Muhammed Shuaibi
Open Materials 2024 (OMat24) Inorganic Materials Dataset and Models
Oct 16, 2024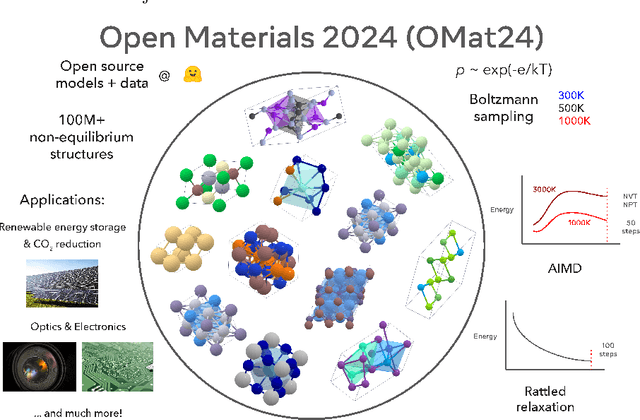
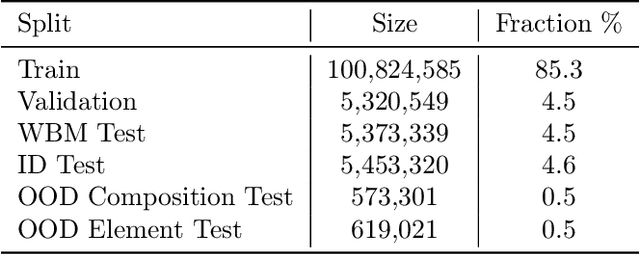
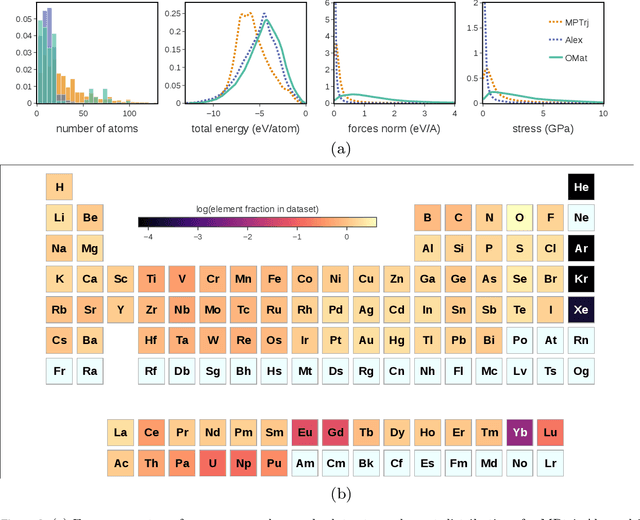
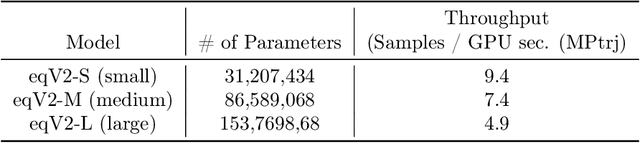
Abstract:The ability to discover new materials with desirable properties is critical for numerous applications from helping mitigate climate change to advances in next generation computing hardware. AI has the potential to accelerate materials discovery and design by more effectively exploring the chemical space compared to other computational methods or by trial-and-error. While substantial progress has been made on AI for materials data, benchmarks, and models, a barrier that has emerged is the lack of publicly available training data and open pre-trained models. To address this, we present a Meta FAIR release of the Open Materials 2024 (OMat24) large-scale open dataset and an accompanying set of pre-trained models. OMat24 contains over 110 million density functional theory (DFT) calculations focused on structural and compositional diversity. Our EquiformerV2 models achieve state-of-the-art performance on the Matbench Discovery leaderboard and are capable of predicting ground-state stability and formation energies to an F1 score above 0.9 and an accuracy of 20 meV/atom, respectively. We explore the impact of model size, auxiliary denoising objectives, and fine-tuning on performance across a range of datasets including OMat24, MPtraj, and Alexandria. The open release of the OMat24 dataset and models enables the research community to build upon our efforts and drive further advancements in AI-assisted materials science.
AdsorbML: Accelerating Adsorption Energy Calculations with Machine Learning
Nov 29, 2022Abstract:Computational catalysis is playing an increasingly significant role in the design of catalysts across a wide range of applications. A common task for many computational methods is the need to accurately compute the minimum binding energy - the adsorption energy - for an adsorbate and a catalyst surface of interest. Traditionally, the identification of low energy adsorbate-surface configurations relies on heuristic methods and researcher intuition. As the desire to perform high-throughput screening increases, it becomes challenging to use heuristics and intuition alone. In this paper, we demonstrate machine learning potentials can be leveraged to identify low energy adsorbate-surface configurations more accurately and efficiently. Our algorithm provides a spectrum of trade-offs between accuracy and efficiency, with one balanced option finding the lowest energy configuration, within a 0.1 eV threshold, 86.63% of the time, while achieving a 1387x speedup in computation. To standardize benchmarking, we introduce the Open Catalyst Dense dataset containing nearly 1,000 diverse surfaces and 87,045 unique configurations.
Spherical Channels for Modeling Atomic Interactions
Jun 29, 2022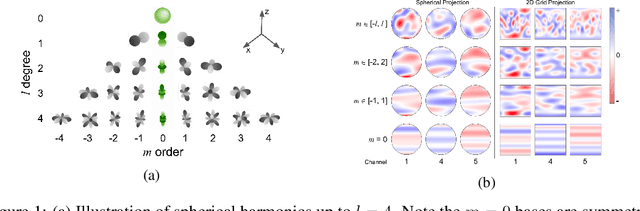
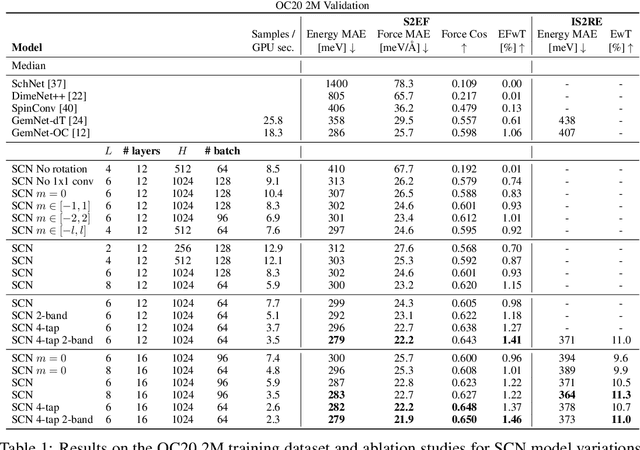
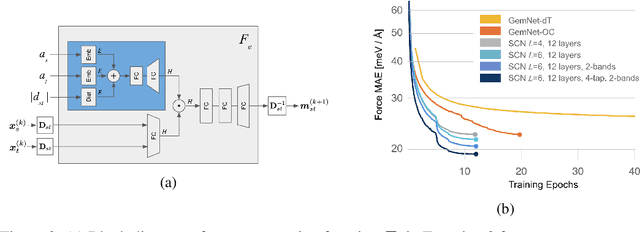
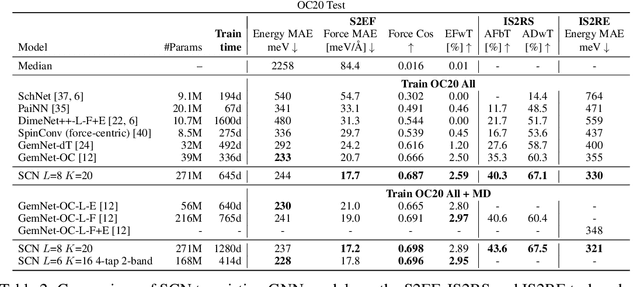
Abstract:Modeling the energy and forces of atomic systems is a fundamental problem in computational chemistry with the potential to help address many of the world's most pressing problems, including those related to energy scarcity and climate change. These calculations are traditionally performed using Density Functional Theory, which is computationally very expensive. Machine learning has the potential to dramatically improve the efficiency of these calculations from days or hours to seconds. We propose the Spherical Channel Network (SCN) to model atomic energies and forces. The SCN is a graph neural network where nodes represent atoms and edges their neighboring atoms. The atom embeddings are a set of spherical functions, called spherical channels, represented using spherical harmonics. We demonstrate, that by rotating the embeddings based on the 3D edge orientation, more information may be utilized while maintaining the rotational equivariance of the messages. While equivariance is a desirable property, we find that by relaxing this constraint in both message passing and aggregation, improved accuracy may be achieved. We demonstrate state-of-the-art results on the large-scale Open Catalyst 2020 dataset in both energy and force prediction for numerous tasks and metrics.
The Open Catalyst 2022 Dataset and Challenges for Oxide Electrocatalysis
Jun 17, 2022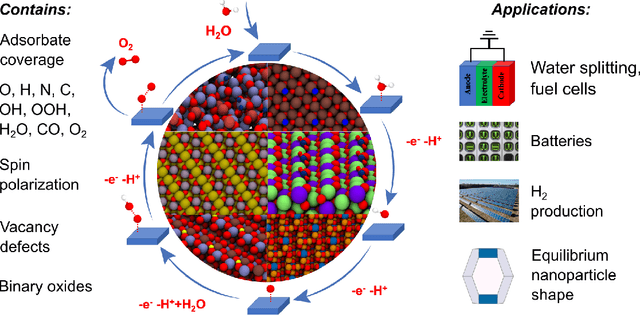
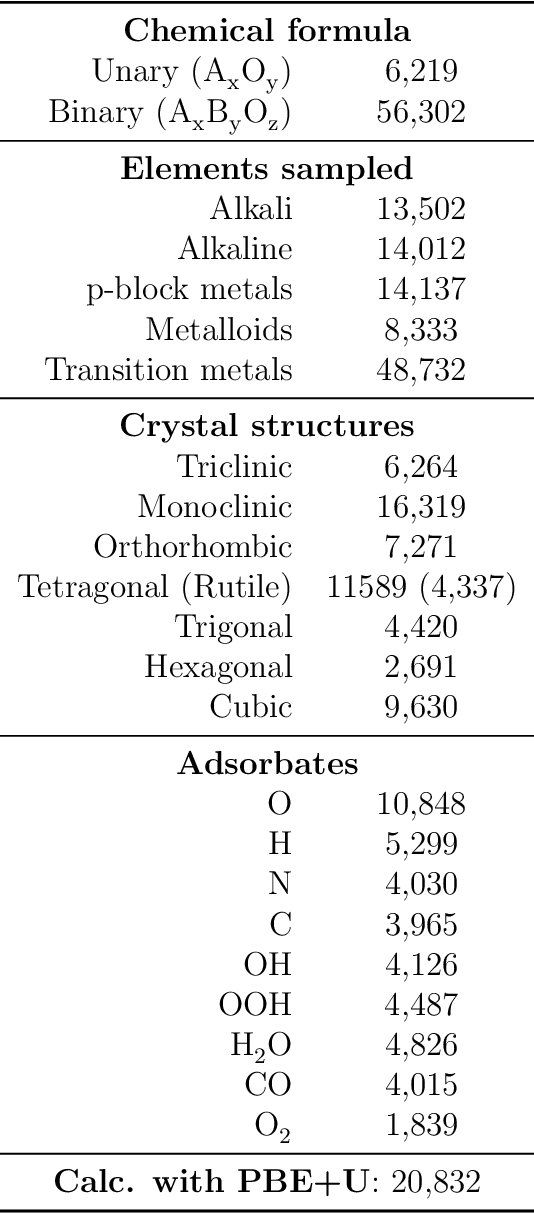
Abstract:Computational catalysis and machine learning communities have made considerable progress in developing machine learning models for catalyst discovery and design. Yet, a general machine learning potential that spans the chemical space of catalysis is still out of reach. A significant hurdle is obtaining access to training data across a wide range of materials. One important class of materials where data is lacking are oxides, which inhibits models from studying the Oxygen Evolution Reaction and oxide electrocatalysis more generally. To address this we developed the Open Catalyst 2022(OC22) dataset, consisting of 62,521 Density Functional Theory (DFT) relaxations (~9,884,504 single point calculations) across a range of oxide materials, coverages, and adsorbates (*H, *O, *N, *C, *OOH, *OH, *OH2, *O2, *CO). We define generalized tasks to predict the total system energy that are applicable across catalysis, develop baseline performance of several graph neural networks (SchNet, DimeNet++, ForceNet, SpinConv, PaiNN, GemNet-dT, GemNet-OC), and provide pre-defined dataset splits to establish clear benchmarks for future efforts. For all tasks, we study whether combining datasets leads to better results, even if they contain different materials or adsorbates. Specifically, we jointly train models on Open Catalyst 2020 (OC20) Dataset and OC22, or fine-tune pretrained OC20 models on OC22. In the most general task, GemNet-OC sees a ~32% improvement in energy predictions through fine-tuning and a ~9% improvement in force predictions via joint training. Surprisingly, joint training on both the OC20 and much smaller OC22 datasets also improves total energy predictions on OC20 by ~19%. The dataset and baseline models are open sourced, and a public leaderboard will follow to encourage continued community developments on the total energy tasks and data.
How Do Graph Networks Generalize to Large and Diverse Molecular Systems?
Apr 06, 2022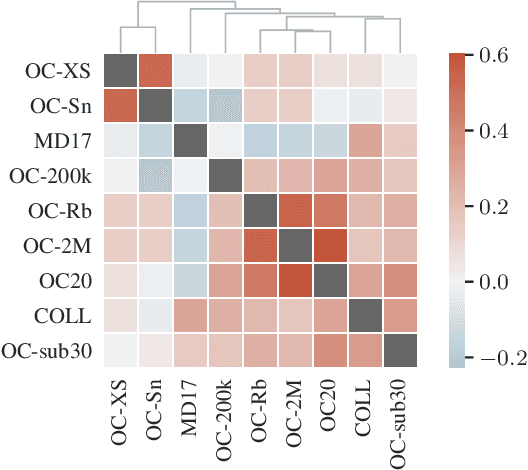
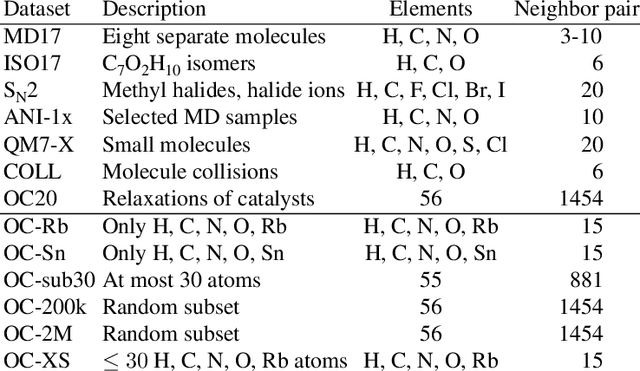
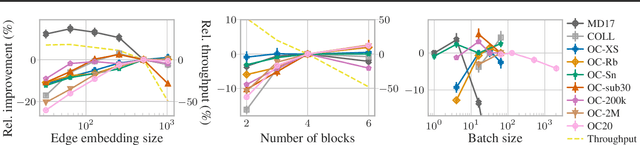
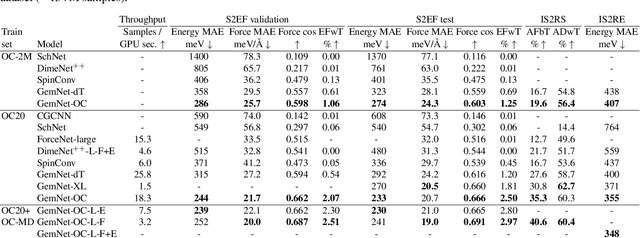
Abstract:The predominant method of demonstrating progress of atomic graph neural networks are benchmarks on small and limited datasets. The implicit hypothesis behind this approach is that progress on these narrow datasets generalize to the large diversity of chemistry. This generalizability would be very helpful for research, but currently remains untested. In this work we test this assumption by identifying four aspects of complexity in which many datasets are lacking: 1. Chemical diversity (number of different elements), 2. system size (number of atoms per sample), 3. dataset size (number of data samples), and 4. domain shift (similarity of the training and test set). We introduce multiple subsets of the large Open Catalyst 2020 (OC20) dataset to independently investigate each of these aspects. We then perform 21 ablation studies and sensitivity analyses on 9 datasets testing both previously proposed and new model enhancements. We find that some improvements are consistent between datasets, but many are not and some even have opposite effects. Based on this analysis, we identify a smaller dataset that correlates well with the full OC20 dataset, and propose the GemNet-OC model, which outperforms the previous state-of-the-art on OC20 by 16%, while reducing training time by a factor of 10. Overall, our findings challenge the common belief that graph neural networks work equally well independent of dataset size and diversity, and suggest that caution must be exercised when making generalizations based on narrow datasets.
Rotation Invariant Graph Neural Networks using Spin Convolutions
Jun 17, 2021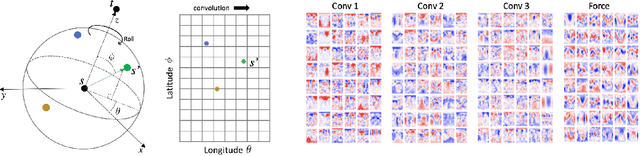
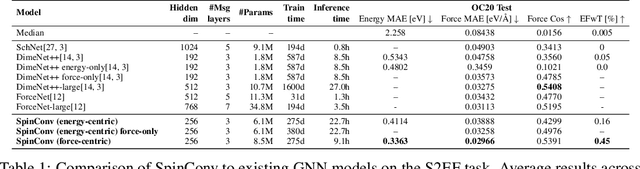
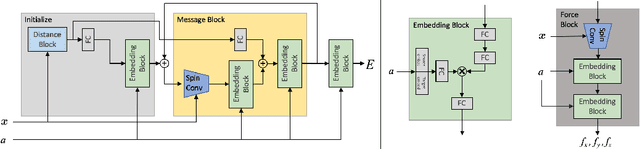
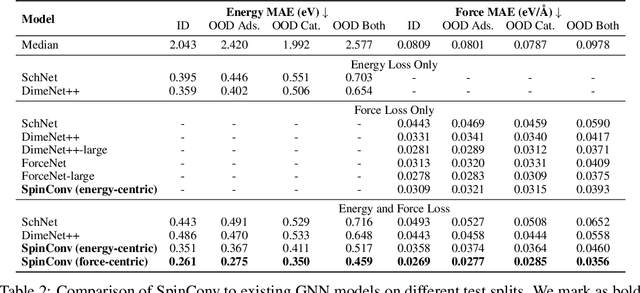
Abstract:Progress towards the energy breakthroughs needed to combat climate change can be significantly accelerated through the efficient simulation of atomic systems. Simulation techniques based on first principles, such as Density Functional Theory (DFT), are limited in their practical use due to their high computational expense. Machine learning approaches have the potential to approximate DFT in a computationally efficient manner, which could dramatically increase the impact of computational simulations on real-world problems. Approximating DFT poses several challenges. These include accurately modeling the subtle changes in the relative positions and angles between atoms, and enforcing constraints such as rotation invariance or energy conservation. We introduce a novel approach to modeling angular information between sets of neighboring atoms in a graph neural network. Rotation invariance is achieved for the network's edge messages through the use of a per-edge local coordinate frame and a novel spin convolution over the remaining degree of freedom. Two model variants are proposed for the applications of structure relaxation and molecular dynamics. State-of-the-art results are demonstrated on the large-scale Open Catalyst 2020 dataset. Comparisons are also performed on the MD17 and QM9 datasets.
ForceNet: A Graph Neural Network for Large-Scale Quantum Calculations
Mar 02, 2021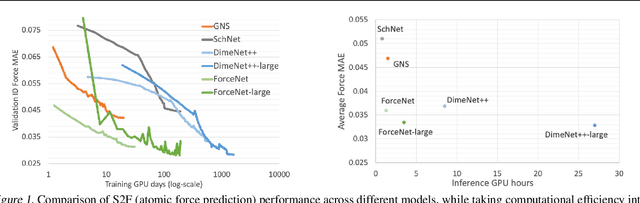
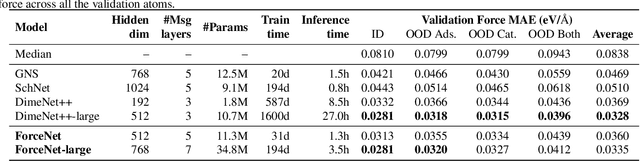
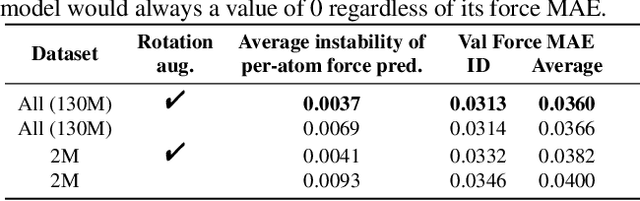
Abstract:With massive amounts of atomic simulation data available, there is a huge opportunity to develop fast and accurate machine learning models to approximate expensive physics-based calculations. The key quantity to estimate is atomic forces, where the state-of-the-art Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) explicitly enforce basic physical constraints such as rotation-covariance. However, to strictly satisfy the physical constraints, existing models have to make tradeoffs between computational efficiency and model expressiveness. Here we explore an alternative approach. By not imposing explicit physical constraints, we can flexibly design expressive models while maintaining their computational efficiency. Physical constraints are implicitly imposed by training the models using physics-based data augmentation. To evaluate the approach, we carefully design a scalable and expressive GNN model, ForceNet, and apply it to OC20 (Chanussot et al., 2020), an unprecedentedly-large dataset of quantum physics calculations. Our proposed ForceNet is able to predict atomic forces more accurately than state-of-the-art physics-based GNNs while being faster both in training and inference. Overall, our promising and counter-intuitive results open up an exciting avenue for future research.
The Open Catalyst 2020 Dataset and Community Challenges
Oct 20, 2020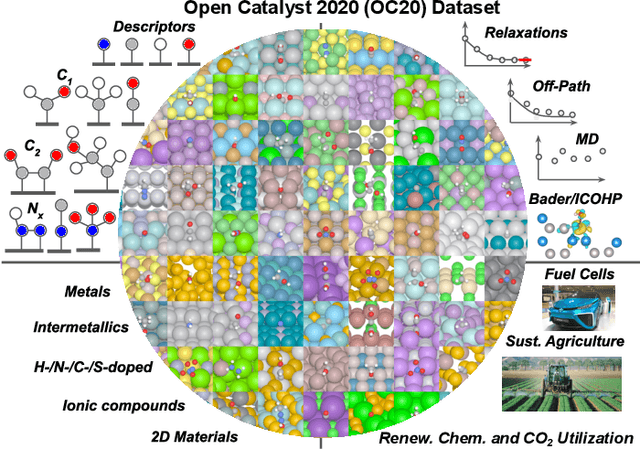

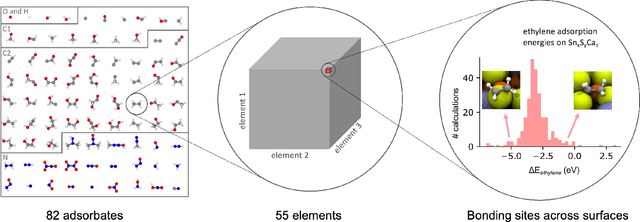
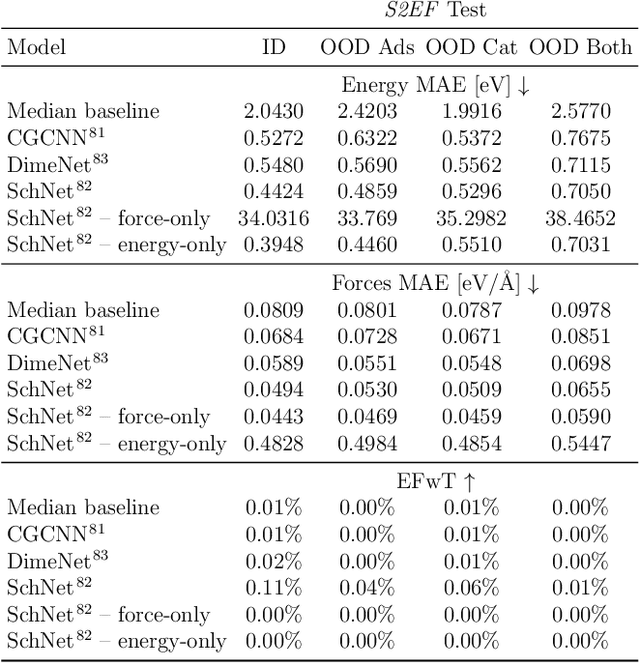
Abstract:Catalyst discovery and optimization is key to solving many societal and energy challenges including solar fuels synthesis, long-term energy storage, and renewable fertilizer production. Despite considerable effort by the catalysis community to apply machine learning models to the computational catalyst discovery process, it remains an open challenge to build models that can generalize across both elemental compositions of surfaces and adsorbate identity/configurations, perhaps because datasets have been smaller in catalysis than related fields. To address this we developed the OC20 dataset, consisting of 1,281,121 Density Functional Theory (DFT) relaxations (264,900,500 single point evaluations) across a wide swath of materials, surfaces, and adsorbates (nitrogen, carbon, and oxygen chemistries). We supplemented this dataset with randomly perturbed structures, short timescale molecular dynamics, and electronic structure analyses. The dataset comprises three central tasks indicative of day-to-day catalyst modeling and comes with pre-defined train/validation/test splits to facilitate direct comparisons with future model development efforts. We applied three state-of-the-art graph neural network models (SchNet, Dimenet, CGCNN) to each of these tasks as baseline demonstrations for the community to build on. In almost every task, no upper limit on model size was identified, suggesting that even larger models are likely to improve on initial results. The dataset and baseline models are both provided as open resources, as well as a public leader board to encourage community contributions to solve these important tasks.
An Introduction to Electrocatalyst Design using Machine Learning for Renewable Energy Storage
Oct 14, 2020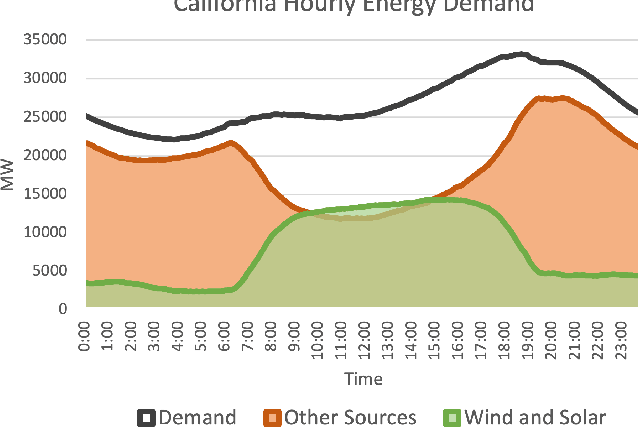
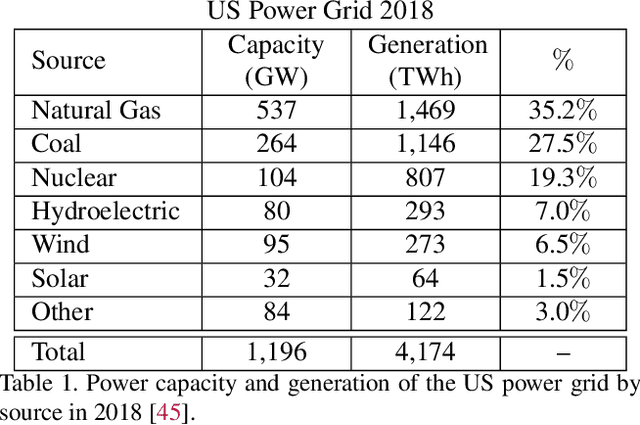
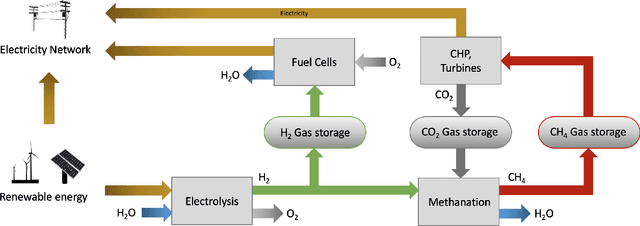
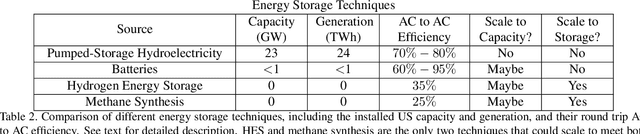
Abstract:Scalable and cost-effective solutions to renewable energy storage are essential to addressing the world's rising energy needs while reducing climate change. As we increase our reliance on renewable energy sources such as wind and solar, which produce intermittent power, storage is needed to transfer power from times of peak generation to peak demand. This may require the storage of power for hours, days, or months. One solution that offers the potential of scaling to nation-sized grids is the conversion of renewable energy to other fuels, such as hydrogen or methane. To be widely adopted, this process requires cost-effective solutions to running electrochemical reactions. An open challenge is finding low-cost electrocatalysts to drive these reactions at high rates. Through the use of quantum mechanical simulations (density functional theory), new catalyst structures can be tested and evaluated. Unfortunately, the high computational cost of these simulations limits the number of structures that may be tested. The use of machine learning may provide a method to efficiently approximate these calculations, leading to new approaches in finding effective electrocatalysts. In this paper, we provide an introduction to the challenges in finding suitable electrocatalysts, how machine learning may be applied to the problem, and the use of the Open Catalyst Project OC20 dataset for model training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge