Nuria Oliver
Beyond Holistic Scores: Automatic Trait-Based Quality Scoring of Argumentative Essays
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Automated Essay Scoring systems have traditionally focused on holistic scores, limiting their pedagogical usefulness, especially in the case of complex essay genres such as argumentative writing. In educational contexts, teachers and learners require interpretable, trait-level feedback that aligns with instructional goals and established rubrics. In this paper, we study trait-based Automatic Argumentative Essay Scoring using two complementary modeling paradigms designed for realistic educational deployment: (1) structured in-context learning with small open-source LLMs, and (2) a supervised, encoder-based BigBird model with a CORAL-style ordinal regression formulation, optimized for long-sequence understanding. We conduct a systematic evaluation on the ASAP++ dataset, which includes essay scores across five quality traits, offering strong coverage of core argumentation dimensions. LLMs are prompted with designed, rubric-aligned in-context examples, along with feedback and confidence requests, while we explicitly model ordinality in scores with the BigBird model via the rank-consistent CORAL framework. Our results show that explicitly modeling score ordinality substantially improves agreement with human raters across all traits, outperforming LLMs and nominal classification and regression-based baselines. This finding reinforces the importance of aligning model objectives with rubric semantics for educational assessment. At the same time, small open-source LLMs achieve a competitive performance without task-specific fine-tuning, particularly for reasoning-oriented traits, while enabling transparent, privacy-preserving, and locally deployable assessment scenarios. Our findings provide methodological, modeling, and practical insights for the design of AI-based educational systems that aim to deliver interpretable, rubric-aligned feedback for argumentative writing.
Aesthetics as Structural Harm: Algorithmic Lookism Across Text-to-Image Generation and Classification
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This paper examines algorithmic lookism-the systematic preferential treatment based on physical appearance-in text-to-image (T2I) generative AI and a downstream gender classification task. Through the analysis of 26,400 synthetic faces created with Stable Diffusion 2.1 and 3.5 Medium, we demonstrate how generative AI models systematically associate facial attractiveness with positive attributes and vice-versa, mirroring socially constructed biases rather than evidence-based correlations. Furthermore, we find significant gender bias in three gender classification algorithms depending on the attributes of the input faces. Our findings reveal three critical harms: (1) the systematic encoding of attractiveness-positive attribute associations in T2I models; (2) gender disparities in classification systems, where women's faces, particularly those generated with negative attributes, suffer substantially higher misclassification rates than men's; and (3) intensifying aesthetic constraints in newer models through age homogenization, gendered exposure patterns, and geographic reductionism. These convergent patterns reveal algorithmic lookism as systematic infrastructure operating across AI vision systems, compounding existing inequalities through both representation and recognition. Disclaimer: This work includes visual and textual content that reflects stereotypical associations between physical appearance and socially constructed attributes, including gender, race, and traits associated with social desirability. Any such associations found in this study emerge from the biases embedded in generative AI systems-not from empirical truths or the authors' views.
ELLIS Alicante at CQs-Gen 2025: Winning the critical thinking questions shared task: LLM-based question generation and selection
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:The widespread adoption of chat interfaces based on Large Language Models (LLMs) raises concerns about promoting superficial learning and undermining the development of critical thinking skills. Instead of relying on LLMs purely for retrieving factual information, this work explores their potential to foster deeper reasoning by generating critical questions that challenge unsupported or vague claims in debate interventions. This study is part of a shared task of the 12th Workshop on Argument Mining, co-located with ACL 2025, focused on automatic critical question generation. We propose a two-step framework involving two small-scale open source language models: a Questioner that generates multiple candidate questions and a Judge that selects the most relevant ones. Our system ranked first in the shared task competition, demonstrating the potential of the proposed LLM-based approach to encourage critical engagement with argumentative texts.
Reconsidering Fairness Through Unawareness from the Perspective of Model Multiplicity
May 22, 2025Abstract:Fairness through Unawareness (FtU) describes the idea that discrimination against demographic groups can be avoided by not considering group membership in the decisions or predictions. This idea has long been criticized in the machine learning literature as not being sufficient to ensure fairness. In addition, the use of additional features is typically thought to increase the accuracy of the predictions for all groups, so that FtU is sometimes thought to be detrimental to all groups. In this paper, we show both theoretically and empirically that FtU can reduce algorithmic discrimination without necessarily reducing accuracy. We connect this insight with the literature on Model Multiplicity, to which we contribute with novel theoretical and empirical results. Furthermore, we illustrate how, in a real-life application, FtU can contribute to the deployment of more equitable policies without losing efficacy. Our findings suggest that FtU is worth considering in practical applications, particularly in high-risk scenarios, and that the use of protected attributes such as gender in predictive models should be accompanied by a clear and well-founded justification.
Diversity-Driven Learning: Tackling Spurious Correlations and Data Heterogeneity in Federated Models
Apr 15, 2025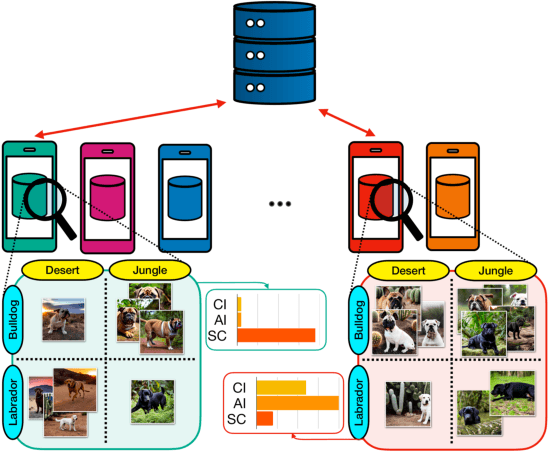
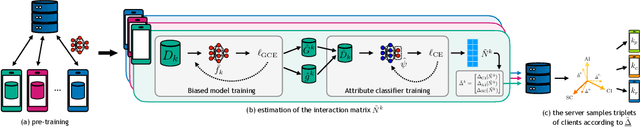
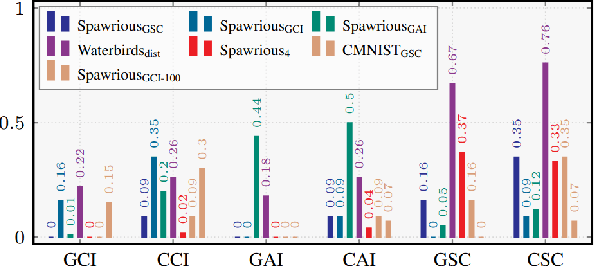
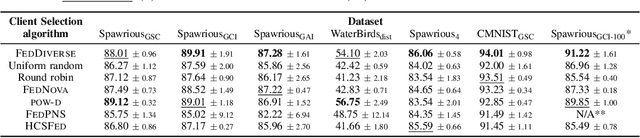
Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) enables decentralized training of machine learning models on distributed data while preserving privacy. However, in real-world FL settings, client data is often non-identically distributed and imbalanced, resulting in statistical data heterogeneity which impacts the generalization capabilities of the server's model across clients, slows convergence and reduces performance. In this paper, we address this challenge by first proposing a characterization of statistical data heterogeneity by means of 6 metrics of global and client attribute imbalance, class imbalance, and spurious correlations. Next, we create and share 7 computer vision datasets for binary and multiclass image classification tasks in Federated Learning that cover a broad range of statistical data heterogeneity and hence simulate real-world situations. Finally, we propose FedDiverse, a novel client selection algorithm in FL which is designed to manage and leverage data heterogeneity across clients by promoting collaboration between clients with complementary data distributions. Experiments on the seven proposed FL datasets demonstrate FedDiverse's effectiveness in enhancing the performance and robustness of a variety of FL methods while having low communication and computational overhead.
ImageSet2Text: Describing Sets of Images through Text
Mar 25, 2025



Abstract:We introduce ImageSet2Text, a novel approach that leverages vision-language foundation models to automatically create natural language descriptions of image sets. Inspired by concept bottleneck models (CBMs) and based on visual-question answering (VQA) chains, ImageSet2Text iteratively extracts key concepts from image subsets, encodes them into a structured graph, and refines insights using an external knowledge graph and CLIP-based validation. This iterative process enhances interpretability and enables accurate and detailed set-level summarization. Through extensive experiments, we evaluate ImageSet2Text's descriptions on accuracy, completeness, readability and overall quality, benchmarking it against existing vision-language models and introducing new datasets for large-scale group image captioning.
Leveraging Small LLMs for Argument Mining in Education: Argument Component Identification, Classification, and Assessment
Feb 20, 2025



Abstract:Argument mining algorithms analyze the argumentative structure of essays, making them a valuable tool for enhancing education by providing targeted feedback on the students' argumentation skills. While current methods often use encoder or encoder-decoder deep learning architectures, decoder-only models remain largely unexplored, offering a promising research direction. This paper proposes leveraging open-source, small Large Language Models (LLMs) for argument mining through few-shot prompting and fine-tuning. These models' small size and open-source nature ensure accessibility, privacy, and computational efficiency, enabling schools and educators to adopt and deploy them locally. Specifically, we perform three tasks: segmentation of student essays into arguments, classification of the arguments by type, and assessment of their quality. We empirically evaluate the models on the Feedback Prize - Predicting Effective Arguments dataset of grade 6-12 students essays and demonstrate how fine-tuned small LLMs outperform baseline methods in segmenting the essays and determining the argument types while few-shot prompting yields comparable performance to that of the baselines in assessing quality. This work highlights the educational potential of small, open-source LLMs to provide real-time, personalized feedback, enhancing independent learning and writing skills while ensuring low computational cost and privacy.
International AI Safety Report
Jan 29, 2025



Abstract:The first International AI Safety Report comprehensively synthesizes the current evidence on the capabilities, risks, and safety of advanced AI systems. The report was mandated by the nations attending the AI Safety Summit in Bletchley, UK. Thirty nations, the UN, the OECD, and the EU each nominated a representative to the report's Expert Advisory Panel. A total of 100 AI experts contributed, representing diverse perspectives and disciplines. Led by the report's Chair, these independent experts collectively had full discretion over the report's content.
Local vs distributed representations: What is the right basis for interpretability?
Nov 06, 2024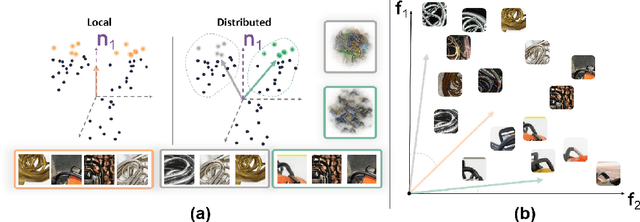


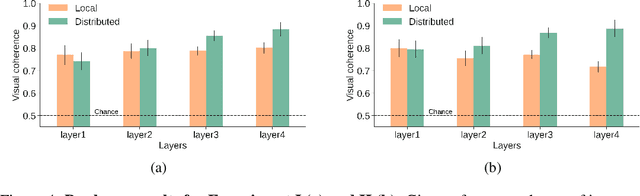
Abstract:Much of the research on the interpretability of deep neural networks has focused on studying the visual features that maximally activate individual neurons. However, recent work has cast doubts on the usefulness of such local representations for understanding the behavior of deep neural networks because individual neurons tend to respond to multiple unrelated visual patterns, a phenomenon referred to as "superposition". A promising alternative to disentangle these complex patterns is learning sparsely distributed vector representations from entire network layers, as the resulting basis vectors seemingly encode single identifiable visual patterns consistently. Thus, one would expect the resulting code to align better with human perceivable visual patterns, but supporting evidence remains, at best, anecdotal. To fill this gap, we conducted three large-scale psychophysics experiments collected from a pool of 560 participants. Our findings provide (i) strong evidence that features obtained from sparse distributed representations are easier to interpret by human observers and (ii) that this effect is more pronounced in the deepest layers of a neural network. Complementary analyses also reveal that (iii) features derived from sparse distributed representations contribute more to the model's decision. Overall, our results highlight that distributed representations constitute a superior basis for interpretability, underscoring a need for the field to move beyond the interpretation of local neural codes in favor of sparsely distributed ones.
The Disparate Benefits of Deep Ensembles
Oct 17, 2024



Abstract:Ensembles of Deep Neural Networks, Deep Ensembles, are widely used as a simple way to boost predictive performance. However, their impact on algorithmic fairness is not well understood yet. Algorithmic fairness investigates how a model's performance varies across different groups, typically defined by protected attributes such as age, gender, or race. In this work, we investigate the interplay between the performance gains from Deep Ensembles and fairness. Our analysis reveals that they unevenly favor different groups in what we refer to as a disparate benefits effect. We empirically investigate this effect with Deep Ensembles applied to popular facial analysis and medical imaging datasets, where protected group attributes are given and find that it occurs for multiple established group fairness metrics, including statistical parity and equal opportunity. Furthermore, we identify the per-group difference in predictive diversity of ensemble members as the potential cause of the disparate benefits effect. Finally, we evaluate different approaches to reduce unfairness due to the disparate benefits effect. Our findings show that post-processing is an effective method to mitigate this unfairness while preserving the improved performance of Deep Ensembles.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge