Brandon M. Wood
A practical guide to machine learning interatomic potentials -- Status and future
Mar 12, 2025
Abstract:The rapid development and large body of literature on machine learning interatomic potentials (MLIPs) can make it difficult to know how to proceed for researchers who are not experts but wish to use these tools. The spirit of this review is to help such researchers by serving as a practical, accessible guide to the state-of-the-art in MLIPs. This review paper covers a broad range of topics related to MLIPs, including (i) central aspects of how and why MLIPs are enablers of many exciting advancements in molecular modeling, (ii) the main underpinnings of different types of MLIPs, including their basic structure and formalism, (iii) the potentially transformative impact of universal MLIPs for both organic and inorganic systems, including an overview of the most recent advances, capabilities, downsides, and potential applications of this nascent class of MLIPs, (iv) a practical guide for estimating and understanding the execution speed of MLIPs, including guidance for users based on hardware availability, type of MLIP used, and prospective simulation size and time, (v) a manual for what MLIP a user should choose for a given application by considering hardware resources, speed requirements, energy and force accuracy requirements, as well as guidance for choosing pre-trained potentials or fitting a new potential from scratch, (vi) discussion around MLIP infrastructure, including sources of training data, pre-trained potentials, and hardware resources for training, (vii) summary of some key limitations of present MLIPs and current approaches to mitigate such limitations, including methods of including long-range interactions, handling magnetic systems, and treatment of excited states, and finally (viii) we finish with some more speculative thoughts on what the future holds for the development and application of MLIPs over the next 3-10+ years.
Learning Smooth and Expressive Interatomic Potentials for Physical Property Prediction
Feb 17, 2025



Abstract:Machine learning interatomic potentials (MLIPs) have become increasingly effective at approximating quantum mechanical calculations at a fraction of the computational cost. However, lower errors on held out test sets do not always translate to improved results on downstream physical property prediction tasks. In this paper, we propose testing MLIPs on their practical ability to conserve energy during molecular dynamic simulations. If passed, improved correlations are found between test errors and their performance on physical property prediction tasks. We identify choices which may lead to models failing this test, and use these observations to improve upon highly-expressive models. The resulting model, eSEN, provides state-of-the-art results on a range of physical property prediction tasks, including materials stability prediction, thermal conductivity prediction, and phonon calculations.
FlowLLM: Flow Matching for Material Generation with Large Language Models as Base Distributions
Oct 30, 2024Abstract:Material discovery is a critical area of research with the potential to revolutionize various fields, including carbon capture, renewable energy, and electronics. However, the immense scale of the chemical space makes it challenging to explore all possible materials experimentally. In this paper, we introduce FlowLLM, a novel generative model that combines large language models (LLMs) and Riemannian flow matching (RFM) to design novel crystalline materials. FlowLLM first fine-tunes an LLM to learn an effective base distribution of meta-stable crystals in a text representation. After converting to a graph representation, the RFM model takes samples from the LLM and iteratively refines the coordinates and lattice parameters. Our approach significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods, increasing the generation rate of stable materials by over three times and increasing the rate for stable, unique, and novel crystals by $\sim50\%$ - a huge improvement on a difficult problem. Additionally, the crystals generated by FlowLLM are much closer to their relaxed state when compared with another leading model, significantly reducing post-hoc computational cost.
Open Materials 2024 (OMat24) Inorganic Materials Dataset and Models
Oct 16, 2024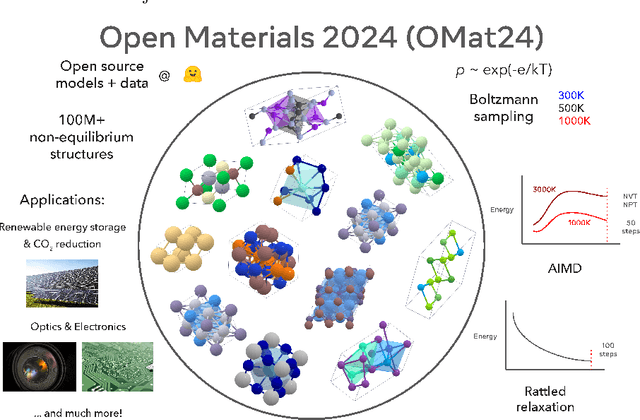
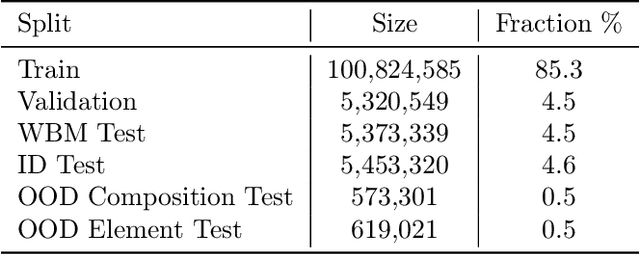
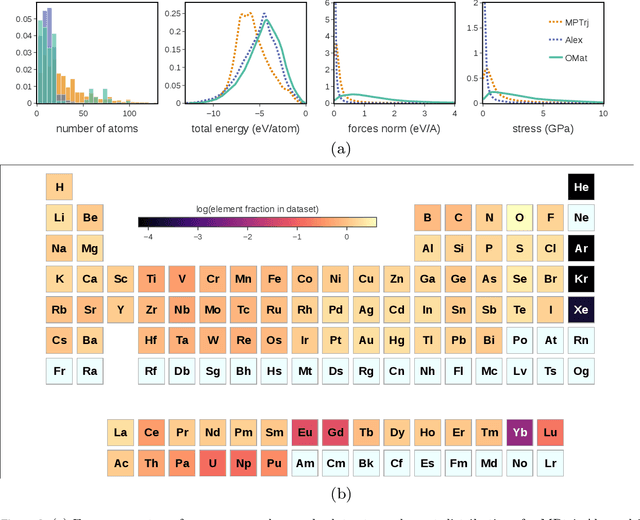
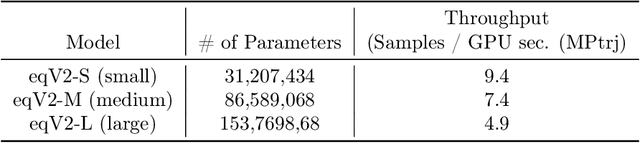
Abstract:The ability to discover new materials with desirable properties is critical for numerous applications from helping mitigate climate change to advances in next generation computing hardware. AI has the potential to accelerate materials discovery and design by more effectively exploring the chemical space compared to other computational methods or by trial-and-error. While substantial progress has been made on AI for materials data, benchmarks, and models, a barrier that has emerged is the lack of publicly available training data and open pre-trained models. To address this, we present a Meta FAIR release of the Open Materials 2024 (OMat24) large-scale open dataset and an accompanying set of pre-trained models. OMat24 contains over 110 million density functional theory (DFT) calculations focused on structural and compositional diversity. Our EquiformerV2 models achieve state-of-the-art performance on the Matbench Discovery leaderboard and are capable of predicting ground-state stability and formation energies to an F1 score above 0.9 and an accuracy of 20 meV/atom, respectively. We explore the impact of model size, auxiliary denoising objectives, and fine-tuning on performance across a range of datasets including OMat24, MPtraj, and Alexandria. The open release of the OMat24 dataset and models enables the research community to build upon our efforts and drive further advancements in AI-assisted materials science.
From Molecules to Materials: Pre-training Large Generalizable Models for Atomic Property Prediction
Oct 25, 2023Abstract:Foundation models have been transformational in machine learning fields such as natural language processing and computer vision. Similar success in atomic property prediction has been limited due to the challenges of training effective models across multiple chemical domains. To address this, we introduce Joint Multi-domain Pre-training (JMP), a supervised pre-training strategy that simultaneously trains on multiple datasets from different chemical domains, treating each dataset as a unique pre-training task within a multi-task framework. Our combined training dataset consists of $\sim$120M systems from OC20, OC22, ANI-1x, and Transition-1x. We evaluate performance and generalization by fine-tuning over a diverse set of downstream tasks and datasets including: QM9, rMD17, MatBench, QMOF, SPICE, and MD22. JMP demonstrates an average improvement of 59% over training from scratch, and matches or sets state-of-the-art on 34 out of 40 tasks. Our work highlights the potential of pre-training strategies that utilize diverse data to advance property prediction across chemical domains, especially for low-data tasks.
AdsorbML: Accelerating Adsorption Energy Calculations with Machine Learning
Nov 29, 2022Abstract:Computational catalysis is playing an increasingly significant role in the design of catalysts across a wide range of applications. A common task for many computational methods is the need to accurately compute the minimum binding energy - the adsorption energy - for an adsorbate and a catalyst surface of interest. Traditionally, the identification of low energy adsorbate-surface configurations relies on heuristic methods and researcher intuition. As the desire to perform high-throughput screening increases, it becomes challenging to use heuristics and intuition alone. In this paper, we demonstrate machine learning potentials can be leveraged to identify low energy adsorbate-surface configurations more accurately and efficiently. Our algorithm provides a spectrum of trade-offs between accuracy and efficiency, with one balanced option finding the lowest energy configuration, within a 0.1 eV threshold, 86.63% of the time, while achieving a 1387x speedup in computation. To standardize benchmarking, we introduce the Open Catalyst Dense dataset containing nearly 1,000 diverse surfaces and 87,045 unique configurations.
The Open Catalyst 2022 Dataset and Challenges for Oxide Electrocatalysis
Jun 17, 2022
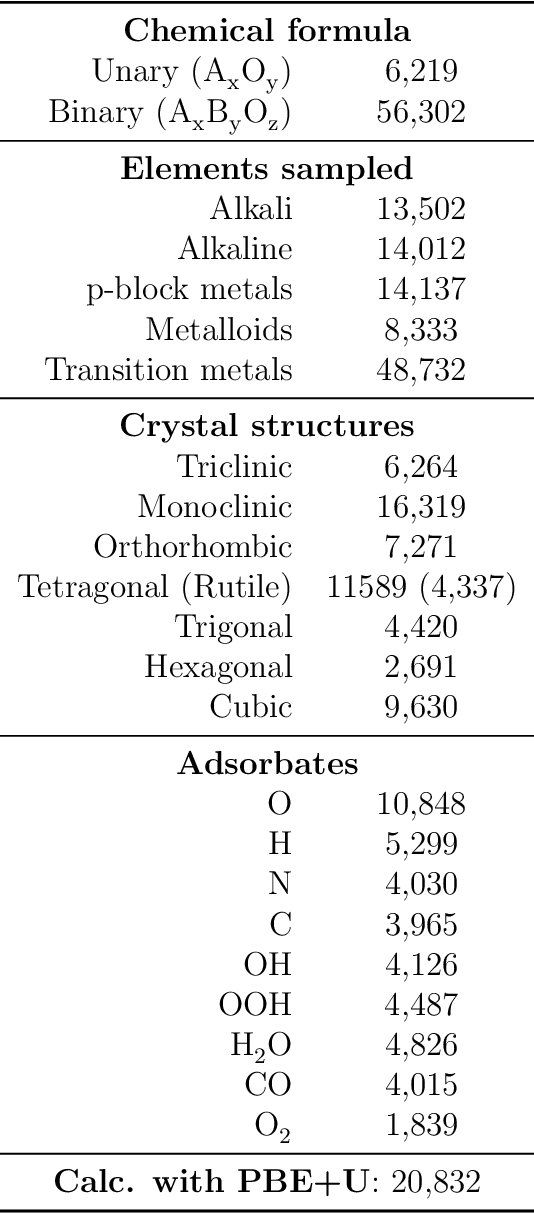
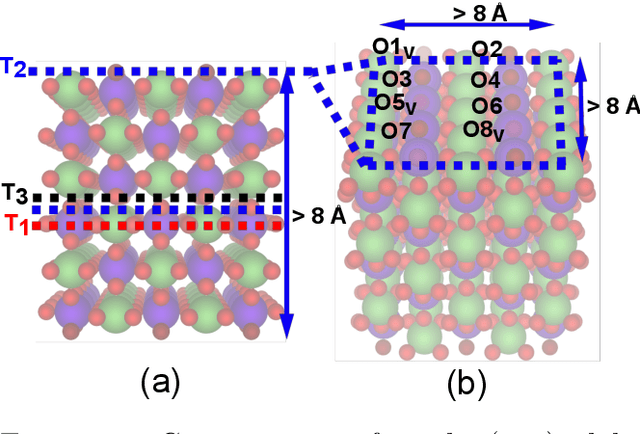
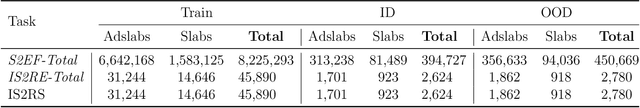
Abstract:Computational catalysis and machine learning communities have made considerable progress in developing machine learning models for catalyst discovery and design. Yet, a general machine learning potential that spans the chemical space of catalysis is still out of reach. A significant hurdle is obtaining access to training data across a wide range of materials. One important class of materials where data is lacking are oxides, which inhibits models from studying the Oxygen Evolution Reaction and oxide electrocatalysis more generally. To address this we developed the Open Catalyst 2022(OC22) dataset, consisting of 62,521 Density Functional Theory (DFT) relaxations (~9,884,504 single point calculations) across a range of oxide materials, coverages, and adsorbates (*H, *O, *N, *C, *OOH, *OH, *OH2, *O2, *CO). We define generalized tasks to predict the total system energy that are applicable across catalysis, develop baseline performance of several graph neural networks (SchNet, DimeNet++, ForceNet, SpinConv, PaiNN, GemNet-dT, GemNet-OC), and provide pre-defined dataset splits to establish clear benchmarks for future efforts. For all tasks, we study whether combining datasets leads to better results, even if they contain different materials or adsorbates. Specifically, we jointly train models on Open Catalyst 2020 (OC20) Dataset and OC22, or fine-tune pretrained OC20 models on OC22. In the most general task, GemNet-OC sees a ~32% improvement in energy predictions through fine-tuning and a ~9% improvement in force predictions via joint training. Surprisingly, joint training on both the OC20 and much smaller OC22 datasets also improves total energy predictions on OC20 by ~19%. The dataset and baseline models are open sourced, and a public leaderboard will follow to encourage continued community developments on the total energy tasks and data.
Towards Training Billion Parameter Graph Neural Networks for Atomic Simulations
Mar 18, 2022
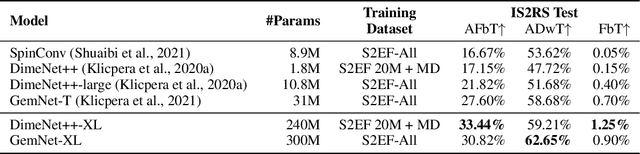


Abstract:Recent progress in Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) for modeling atomic simulations has the potential to revolutionize catalyst discovery, which is a key step in making progress towards the energy breakthroughs needed to combat climate change. However, the GNNs that have proven most effective for this task are memory intensive as they model higher-order interactions in the graphs such as those between triplets or quadruplets of atoms, making it challenging to scale these models. In this paper, we introduce Graph Parallelism, a method to distribute input graphs across multiple GPUs, enabling us to train very large GNNs with hundreds of millions or billions of parameters. We empirically evaluate our method by scaling up the number of parameters of the recently proposed DimeNet++ and GemNet models by over an order of magnitude. On the large-scale Open Catalyst 2020 (OC20) dataset, these graph-parallelized models lead to relative improvements of 1) 15% on the force MAE metric for the S2EF task and 2) 21% on the AFbT metric for the IS2RS task, establishing new state-of-the-art results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge