Zhenhai Zhu
Wavelet-Based Image Tokenizer for Vision Transformers
May 28, 2024

Abstract:Non-overlapping patch-wise convolution is the default image tokenizer for all state-of-the-art vision Transformer (ViT) models. Even though many ViT variants have been proposed to improve its efficiency and accuracy, little research on improving the image tokenizer itself has been reported in the literature. In this paper, we propose a new image tokenizer based on wavelet transformation. We show that ViT models with the new tokenizer achieve both higher training throughput and better top-1 precision for the ImageNet validation set. We present a theoretical analysis on why the proposed tokenizer improves the training throughput without any change to ViT model architecture. Our analysis suggests that the new tokenizer can effectively handle high-resolution images and is naturally resistant to adversarial attack. Furthermore, the proposed image tokenizer offers a fresh perspective on important new research directions for ViT-based model design, such as image tokens on a non-uniform grid for image understanding.
H-Transformer-1D: Fast One-Dimensional Hierarchical Attention for Sequences
Jul 25, 2021



Abstract:We describe an efficient hierarchical method to compute attention in the Transformer architecture. The proposed attention mechanism exploits a matrix structure similar to the Hierarchical Matrix (H-Matrix) developed by the numerical analysis community, and has linear run time and memory complexity. We perform extensive experiments to show that the inductive bias embodied by our hierarchical attention is effective in capturing the hierarchical structure in the sequences typical for natural language and vision tasks. Our method is superior to alternative sub-quadratic proposals by over +6 points on average on the Long Range Arena benchmark. It also sets a new SOTA test perplexity on One-Billion Word dataset with 5x fewer model parameters than that of the previous-best Transformer-based models.
Beyond Instructional Videos: Probing for More Diverse Visual-Textual Grounding on YouTube
Apr 29, 2020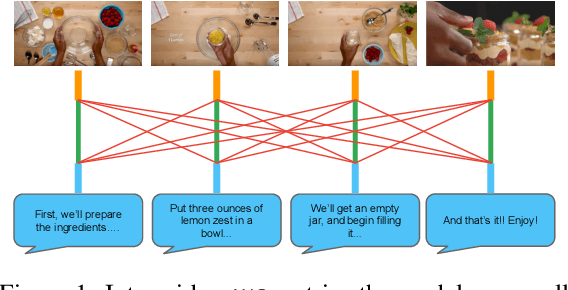
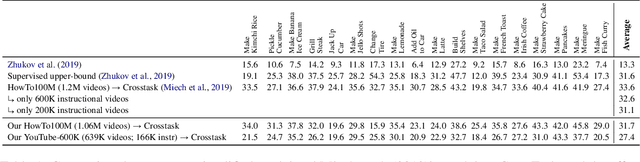
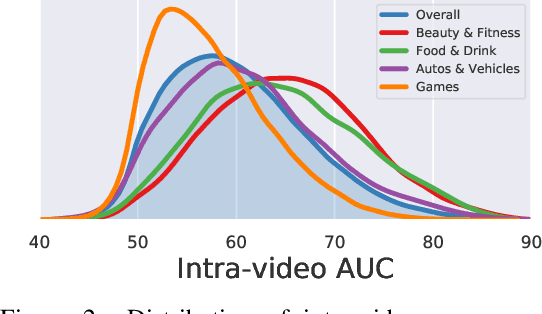
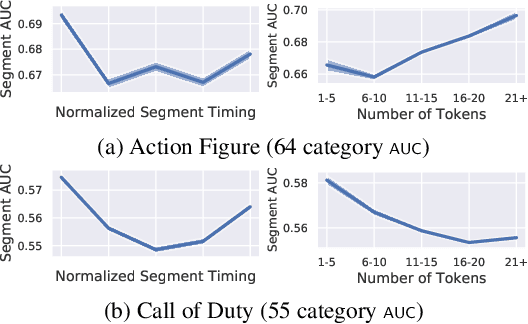
Abstract:Pretraining from unlabelled web videos has quickly become the de-facto means of achieving high performance on many video understanding tasks. Features are learned via prediction of grounded relationships between visual content and automatic speech recognition (ASR) tokens. However, prior pretraining work has been limited to only instructional videos, a domain that, a priori, we expect to be relatively "easy:" speakers in instructional videos will often reference the literal objects/actions being depicted. Because instructional videos make up only a fraction of the web's diverse video content, we ask: can similar models be trained on broader corpora? And, if so, what types of videos are "grounded" and what types are not? We examine the diverse YouTube8M corpus, first verifying that it contains many non-instructional videos via crowd labeling. We pretrain a representative model on YouTube8M and study its success and failure cases. We find that visual-textual grounding is indeed possible across previously unexplored video categories, and that pretraining on a more diverse set still results in representations that generalize to both non-instructional and instructional domains.
A Case Study on Combining ASR and Visual Features for Generating Instructional Video Captions
Oct 07, 2019



Abstract:Instructional videos get high-traffic on video sharing platforms, and prior work suggests that providing time-stamped, subtask annotations (e.g., "heat the oil in the pan") improves user experiences. However, current automatic annotation methods based on visual features alone perform only slightly better than constant prediction. Taking cues from prior work, we show that we can improve performance significantly by considering automatic speech recognition (ASR) tokens as input. Furthermore, jointly modeling ASR tokens and visual features results in higher performance compared to training individually on either modality. We find that unstated background information is better explained by visual features, whereas fine-grained distinctions (e.g., "add oil" vs. "add olive oil") are disambiguated more easily via ASR tokens.
Improved Image Captioning via Policy Gradient optimization of SPIDEr
Mar 12, 2018



Abstract:Current image captioning methods are usually trained via (penalized) maximum likelihood estimation. However, the log-likelihood score of a caption does not correlate well with human assessments of quality. Standard syntactic evaluation metrics, such as BLEU, METEOR and ROUGE, are also not well correlated. The newer SPICE and CIDEr metrics are better correlated, but have traditionally been hard to optimize for. In this paper, we show how to use a policy gradient (PG) method to directly optimize a linear combination of SPICE and CIDEr (a combination we call SPIDEr): the SPICE score ensures our captions are semantically faithful to the image, while CIDEr score ensures our captions are syntactically fluent. The PG method we propose improves on the prior MIXER approach, by using Monte Carlo rollouts instead of mixing MLE training with PG. We show empirically that our algorithm leads to easier optimization and improved results compared to MIXER. Finally, we show that using our PG method we can optimize any of the metrics, including the proposed SPIDEr metric which results in image captions that are strongly preferred by human raters compared to captions generated by the same model but trained to optimize MLE or the COCO metrics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge