Michael A. Pfeffer
Monitoring Deployed AI Systems in Health Care
Dec 09, 2025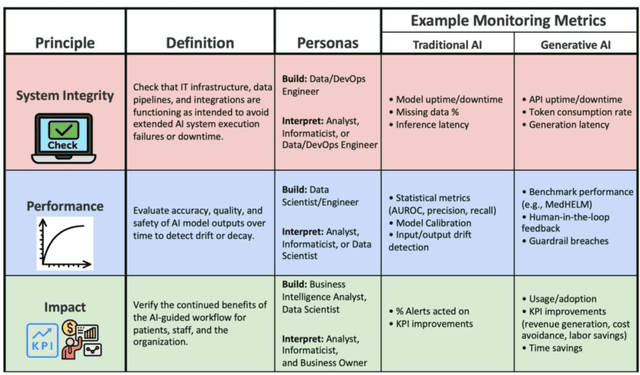
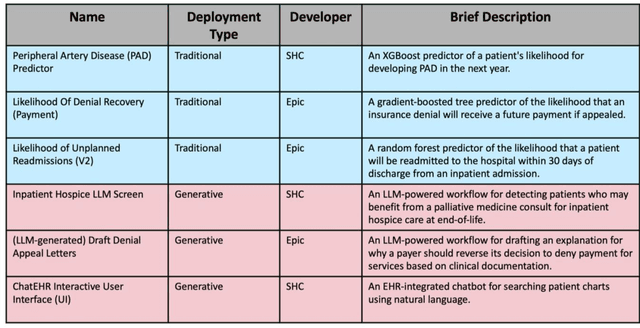
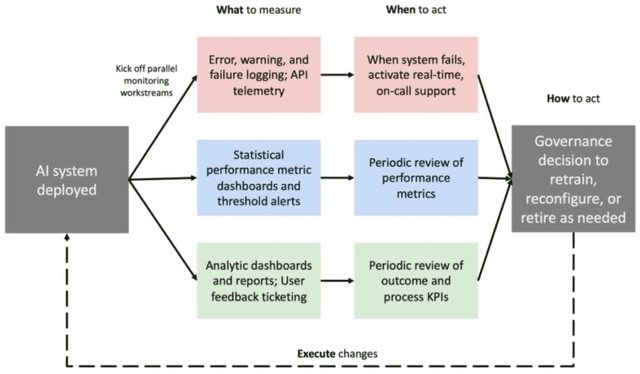
Abstract:Post-deployment monitoring of artificial intelligence (AI) systems in health care is essential to ensure their safety, quality, and sustained benefit-and to support governance decisions about which systems to update, modify, or decommission. Motivated by these needs, we developed a framework for monitoring deployed AI systems grounded in the mandate to take specific actions when they fail to behave as intended. This framework, which is now actively used at Stanford Health Care, is organized around three complementary principles: system integrity, performance, and impact. System integrity monitoring focuses on maximizing system uptime, detecting runtime errors, and identifying when changes to the surrounding IT ecosystem have unintended effects. Performance monitoring focuses on maintaining accurate system behavior in the face of changing health care practices (and thus input data) over time. Impact monitoring assesses whether a deployed system continues to have value in the form of benefit to clinicians and patients. Drawing on examples of deployed AI systems at our academic medical center, we provide practical guidance for creating monitoring plans based on these principles that specify which metrics to measure, when those metrics should be reviewed, who is responsible for acting when metrics change, and what concrete follow-up actions should be taken-for both traditional and generative AI. We also discuss challenges to implementing this framework, including the effort and cost of monitoring for health systems with limited resources and the difficulty of incorporating data-driven monitoring practices into complex organizations where conflicting priorities and definitions of success often coexist. This framework offers a practical template and starting point for health systems seeking to ensure that AI deployments remain safe and effective over time.
Optimizing Large Language Models for Detecting Symptoms of Comorbid Depression or Anxiety in Chronic Diseases: Insights from Patient Messages
Mar 14, 2025



Abstract:Patients with diabetes are at increased risk of comorbid depression or anxiety, complicating their management. This study evaluated the performance of large language models (LLMs) in detecting these symptoms from secure patient messages. We applied multiple approaches, including engineered prompts, systemic persona, temperature adjustments, and zero-shot and few-shot learning, to identify the best-performing model and enhance performance. Three out of five LLMs demonstrated excellent performance (over 90% of F-1 and accuracy), with Llama 3.1 405B achieving 93% in both F-1 and accuracy using a zero-shot approach. While LLMs showed promise in binary classification and handling complex metrics like Patient Health Questionnaire-4, inconsistencies in challenging cases warrant further real-life assessment. The findings highlight the potential of LLMs to assist in timely screening and referrals, providing valuable empirical knowledge for real-world triage systems that could improve mental health care for patients with chronic diseases.
Standing on FURM ground -- A framework for evaluating Fair, Useful, and Reliable AI Models in healthcare systems
Mar 14, 2024



Abstract:The impact of using artificial intelligence (AI) to guide patient care or operational processes is an interplay of the AI model's output, the decision-making protocol based on that output, and the capacity of the stakeholders involved to take the necessary subsequent action. Estimating the effects of this interplay before deployment, and studying it in real time afterwards, are essential to bridge the chasm between AI model development and achievable benefit. To accomplish this, the Data Science team at Stanford Health Care has developed a Testing and Evaluation (T&E) mechanism to identify fair, useful and reliable AI models (FURM) by conducting an ethical review to identify potential value mismatches, simulations to estimate usefulness, financial projections to assess sustainability, as well as analyses to determine IT feasibility, design a deployment strategy, and recommend a prospective monitoring and evaluation plan. We report on FURM assessments done to evaluate six AI guided solutions for potential adoption, spanning clinical and operational settings, each with the potential to impact from several dozen to tens of thousands of patients each year. We describe the assessment process, summarize the six assessments, and share our framework to enable others to conduct similar assessments. Of the six solutions we assessed, two have moved into a planning and implementation phase. Our novel contributions - usefulness estimates by simulation, financial projections to quantify sustainability, and a process to do ethical assessments - as well as their underlying methods and open source tools, are available for other healthcare systems to conduct actionable evaluations of candidate AI solutions.
MedAlign: A Clinician-Generated Dataset for Instruction Following with Electronic Medical Records
Aug 27, 2023
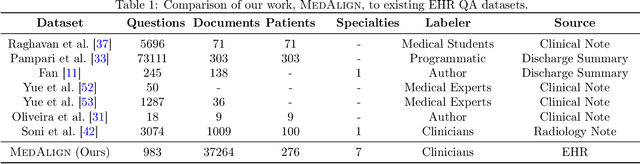
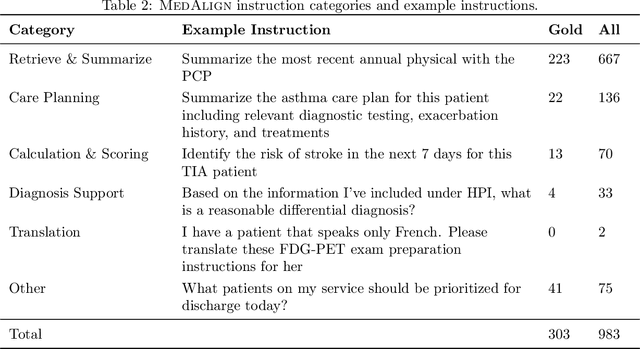

Abstract:The ability of large language models (LLMs) to follow natural language instructions with human-level fluency suggests many opportunities in healthcare to reduce administrative burden and improve quality of care. However, evaluating LLMs on realistic text generation tasks for healthcare remains challenging. Existing question answering datasets for electronic health record (EHR) data fail to capture the complexity of information needs and documentation burdens experienced by clinicians. To address these challenges, we introduce MedAlign, a benchmark dataset of 983 natural language instructions for EHR data. MedAlign is curated by 15 clinicians (7 specialities), includes clinician-written reference responses for 303 instructions, and provides 276 longitudinal EHRs for grounding instruction-response pairs. We used MedAlign to evaluate 6 general domain LLMs, having clinicians rank the accuracy and quality of each LLM response. We found high error rates, ranging from 35% (GPT-4) to 68% (MPT-7B-Instruct), and an 8.3% drop in accuracy moving from 32k to 2k context lengths for GPT-4. Finally, we report correlations between clinician rankings and automated natural language generation metrics as a way to rank LLMs without human review. We make MedAlign available under a research data use agreement to enable LLM evaluations on tasks aligned with clinician needs and preferences.
The Shaky Foundations of Clinical Foundation Models: A Survey of Large Language Models and Foundation Models for EMRs
Mar 24, 2023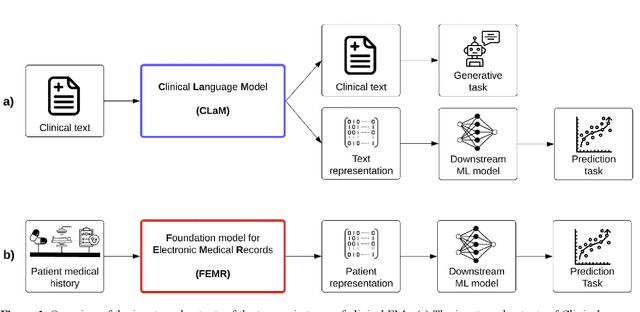
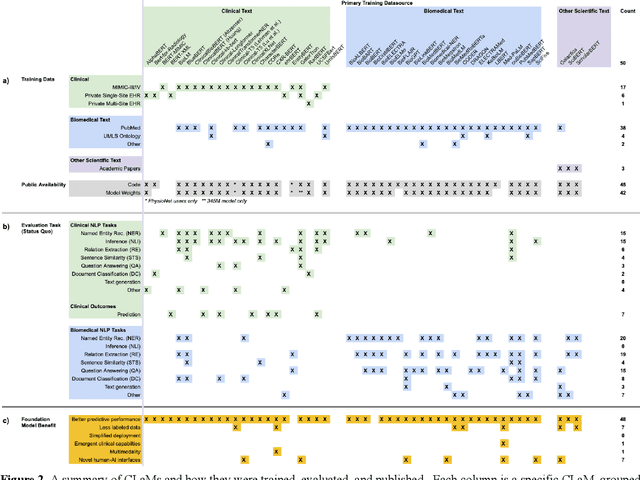
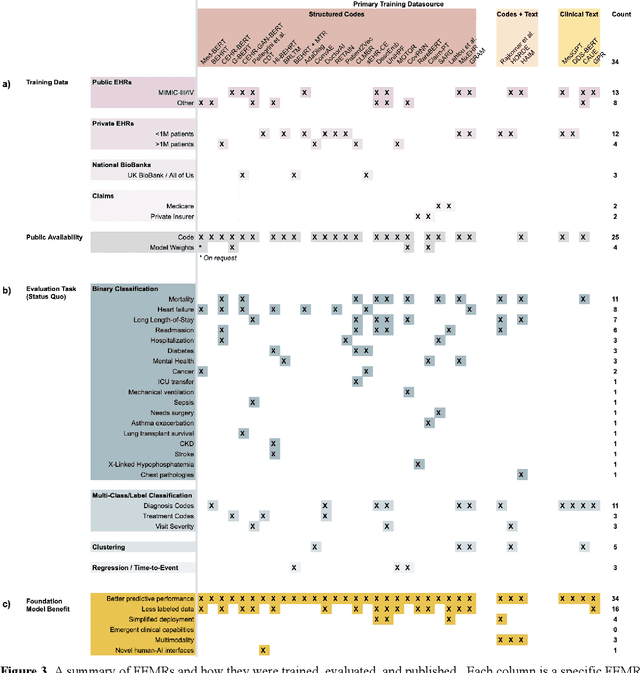

Abstract:The successes of foundation models such as ChatGPT and AlphaFold have spurred significant interest in building similar models for electronic medical records (EMRs) to improve patient care and hospital operations. However, recent hype has obscured critical gaps in our understanding of these models' capabilities. We review over 80 foundation models trained on non-imaging EMR data (i.e. clinical text and/or structured data) and create a taxonomy delineating their architectures, training data, and potential use cases. We find that most models are trained on small, narrowly-scoped clinical datasets (e.g. MIMIC-III) or broad, public biomedical corpora (e.g. PubMed) and are evaluated on tasks that do not provide meaningful insights on their usefulness to health systems. In light of these findings, we propose an improved evaluation framework for measuring the benefits of clinical foundation models that is more closely grounded to metrics that matter in healthcare.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge