Ryan Jacobs
A practical guide to machine learning interatomic potentials -- Status and future
Mar 12, 2025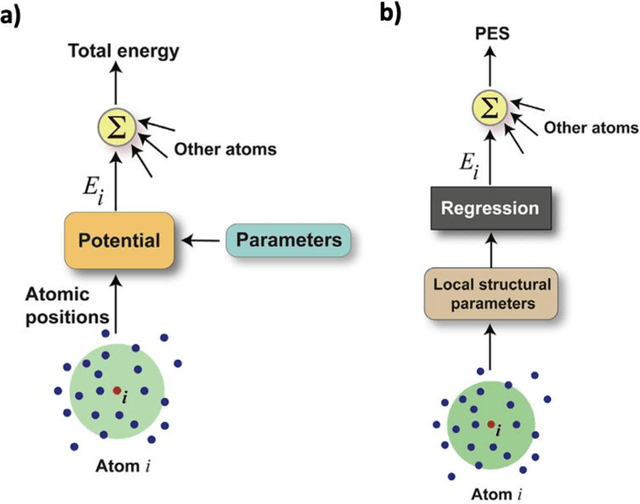
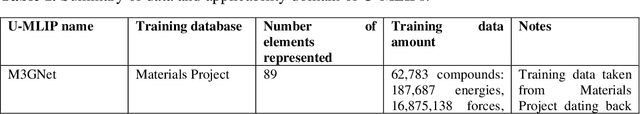
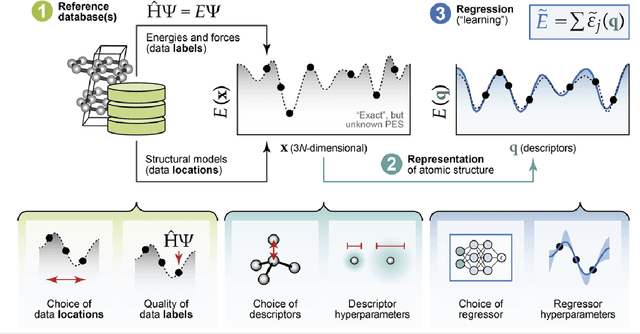
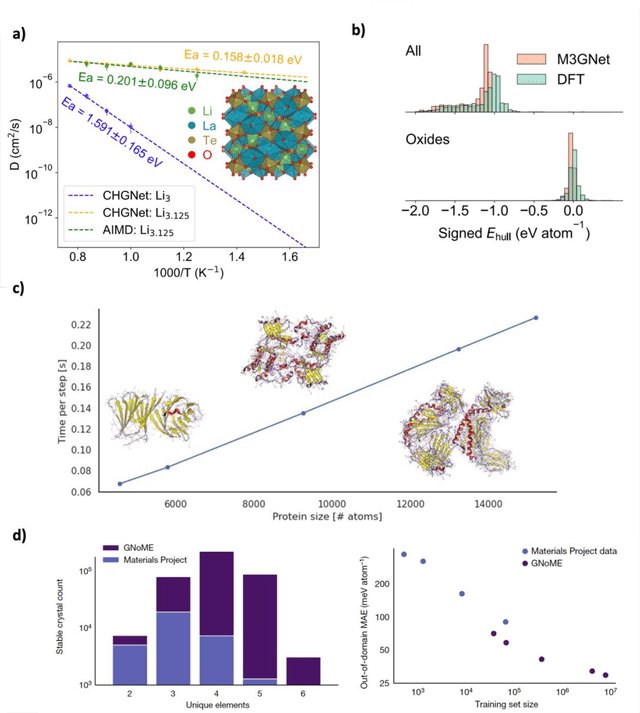
Abstract:The rapid development and large body of literature on machine learning interatomic potentials (MLIPs) can make it difficult to know how to proceed for researchers who are not experts but wish to use these tools. The spirit of this review is to help such researchers by serving as a practical, accessible guide to the state-of-the-art in MLIPs. This review paper covers a broad range of topics related to MLIPs, including (i) central aspects of how and why MLIPs are enablers of many exciting advancements in molecular modeling, (ii) the main underpinnings of different types of MLIPs, including their basic structure and formalism, (iii) the potentially transformative impact of universal MLIPs for both organic and inorganic systems, including an overview of the most recent advances, capabilities, downsides, and potential applications of this nascent class of MLIPs, (iv) a practical guide for estimating and understanding the execution speed of MLIPs, including guidance for users based on hardware availability, type of MLIP used, and prospective simulation size and time, (v) a manual for what MLIP a user should choose for a given application by considering hardware resources, speed requirements, energy and force accuracy requirements, as well as guidance for choosing pre-trained potentials or fitting a new potential from scratch, (vi) discussion around MLIP infrastructure, including sources of training data, pre-trained potentials, and hardware resources for training, (vii) summary of some key limitations of present MLIPs and current approaches to mitigate such limitations, including methods of including long-range interactions, handling magnetic systems, and treatment of excited states, and finally (viii) we finish with some more speculative thoughts on what the future holds for the development and application of MLIPs over the next 3-10+ years.
Predicting Performance of Object Detection Models in Electron Microscopy Using Random Forests
Jan 14, 2025



Abstract:Quantifying prediction uncertainty when applying object detection models to new, unlabeled datasets is critical in applied machine learning. This study introduces an approach to estimate the performance of deep learning-based object detection models for quantifying defects in transmission electron microscopy (TEM) images, focusing on detecting irradiation-induced cavities in TEM images of metal alloys. We developed a random forest regression model that predicts the object detection F1 score, a statistical metric used to evaluate the ability to accurately locate and classify objects of interest. The random forest model uses features extracted from the predictions of the object detection model whose uncertainty is being quantified, enabling fast prediction on new, unlabeled images. The mean absolute error (MAE) for predicting F1 of the trained model on test data is 0.09, and the $R^2$ score is 0.77, indicating there is a significant correlation between the random forest regression model predicted and true defect detection F1 scores. The approach is shown to be robust across three distinct TEM image datasets with varying imaging and material domains. Our approach enables users to estimate the reliability of a defect detection and segmentation model predictions and assess the applicability of the model to their specific datasets, providing valuable information about possible domain shifts and whether the model needs to be fine-tuned or trained on additional data to be maximally effective for the desired use case.
Regression with Large Language Models for Materials and Molecular Property Prediction
Sep 09, 2024Abstract:We demonstrate the ability of large language models (LLMs) to perform material and molecular property regression tasks, a significant deviation from the conventional LLM use case. We benchmark the Large Language Model Meta AI (LLaMA) 3 on several molecular properties in the QM9 dataset and 24 materials properties. Only composition-based input strings are used as the model input and we fine tune on only the generative loss. We broadly find that LLaMA 3, when fine-tuned using the SMILES representation of molecules, provides useful regression results which can rival standard materials property prediction models like random forest or fully connected neural networks on the QM9 dataset. Not surprisingly, LLaMA 3 errors are 5-10x higher than those of the state-of-the-art models that were trained using far more granular representation of molecules (e.g., atom types and their coordinates) for the same task. Interestingly, LLaMA 3 provides improved predictions compared to GPT-3.5 and GPT-4o. This work highlights the versatility of LLMs, suggesting that LLM-like generative models can potentially transcend their traditional applications to tackle complex physical phenomena, thus paving the way for future research and applications in chemistry, materials science and other scientific domains.
Accelerating Domain-Aware Electron Microscopy Analysis Using Deep Learning Models with Synthetic Data and Image-Wide Confidence Scoring
Aug 02, 2024Abstract:The integration of machine learning (ML) models enhances the efficiency, affordability, and reliability of feature detection in microscopy, yet their development and applicability are hindered by the dependency on scarce and often flawed manually labeled datasets and a lack of domain awareness. We addressed these challenges by creating a physics-based synthetic image and data generator, resulting in a machine learning model that achieves comparable precision (0.86), recall (0.63), F1 scores (0.71), and engineering property predictions (R2=0.82) to a model trained on human-labeled data. We enhanced both models by using feature prediction confidence scores to derive an image-wide confidence metric, enabling simple thresholding to eliminate ambiguous and out-of-domain images resulting in performance boosts of 5-30% with a filtering-out rate of 25%. Our study demonstrates that synthetic data can eliminate human reliance in ML and provides a means for domain awareness in cases where many feature detections per image are needed.
Determining Domain of Machine Learning Models using Kernel Density Estimates: Applications in Materials Property Prediction
May 28, 2024



Abstract:Knowledge of the domain of applicability of a machine learning model is essential to ensuring accurate and reliable model predictions. In this work, we develop a new approach of assessing model domain and demonstrate that our approach provides accurate and meaningful designation of in-domain versus out-of-domain when applied across multiple model types and material property data sets. Our approach assesses the distance between a test and training data point in feature space by using kernel density estimation and shows that this distance provides an effective tool for domain determination. We show that chemical groups considered unrelated based on established chemical knowledge exhibit significant dissimilarities by our measure. We also show that high measures of dissimilarity are associated with poor model performance (i.e., high residual magnitudes) and poor estimates of model uncertainty (i.e., unreliable uncertainty estimation). Automated tools are provided to enable researchers to establish acceptable dissimilarity thresholds to identify whether new predictions of their own machine learning models are in-domain versus out-of-domain.
Performance, Successes and Limitations of Deep Learning Semantic Segmentation of Multiple Defects in Transmission Electron Micrographs
Oct 15, 2021


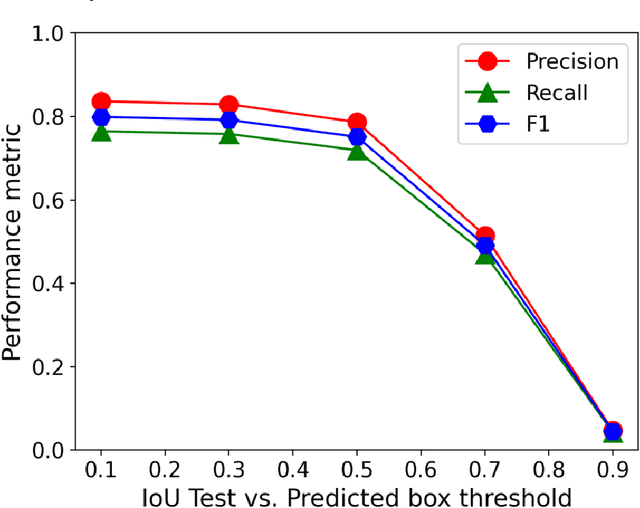
Abstract:In this work, we perform semantic segmentation of multiple defect types in electron microscopy images of irradiated FeCrAl alloys using a deep learning Mask Regional Convolutional Neural Network (Mask R-CNN) model. We conduct an in-depth analysis of key model performance statistics, with a focus on quantities such as predicted distributions of defect shapes, defect sizes, and defect areal densities relevant to informing modeling and understanding of irradiated Fe-based materials properties. To better understand the performance and present limitations of the model, we provide examples of useful evaluation tests which include a suite of random splits, and dataset size-dependent and domain-targeted cross validation tests. Overall, we find that the current model is a fast, effective tool for automatically characterizing and quantifying multiple defect types in microscopy images, with a level of accuracy on par with human domain expert labelers. More specifically, the model can achieve average defect identification F1 scores as high as 0.8, and, based on random cross validation, have low overall average (+/- standard deviation) defect size and density percentage errors of 7.3 (+/- 3.8)% and 12.7 (+/- 5.3)%, respectively. Further, our model predicts the expected material hardening to within 10-20 MPa (about 10% of total hardening), which is about the same error level as experiments. Our targeted evaluation tests also suggest the best path toward improving future models is not expanding existing databases with more labeled images but instead data additions that target weak points of the model domain, such as images from different microscopes, imaging conditions, irradiation environments, and alloy types. Finally, we discuss the first phase of an effort to provide an easy-to-use, open-source object detection tool to the broader community for identifying defects in new images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge