Erik Derner
Leveraging Large Language Models to Measure Gender Bias in Gendered Languages
Jun 19, 2024Abstract:Gender bias in text corpora used in various natural language processing (NLP) contexts, such as for training large language models (LLMs), can lead to the perpetuation and amplification of societal inequalities. This is particularly pronounced in gendered languages like Spanish or French, where grammatical structures inherently encode gender, making the bias analysis more challenging. Existing methods designed for English are inadequate for this task due to the intrinsic linguistic differences between English and gendered languages. This paper introduces a novel methodology that leverages the contextual understanding capabilities of LLMs to quantitatively analyze gender representation in Spanish corpora. By utilizing LLMs to identify and classify gendered nouns and pronouns in relation to their reference to human entities, our approach provides a nuanced analysis of gender biases. We empirically validate our method on four widely-used benchmark datasets, uncovering significant gender disparities with a male-to-female ratio ranging from 4:1 to 6:1. These findings demonstrate the value of our methodology for bias quantification in gendered languages and suggest its application in NLP, contributing to the development of more equitable language technologies.
Can ChatGPT Read Who You Are?
Dec 26, 2023
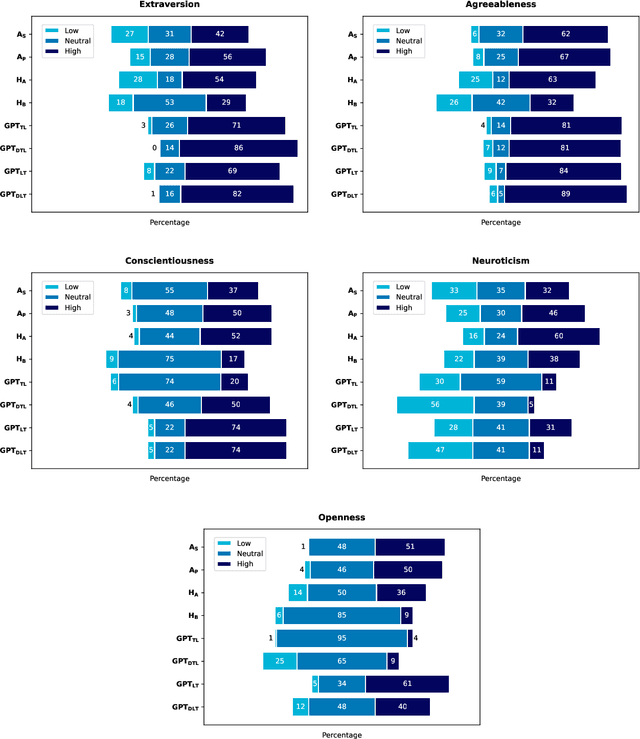
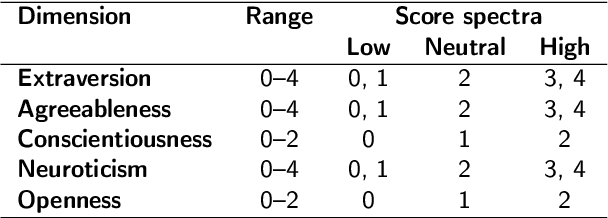
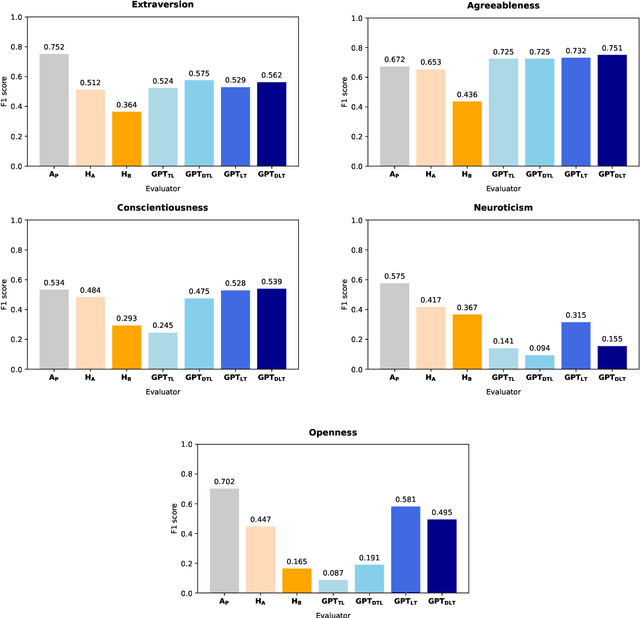
Abstract:The interplay between artificial intelligence (AI) and psychology, particularly in personality assessment, represents an important emerging area of research. Accurate personality trait estimation is crucial not only for enhancing personalization in human-computer interaction but also for a wide variety of applications ranging from mental health to education. This paper analyzes the capability of a generic chatbot, ChatGPT, to effectively infer personality traits from short texts. We report the results of a comprehensive user study featuring texts written in Czech by a representative population sample of 155 participants. Their self-assessments based on the Big Five Inventory (BFI) questionnaire serve as the ground truth. We compare the personality trait estimations made by ChatGPT against those by human raters and report ChatGPT's competitive performance in inferring personality traits from text. We also uncover a 'positivity bias' in ChatGPT's assessments across all personality dimensions and explore the impact of prompt composition on accuracy. This work contributes to the understanding of AI capabilities in psychological assessment, highlighting both the potential and limitations of using large language models for personality inference. Our research underscores the importance of responsible AI development, considering ethical implications such as privacy, consent, autonomy, and bias in AI applications.
A Security Risk Taxonomy for Large Language Models
Nov 19, 2023



Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) permeate more and more applications, an assessment of their associated security risks becomes increasingly necessary. The potential for exploitation by malicious actors, ranging from disinformation to data breaches and reputation damage, is substantial. This paper addresses a gap in current research by focusing on the security risks posed by LLMs, which extends beyond the widely covered ethical and societal implications. Our work proposes a taxonomy of security risks along the user-model communication pipeline, explicitly focusing on prompt-based attacks on LLMs. We categorize the attacks by target and attack type within a prompt-based interaction scheme. The taxonomy is reinforced with specific attack examples to showcase the real-world impact of these risks. Through this taxonomy, we aim to inform the development of robust and secure LLM applications, enhancing their safety and trustworthiness.
Beyond the Safeguards: Exploring the Security Risks of ChatGPT
May 13, 2023Abstract:The increasing popularity of large language models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT has led to growing concerns about their safety, security risks, and ethical implications. This paper aims to provide an overview of the different types of security risks associated with ChatGPT, including malicious text and code generation, private data disclosure, fraudulent services, information gathering, and producing unethical content. We present an empirical study examining the effectiveness of ChatGPT's content filters and explore potential ways to bypass these safeguards, demonstrating the ethical implications and security risks that persist in LLMs even when protections are in place. Based on a qualitative analysis of the security implications, we discuss potential strategies to mitigate these risks and inform researchers, policymakers, and industry professionals about the complex security challenges posed by LLMs like ChatGPT. This study contributes to the ongoing discussion on the ethical and security implications of LLMs, underscoring the need for continued research in this area.
Neural Networks for Symbolic Regression
Feb 03, 2023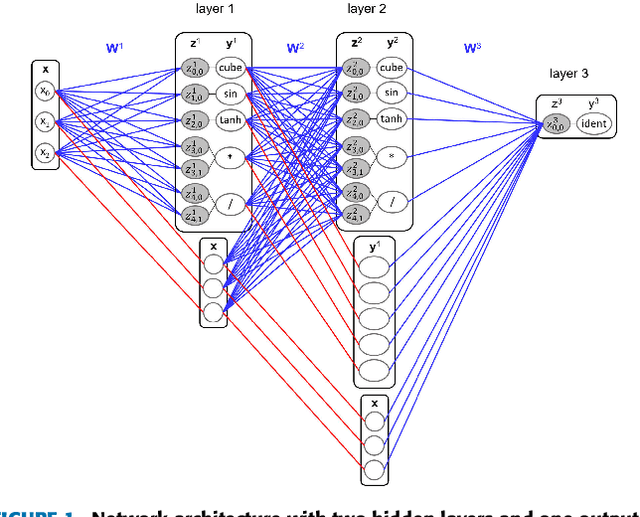
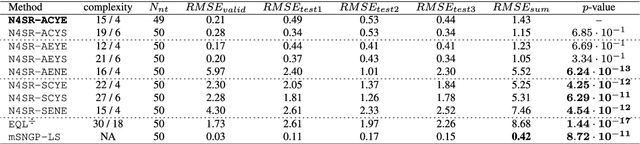
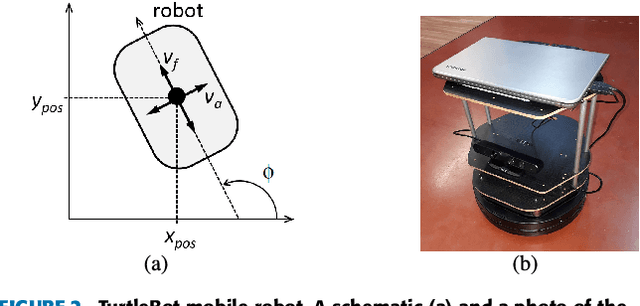
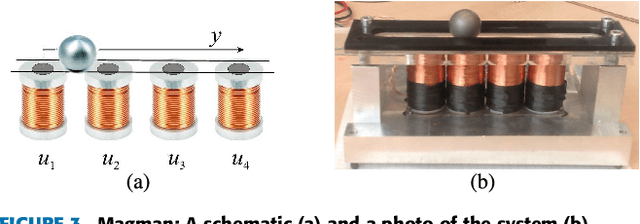
Abstract:Many real-world systems can be described by mathematical formulas that are human-comprehensible, easy to analyze and can be helpful in explaining the system's behaviour. Symbolic regression is a method that generates nonlinear models from data in the form of analytic expressions. Historically, symbolic regression has been predominantly realized using genetic programming, a method that iteratively evolves a population of candidate solutions that are sampled by genetic operators crossover and mutation. This gradient-free evolutionary approach suffers from several deficiencies: it does not scale well with the number of variables and samples in the training data, models tend to grow in size and complexity without an adequate accuracy gain, and it is hard to fine-tune the inner model coefficients using just genetic operators. Recently, neural networks have been applied to learn the whole analytic formula, i.e., its structure as well as the coefficients, by means of gradient-based optimization algorithms. We propose a novel neural network-based symbolic regression method that constructs physically plausible models based on limited training data and prior knowledge about the system. The method employs an adaptive weighting scheme to effectively deal with multiple loss function terms and an epoch-wise learning process to reduce the chance of getting stuck in poor local optima. Furthermore, we propose a parameter-free method for choosing the model with the best interpolation and extrapolation performance out of all models generated through the whole learning process. We experimentally evaluate the approach on the TurtleBot 2 mobile robot, the magnetic manipulation system, the equivalent resistance of two resistors in parallel, and the anti-lock braking system. The results clearly show the potential of the method to find sparse and accurate models that comply with the prior knowledge provided.
SymFormer: End-to-end symbolic regression using transformer-based architecture
Jun 01, 2022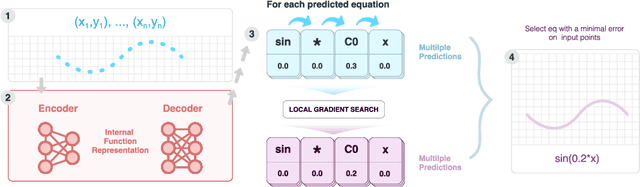
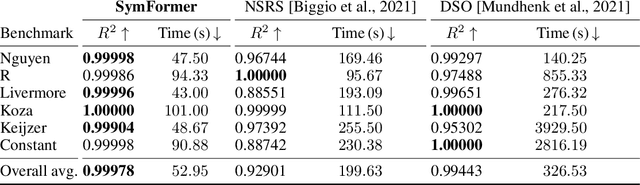
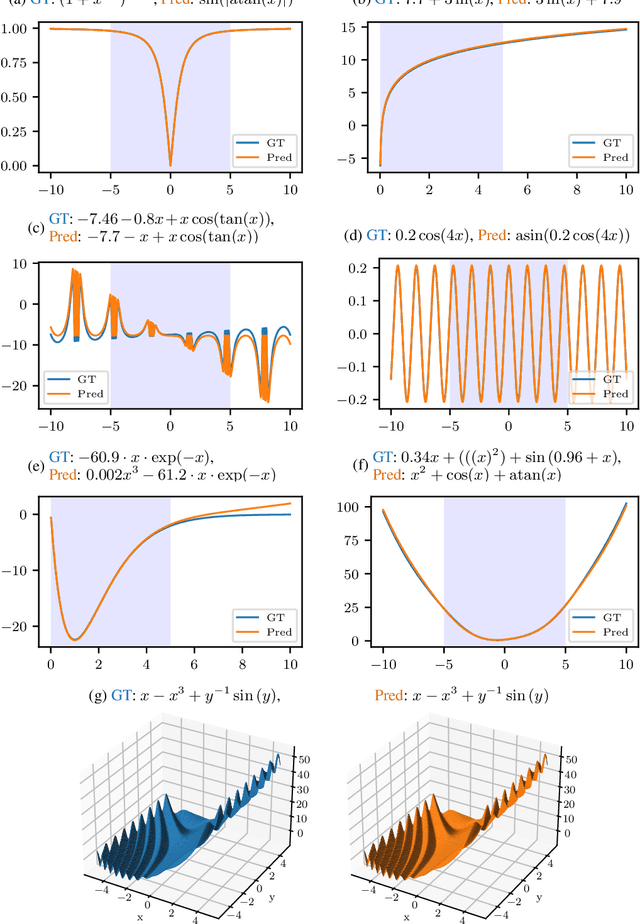
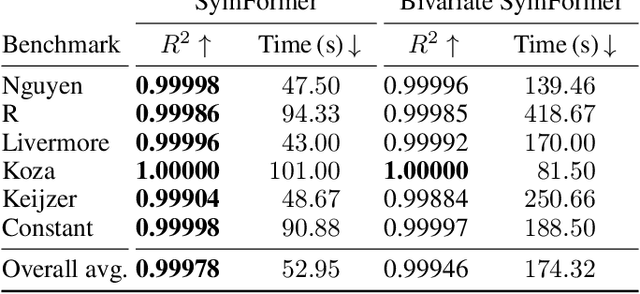
Abstract:Many real-world problems can be naturally described by mathematical formulas. The task of finding formulas from a set of observed inputs and outputs is called symbolic regression. Recently, neural networks have been applied to symbolic regression, among which the transformer-based ones seem to be the most promising. After training the transformer on a large number of formulas (in the order of days), the actual inference, i.e., finding a formula for new, unseen data, is very fast (in the order of seconds). This is considerably faster than state-of-the-art evolutionary methods. The main drawback of transformers is that they generate formulas without numerical constants, which have to be optimized separately, so yielding suboptimal results. We propose a transformer-based approach called SymFormer, which predicts the formula by outputting the individual symbols and the corresponding constants simultaneously. This leads to better performance in terms of fitting the available data. In addition, the constants provided by SymFormer serve as a good starting point for subsequent tuning via gradient descent to further improve the performance. We show on a set of benchmarks that SymFormer outperforms two state-of-the-art methods while having faster inference.
ViewFormer: NeRF-free Neural Rendering from Few Images Using Transformers
Mar 18, 2022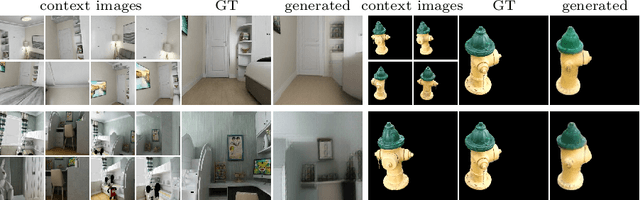
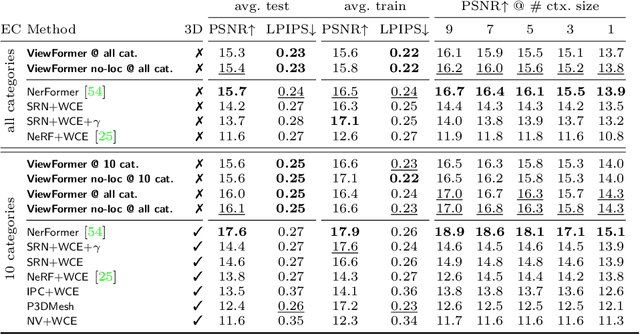
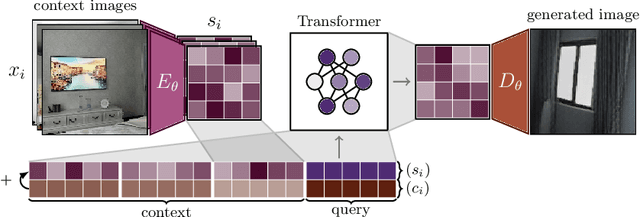
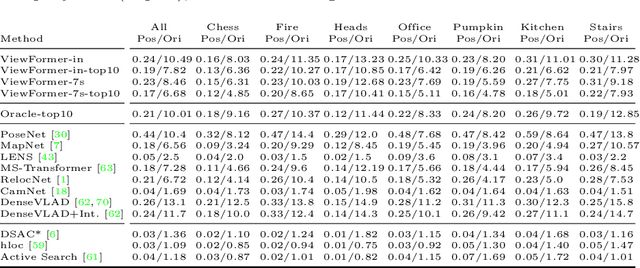
Abstract:Novel view synthesis is a long-standing problem. In this work, we consider a variant of the problem where we are given only a few context views sparsely covering a scene or an object. The goal is to predict novel viewpoints in the scene, which requires learning priors. The current state of the art is based on Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs), and while achieving impressive results, the methods suffer from long training times as they require evaluating thousands of 3D point samples via a deep neural network for each image. We propose a 2D-only method that maps multiple context views and a query pose to a new image in a single pass of a neural network. Our model uses a two-stage architecture consisting of a codebook and a transformer model. The codebook is used to embed individual images into a smaller latent space, and the transformer solves the view synthesis task in this more compact space. To train our model efficiently, we introduce a novel branching attention mechanism that allows us to use the same model not only for neural rendering but also for camera pose estimation. Experimental results on real-world scenes show that our approach is competitive compared to NeRF-based methods while not reasoning in 3D, and it is faster to train.
Visual Navigation in Real-World Indoor Environments Using End-to-End Deep Reinforcement Learning
Oct 21, 2020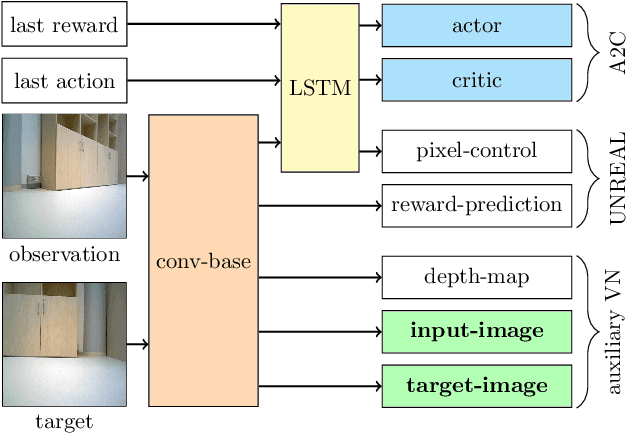
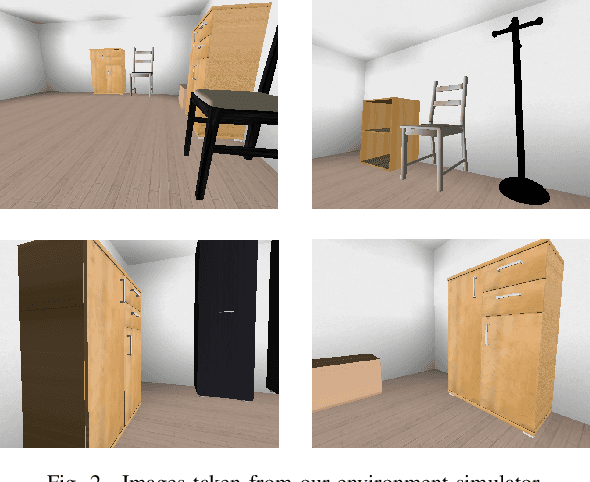

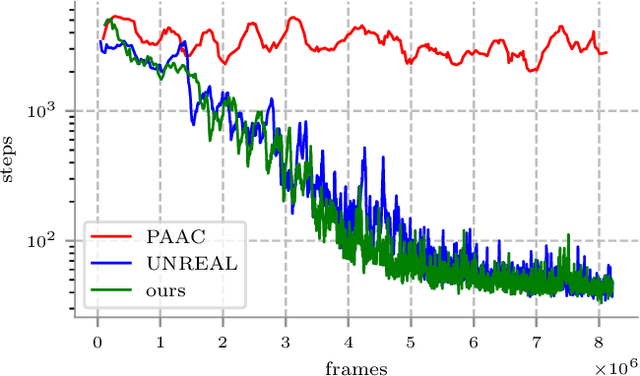
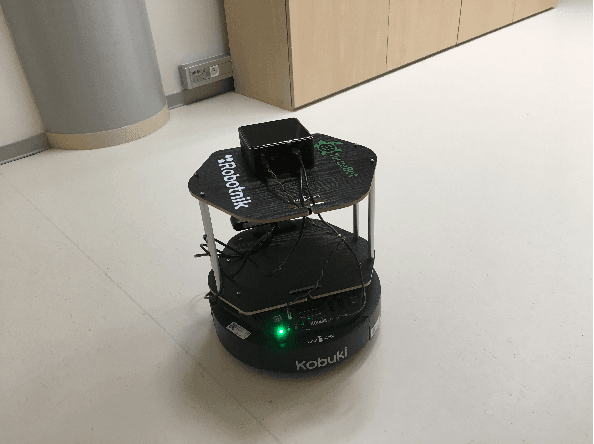
Abstract:Visual navigation is essential for many applications in robotics, from manipulation, through mobile robotics to automated driving. Deep reinforcement learning (DRL) provides an elegant map-free approach integrating image processing, localization, and planning in one module, which can be trained and therefore optimized for a given environment. However, to date, DRL-based visual navigation was validated exclusively in simulation, where the simulator provides information that is not available in the real world, e.g., the robot's position or image segmentation masks. This precludes the use of the learned policy on a real robot. Therefore, we propose a novel approach that enables a direct deployment of the trained policy on real robots. We have designed visual auxiliary tasks, a tailored reward scheme, and a new powerful simulator to facilitate domain randomization. The policy is fine-tuned on images collected from real-world environments. We have evaluated the method on a mobile robot in a real office environment. The training took ~30 hours on a single GPU. In 30 navigation experiments, the robot reached a 0.3-meter neighborhood of the goal in more than 86.7% of cases. This result makes the proposed method directly applicable to tasks like mobile manipulation.
Vision-based Navigation Using Deep Reinforcement Learning
Aug 08, 2019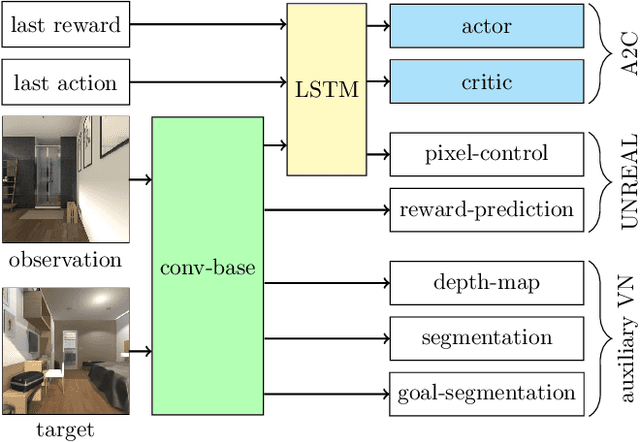
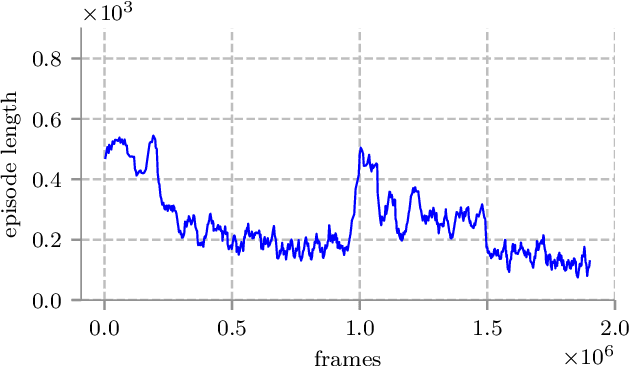
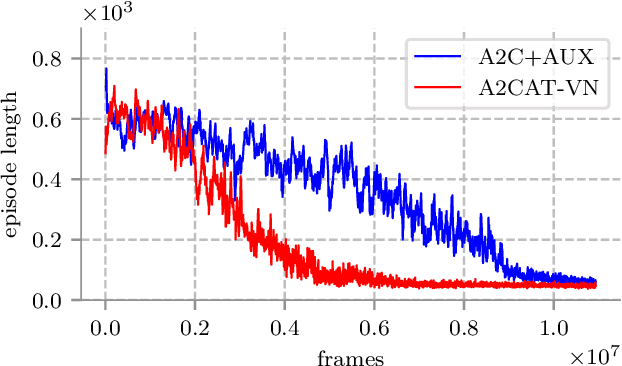
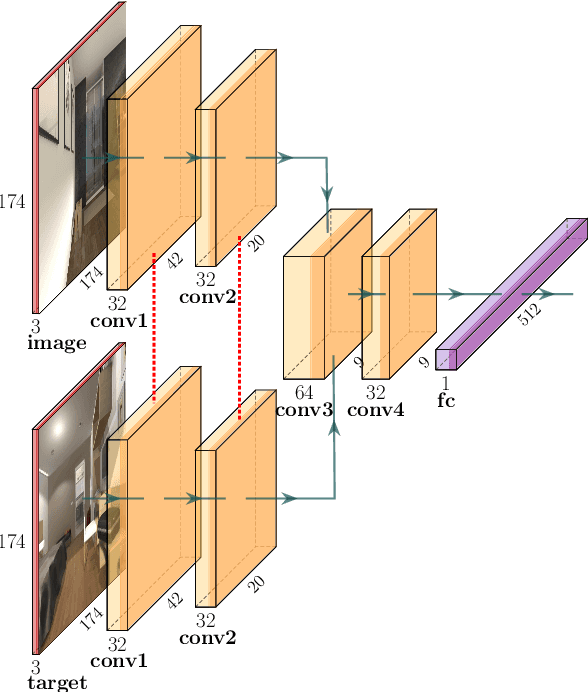
Abstract:Deep reinforcement learning (RL) has been successfully applied to a variety of game-like environments. However, the application of deep RL to visual navigation with realistic environments is a challenging task. We propose a novel learning architecture capable of navigating an agent, e.g. a mobile robot, to a target given by an image. To achieve this, we have extended the batched A2C algorithm with auxiliary tasks designed to improve visual navigation performance. We propose three additional auxiliary tasks: predicting the segmentation of the observation image and of the target image and predicting the depth-map. These tasks enable the use of supervised learning to pre-train a large part of the network and to reduce the number of training steps substantially. The training performance has been further improved by increasing the environment complexity gradually over time. An efficient neural network structure is proposed, which is capable of learning for multiple targets in multiple environments. Our method navigates in continuous state spaces and on the AI2-THOR environment simulator outperforms state-of-the-art goal-oriented visual navigation methods from the literature.
Symbolic Regression for Constructing Analytic Models in Reinforcement Learning
Mar 27, 2019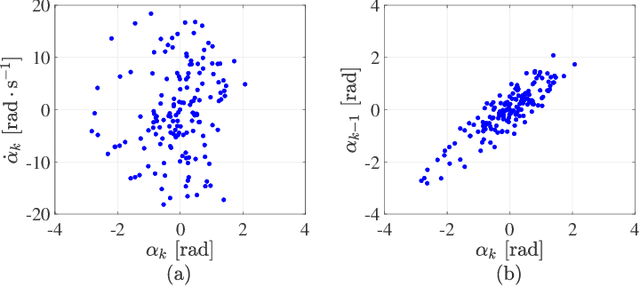
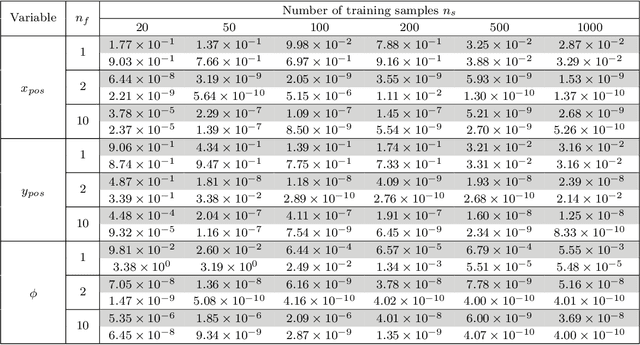
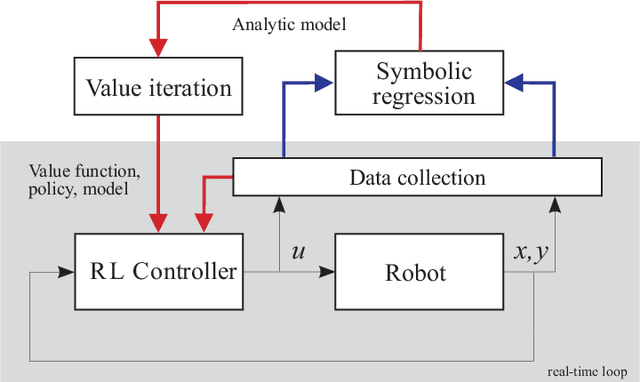
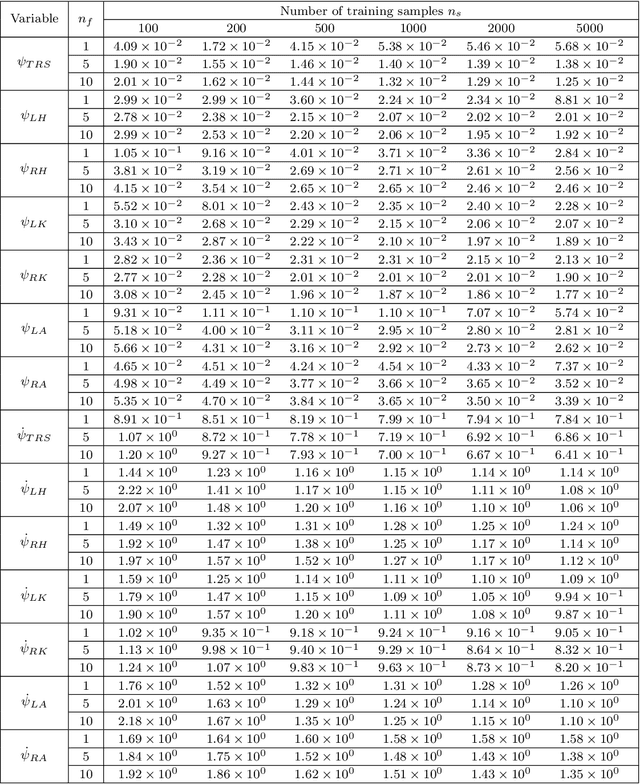
Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) is a widely used approach for controlling systems with unknown or time-varying dynamics. Even though RL does not require a model of the system, it is known to be faster and safer when using models learned online. We propose to employ symbolic regression (SR) to construct parsimonious process models described by analytic equations for real-time RL control. We have tested our method with two different state-of-the-art SR algorithms which automatically search for equations that fit the measured data. In addition to the standard problem formulation in the state-space domain, we show how the method can also be applied to input-output models of the NARX (nonlinear autoregressive with exogenous input) type. We present the approach on three simulated examples with up to 14-dimensional state space: an inverted pendulum, a mobile robot, and a biped walking robot. A comparison with deep neural networks and local linear regression shows that SR in most cases outperforms these commonly used alternative methods. We demonstrate on a real pendulum system that the analytic model found enables RL to successfully perform the swing-up task, based on a model constructed from only 100 data samples.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge