into a taxonomy of sixteen NPI types. NPI measures are automatically extracted daily from Wikipedia articles using natural language processing techniques and manually validated to ensure accuracy and veracity. We hope that the dataset is valuable for policymakers, public health leaders, and researchers in modeling and analysis efforts for controlling the spread of COVID-19.
A Canonical Architecture For Predictive Analytics on Longitudinal Patient Records
Jul 24, 2020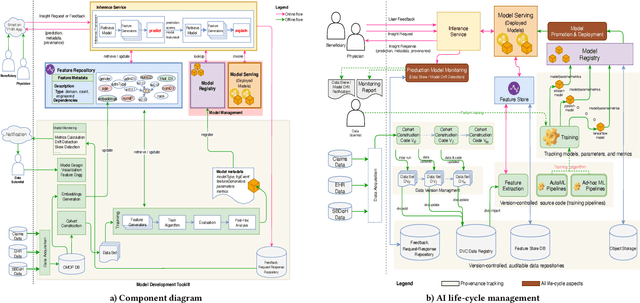
Abstract:Many institutions within the healthcare ecosystem are making significant investments in AI technologies to optimize their business operations at lower cost with improved patient outcomes. Despite the hype with AI, the full realization of this potential is seriously hindered by several systemic problems, including data privacy, security, bias, fairness, and explainability. In this paper, we propose a novel canonical architecture for the development of AI models in healthcare that addresses these challenges. This system enables the creation and management of AI predictive models throughout all the phases of their life cycle, including data ingestion, model building, and model promotion in production environments. This paper describes this architecture in detail, along with a qualitative evaluation of our experience of using it on real world problems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge