Ning Ye
Establishing Rigorous and Cost-effective Clinical Trials for Artificial Intelligence Models
Jul 11, 2024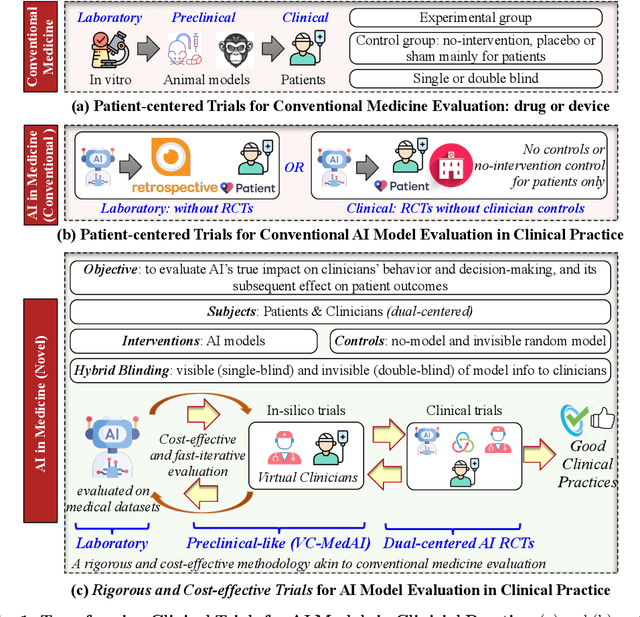
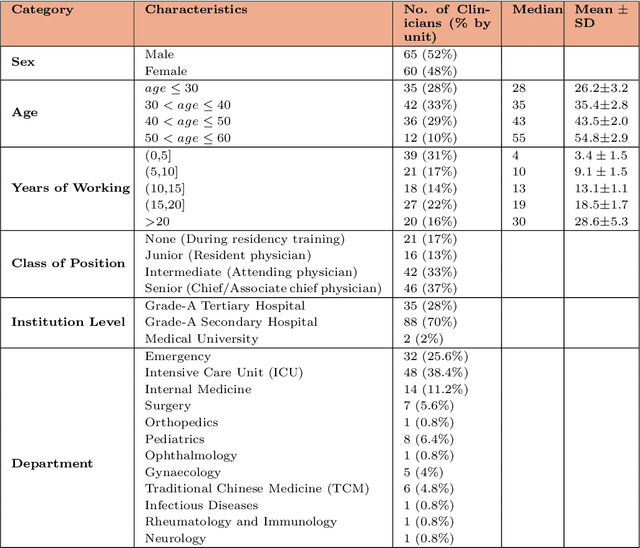
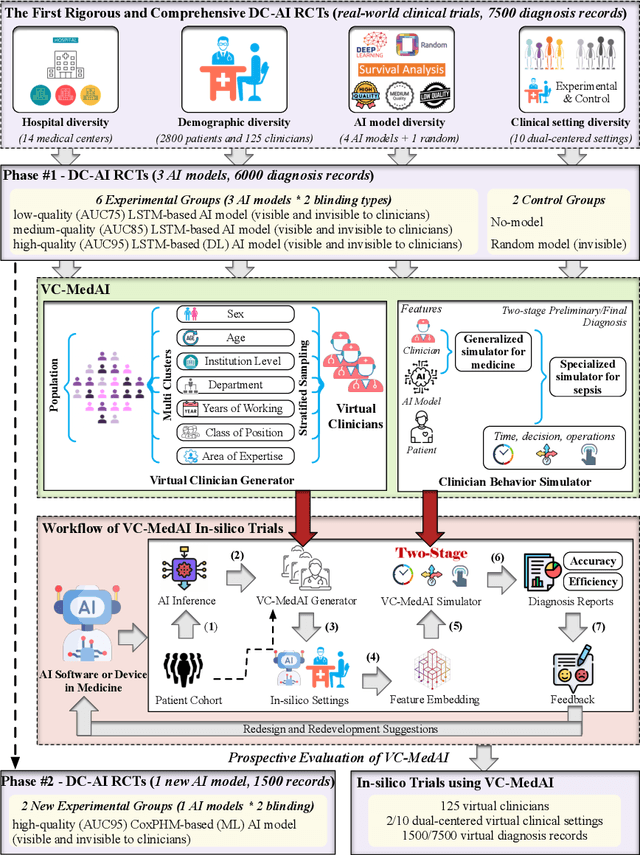
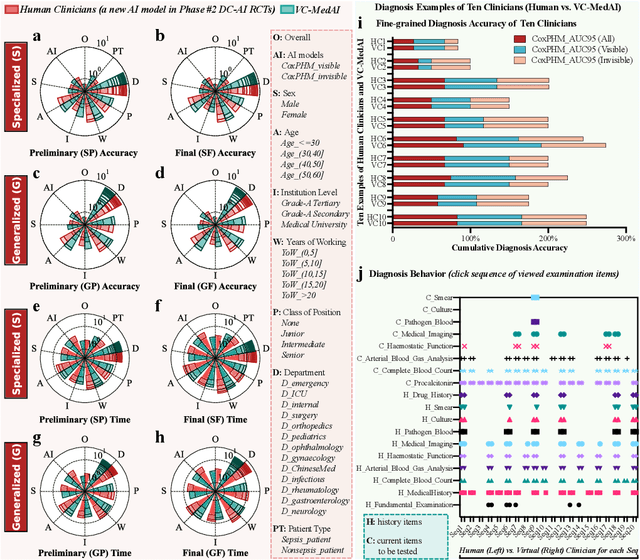
Abstract:A profound gap persists between artificial intelligence (AI) and clinical practice in medicine, primarily due to the lack of rigorous and cost-effective evaluation methodologies. State-of-the-art and state-of-the-practice AI model evaluations are limited to laboratory studies on medical datasets or direct clinical trials with no or solely patient-centered controls. Moreover, the crucial role of clinicians in collaborating with AI, pivotal for determining its impact on clinical practice, is often overlooked. For the first time, we emphasize the critical necessity for rigorous and cost-effective evaluation methodologies for AI models in clinical practice, featuring patient/clinician-centered (dual-centered) AI randomized controlled trials (DC-AI RCTs) and virtual clinician-based in-silico trials (VC-MedAI) as an effective proxy for DC-AI RCTs. Leveraging 7500 diagnosis records from two-phase inaugural DC-AI RCTs across 14 medical centers with 125 clinicians, our results demonstrate the necessity of DC-AI RCTs and the effectiveness of VC-MedAI. Notably, VC-MedAI performs comparably to human clinicians, replicating insights and conclusions from prospective DC-AI RCTs. We envision DC-AI RCTs and VC-MedAI as pivotal advancements, presenting innovative and transformative evaluation methodologies for AI models in clinical practice, offering a preclinical-like setting mirroring conventional medicine, and reshaping development paradigms in a cost-effective and fast-iterative manner. Chinese Clinical Trial Registration: ChiCTR2400086816.
Neural Topic Modeling with Deep Mutual Information Estimation
Mar 12, 2022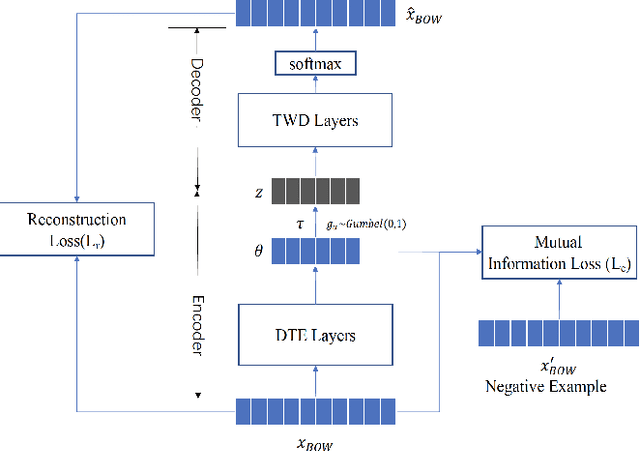

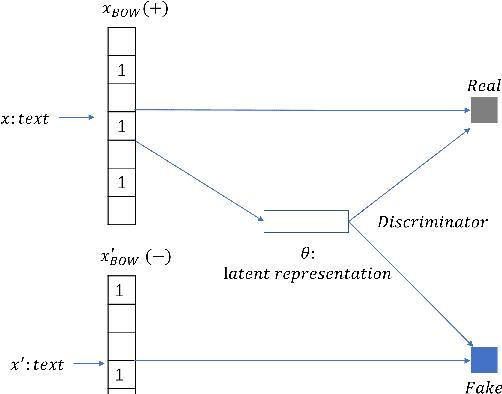

Abstract:The emerging neural topic models make topic modeling more easily adaptable and extendable in unsupervised text mining. However, the existing neural topic models is difficult to retain representative information of the documents within the learnt topic representation. In this paper, we propose a neural topic model which incorporates deep mutual information estimation, i.e., Neural Topic Modeling with Deep Mutual Information Estimation(NTM-DMIE). NTM-DMIE is a neural network method for topic learning which maximizes the mutual information between the input documents and their latent topic representation. To learn robust topic representation, we incorporate the discriminator to discriminate negative examples and positive examples via adversarial learning. Moreover, we use both global and local mutual information to preserve the rich information of the input documents in the topic representation. We evaluate NTM-DMIE on several metrics, including accuracy of text clustering, with topic representation, topic uniqueness and topic coherence. Compared to the existing methods, the experimental results show that NTM-DMIE can outperform in all the metrics on the four datasets.
A general framework for adaptive two-index fusion attribute weighted naive Bayes
Feb 24, 2022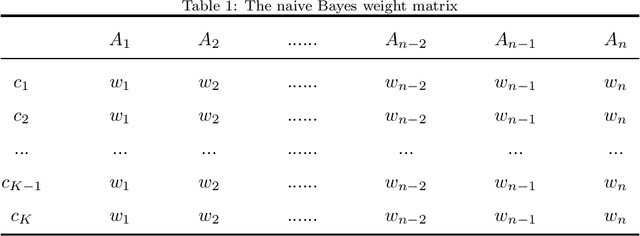
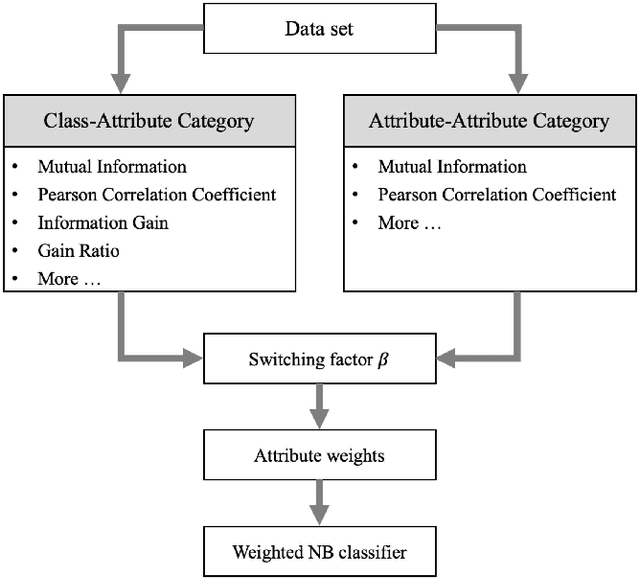
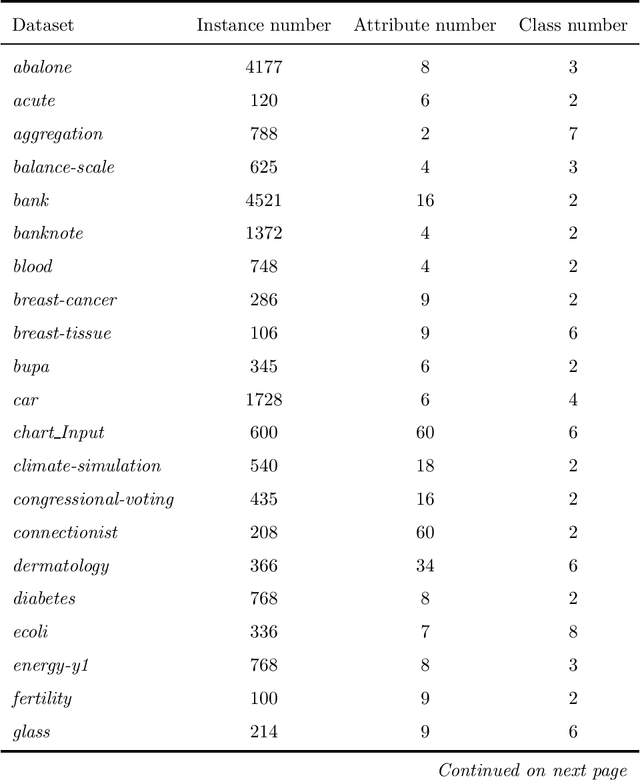
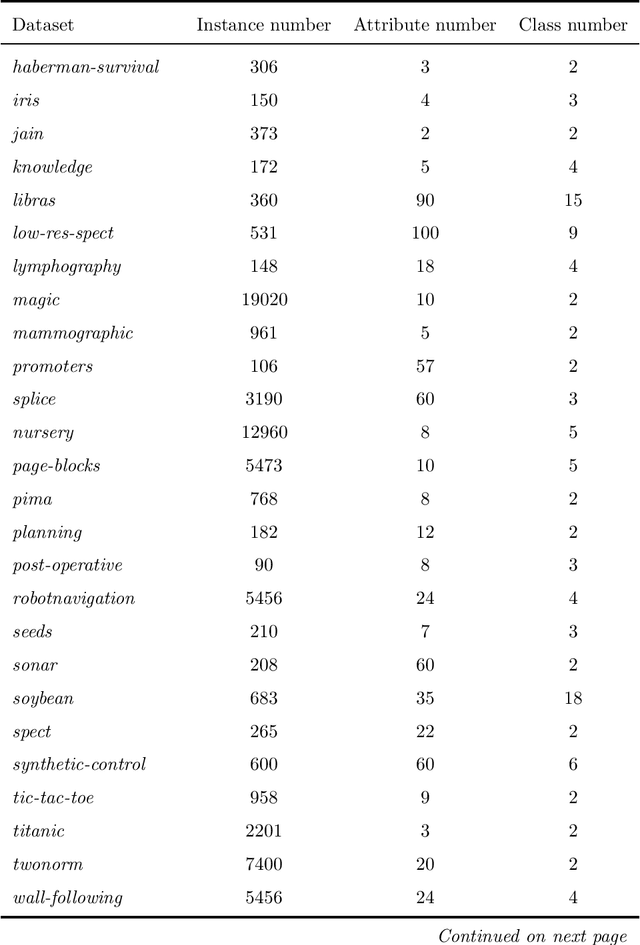
Abstract:Naive Bayes(NB) is one of the essential algorithms in data mining. However, it is rarely used in reality because of the attribute independent assumption. Researchers have proposed many improved NB methods to alleviate this assumption. Among these methods, due to high efficiency and easy implementation, the filter attribute weighted NB methods receive great attentions. However, there still exists several challenges, such as the poor representation ability for single index and the fusion problem of two indexes. To overcome above challenges, we propose a general framework for Adaptive Two-index Fusion attribute weighted NB(ATFNB). Two types of data description category are used to represent the correlation between classes and attributes, intercorrelation between attributes and attributes, respectively. ATFNB can select any one index from each category. Then, we introduce a switching factor \{beta} to fuse two indexes, which can adaptively adjust the optimal ratio of the two index on various datasets. And a quick algorithm is proposed to infer the optimal interval of switching factor \{beta}. Finally, the weight of each attribute is calculated using the optimal value \{beta} and is integrated into NB classifier to improve the accuracy. The experimental results on 50 benchmark datasets and a Flavia dataset show that ATFNB outperforms the basic NB and state-of-the-art filter weighted NB models. In addition, the ATFNB framework can improve the existing two-index NB model by introducing the adaptive switching factor \{beta}. Auxiliary experimental results demonstrate the improved model significantly increases the accuracy compared to the original model without the adaptive switching factor \{beta}.
Robust Multi-Modal Policies for Industrial Assembly via Reinforcement Learning and Demonstrations: A Large-Scale Study
Mar 23, 2021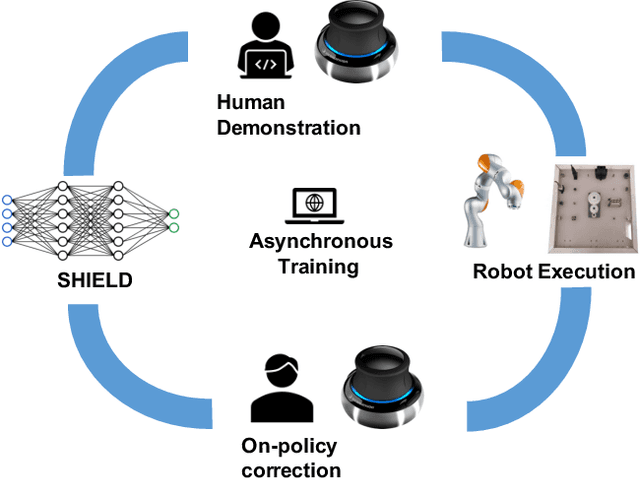
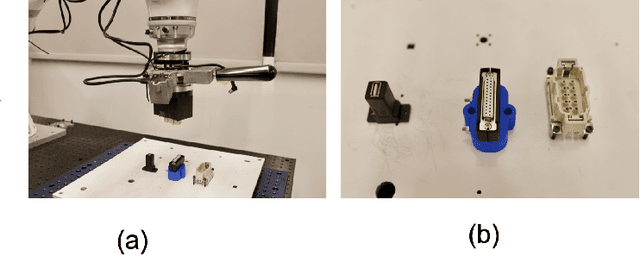

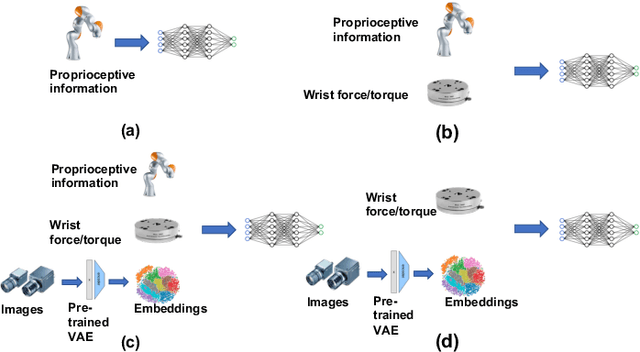
Abstract:Over the past several years there has been a considerable research investment into learning-based approaches to industrial assembly, but despite significant progress these techniques have yet to be adopted by industry. We argue that it is the prohibitively large design space for Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL), rather than algorithmic limitations per se, that are truly responsible for this lack of adoption. Pushing these techniques into the industrial mainstream requires an industry-oriented paradigm which differs significantly from the academic mindset. In this paper we define criteria for industry-oriented DRL, and perform a thorough comparison according to these criteria of one family of learning approaches, DRL from demonstration, against a professional industrial integrator on the recently established NIST assembly benchmark. We explain the design choices, representing several years of investigation, which enabled our DRL system to consistently outperform the integrator baseline in terms of both speed and reliability. Finally, we conclude with a competition between our DRL system and a human on a challenge task of insertion into a randomly moving target. This study suggests that DRL is capable of outperforming not only established engineered approaches, but the human motor system as well, and that there remains significant room for improvement. Videos can be found on our project website: https://sites.google.com/view/shield-nist.
Improved Image Captioning via Policy Gradient optimization of SPIDEr
Mar 12, 2018



Abstract:Current image captioning methods are usually trained via (penalized) maximum likelihood estimation. However, the log-likelihood score of a caption does not correlate well with human assessments of quality. Standard syntactic evaluation metrics, such as BLEU, METEOR and ROUGE, are also not well correlated. The newer SPICE and CIDEr metrics are better correlated, but have traditionally been hard to optimize for. In this paper, we show how to use a policy gradient (PG) method to directly optimize a linear combination of SPICE and CIDEr (a combination we call SPIDEr): the SPICE score ensures our captions are semantically faithful to the image, while CIDEr score ensures our captions are syntactically fluent. The PG method we propose improves on the prior MIXER approach, by using Monte Carlo rollouts instead of mixing MLE training with PG. We show empirically that our algorithm leads to easier optimization and improved results compared to MIXER. Finally, we show that using our PG method we can optimize any of the metrics, including the proposed SPIDEr metric which results in image captions that are strongly preferred by human raters compared to captions generated by the same model but trained to optimize MLE or the COCO metrics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge