Najmul Hassan
Hybrid CNN-BYOL Approach for Fault Detection in Induction Motors Using Thermal Images
Oct 09, 2025Abstract:Induction motors (IMs) are indispensable in industrial and daily life, but they are susceptible to various faults that can lead to overheating, wasted energy consumption, and service failure. Early detection of faults is essential to protect the motor and prolong its lifespan. This paper presents a hybrid method that integrates BYOL with CNNs for classifying thermal images of induction motors for fault detection. The thermal dataset used in this work includes different operating states of the motor, such as normal operation, overload, and faults. We employed multiple deep learning (DL) models for the BYOL technique, ranging from popular architectures such as ResNet-50, DenseNet-121, DenseNet-169, EfficientNetB0, VGG16, and MobileNetV2. Additionally, we introduced a new high-performance yet lightweight CNN model named BYOL-IMNet, which comprises four custom-designed blocks tailored for fault classification in thermal images. Our experimental results demonstrate that the proposed BYOL-IMNet achieves 99.89\% test accuracy and an inference time of 5.7 ms per image, outperforming state-of-the-art models. This study highlights the promising performance of the CNN-BYOL hybrid method in enhancing accuracy for detecting faults in induction motors, offering a robust methodology for online monitoring in industrial settings.
Multimodal Attention-Enhanced Feature Fusion-based Weekly Supervised Anomaly Violence Detection
Sep 17, 2024Abstract:Weakly supervised video anomaly detection (WS-VAD) is a crucial area in computer vision for developing intelligent surveillance systems. This system uses three feature streams: RGB video, optical flow, and audio signals, where each stream extracts complementary spatial and temporal features using an enhanced attention module to improve detection accuracy and robustness. In the first stream, we employed an attention-based, multi-stage feature enhancement approach to improve spatial and temporal features from the RGB video where the first stage consists of a ViT-based CLIP module, with top-k features concatenated in parallel with I3D and Temporal Contextual Aggregation (TCA) based rich spatiotemporal features. The second stage effectively captures temporal dependencies using the Uncertainty-Regulated Dual Memory Units (UR-DMU) model, which learns representations of normal and abnormal data simultaneously, and the third stage is employed to select the most relevant spatiotemporal features. The second stream extracted enhanced attention-based spatiotemporal features from the flow data modality-based feature by taking advantage of the integration of the deep learning and attention module. The audio stream captures auditory cues using an attention module integrated with the VGGish model, aiming to detect anomalies based on sound patterns. These streams enrich the model by incorporating motion and audio signals often indicative of abnormal events undetectable through visual analysis alone. The concatenation of the multimodal fusion leverages the strengths of each modality, resulting in a comprehensive feature set that significantly improves anomaly detection accuracy and robustness across three datasets. The extensive experiment and high performance with the three benchmark datasets proved the effectiveness of the proposed system over the existing state-of-the-art system.
A Comprehensive Methodological Survey of Human Activity Recognition Across Divers Data Modalities
Sep 15, 2024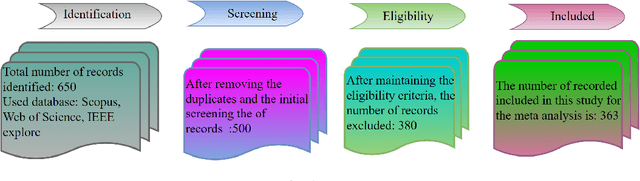
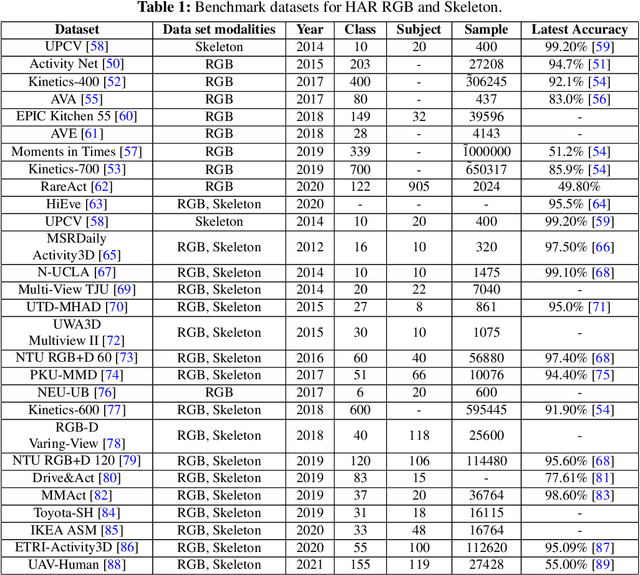
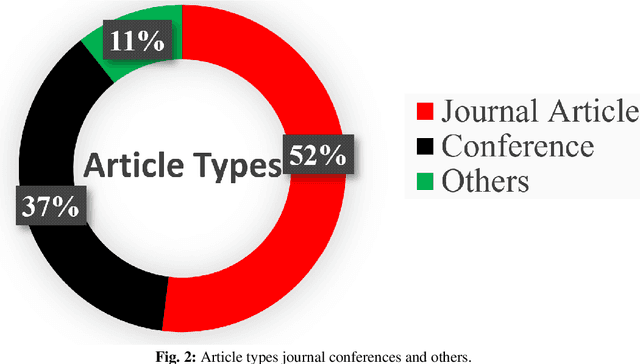
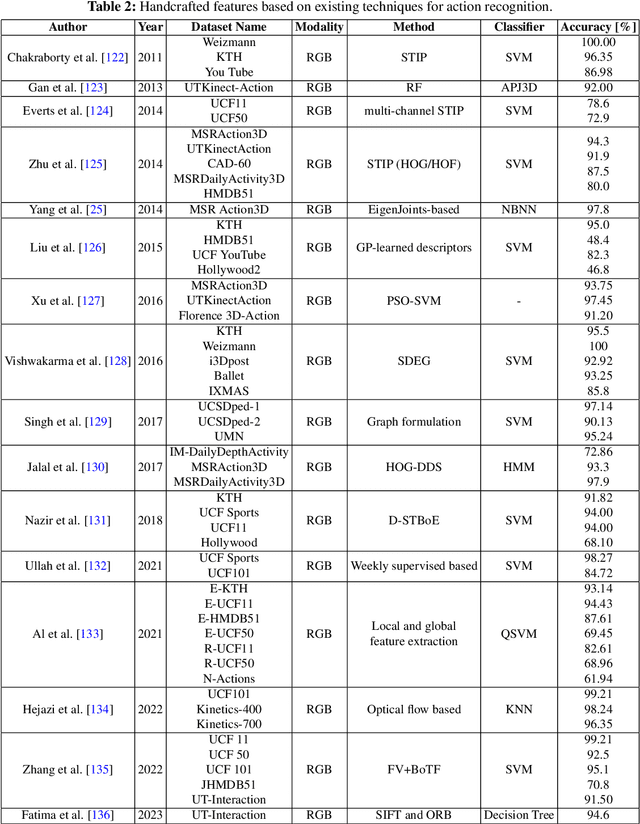
Abstract:Human Activity Recognition (HAR) systems aim to understand human behaviour and assign a label to each action, attracting significant attention in computer vision due to their wide range of applications. HAR can leverage various data modalities, such as RGB images and video, skeleton, depth, infrared, point cloud, event stream, audio, acceleration, and radar signals. Each modality provides unique and complementary information suited to different application scenarios. Consequently, numerous studies have investigated diverse approaches for HAR using these modalities. This paper presents a comprehensive survey of the latest advancements in HAR from 2014 to 2024, focusing on machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) approaches categorized by input data modalities. We review both single-modality and multi-modality techniques, highlighting fusion-based and co-learning frameworks. Additionally, we cover advancements in hand-crafted action features, methods for recognizing human-object interactions, and activity detection. Our survey includes a detailed dataset description for each modality and a summary of the latest HAR systems, offering comparative results on benchmark datasets. Finally, we provide insightful observations and propose effective future research directions in HAR.
EMG-Based Hand Gesture Recognition through Diverse Domain Feature Enhancement and Machine Learning-Based Approach
Aug 25, 2024
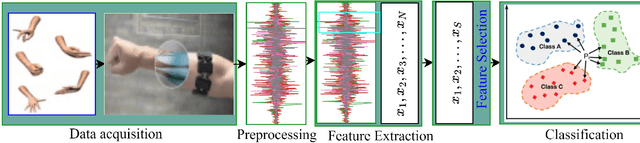
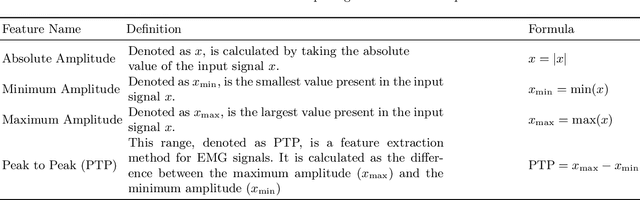
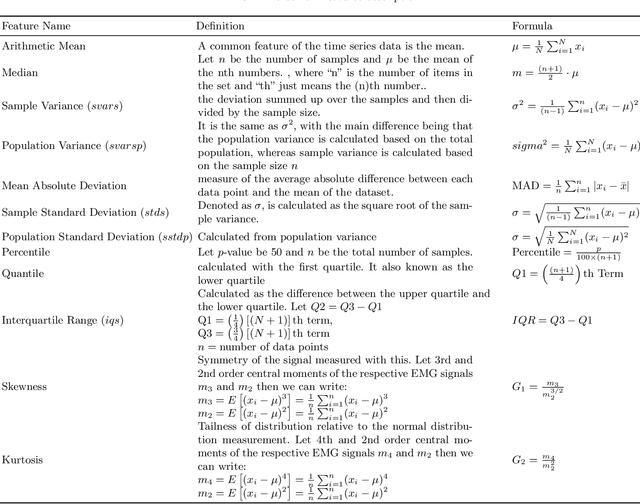
Abstract:Surface electromyography (EMG) serves as a pivotal tool in hand gesture recognition and human-computer interaction, offering a non-invasive means of signal acquisition. This study presents a novel methodology for classifying hand gestures using EMG signals. To address the challenges associated with feature extraction where, we explored 23 distinct morphological, time domain and frequency domain feature extraction techniques. However, the substantial size of the features may increase the computational complexity issues that can hinder machine learning algorithm performance. We employ an efficient feature selection approach, specifically an extra tree classifier, to mitigate this. The selected potential feature fed into the various machine learning-based classification algorithms where our model achieved 97.43\% accuracy with the KNN algorithm and selected feature. By leveraging a comprehensive feature extraction and selection strategy, our methodology enhances the accuracy and usability of EMG-based hand gesture recognition systems. The higher performance accuracy proves the effectiveness of the proposed model over the existing system. \keywords{EMG signal, machine learning approach, hand gesture recognition.
FarSight: A Physics-Driven Whole-Body Biometric System at Large Distance and Altitude
Jun 29, 2023



Abstract:Whole-body biometric recognition is an important area of research due to its vast applications in law enforcement, border security, and surveillance. This paper presents the end-to-end design, development and evaluation of FarSight, an innovative software system designed for whole-body (fusion of face, gait and body shape) biometric recognition. FarSight accepts videos from elevated platforms and drones as input and outputs a candidate list of identities from a gallery. The system is designed to address several challenges, including (i) low-quality imagery, (ii) large yaw and pitch angles, (iii) robust feature extraction to accommodate large intra-person variabilities and large inter-person similarities, and (iv) the large domain gap between training and test sets. FarSight combines the physics of imaging and deep learning models to enhance image restoration and biometric feature encoding. We test FarSight's effectiveness using the newly acquired IARPA Biometric Recognition and Identification at Altitude and Range (BRIAR) dataset. Notably, FarSight demonstrated a substantial performance increase on the BRIAR dataset, with gains of +11.82% Rank-20 identification and +11.3% TAR@1% FAR.
Point-to-Box Network for Accurate Object Detection via Single Point Supervision
Jul 14, 2022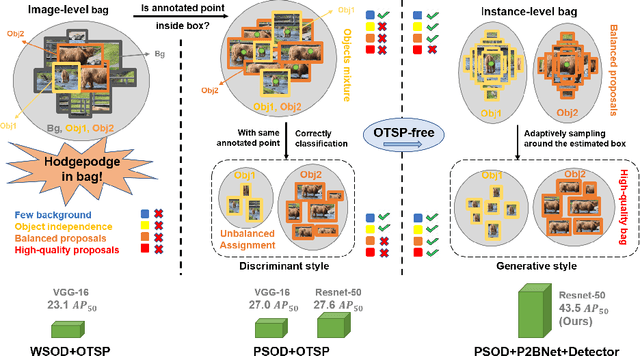
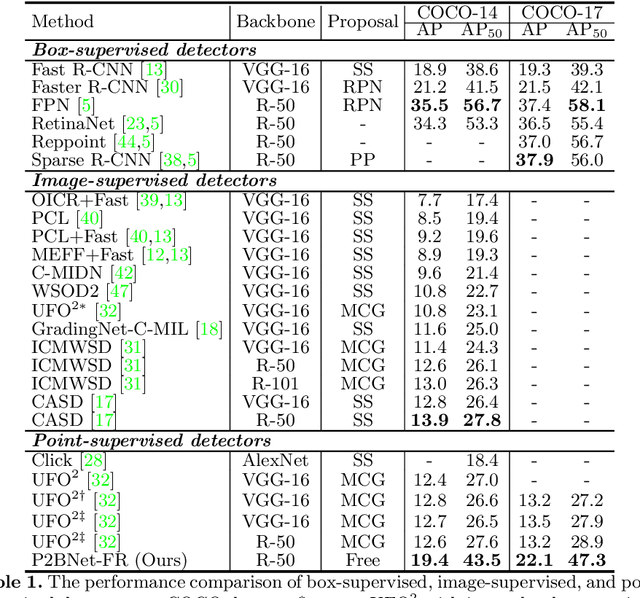
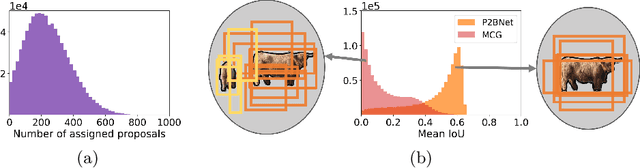
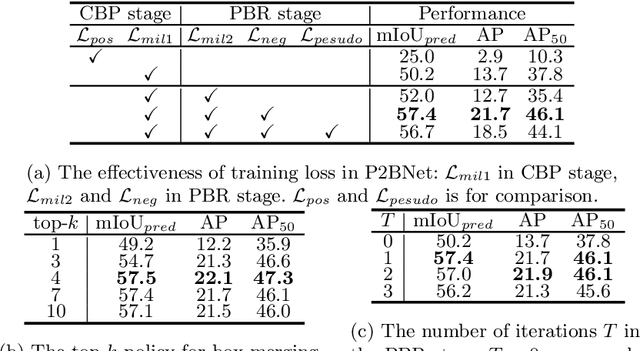
Abstract:Object detection using single point supervision has received increasing attention over the years. In this paper, we attribute such a large performance gap to the failure of generating high-quality proposal bags which are crucial for multiple instance learning (MIL). To address this problem, we introduce a lightweight alternative to the off-the-shelf proposal (OTSP) method and thereby create the Point-to-Box Network (P2BNet), which can construct an inter-objects balanced proposal bag by generating proposals in an anchor-like way. By fully investigating the accurate position information, P2BNet further constructs an instance-level bag, avoiding the mixture of multiple objects. Finally, a coarse-to-fine policy in a cascade fashion is utilized to improve the IoU between proposals and ground-truth (GT). Benefiting from these strategies, P2BNet is able to produce high-quality instance-level bags for object detection. P2BNet improves the mean average precision (AP) by more than 50% relative to the previous best PSOD method on the MS COCO dataset. It also demonstrates the great potential to bridge the performance gap between point supervised and bounding-box supervised detectors. The code will be released at github.com/ucas-vg/P2BNet.
Object Localization under Single Coarse Point Supervision
Mar 17, 2022



Abstract:Point-based object localization (POL), which pursues high-performance object sensing under low-cost data annotation, has attracted increased attention. However, the point annotation mode inevitably introduces semantic variance for the inconsistency of annotated points. Existing POL methods heavily reply on accurate key-point annotations which are difficult to define. In this study, we propose a POL method using coarse point annotations, relaxing the supervision signals from accurate key points to freely spotted points. To this end, we propose a coarse point refinement (CPR) approach, which to our best knowledge is the first attempt to alleviate semantic variance from the perspective of algorithm. CPR constructs point bags, selects semantic-correlated points, and produces semantic center points through multiple instance learning (MIL). In this way, CPR defines a weakly supervised evolution procedure, which ensures training high-performance object localizer under coarse point supervision. Experimental results on COCO, DOTA and our proposed SeaPerson dataset validate the effectiveness of the CPR approach. The dataset and code will be available at https://github.com/ucas-vg/PointTinyBenchmark/.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge