Mehdi Khamassi
ISIR
Morality is Contextual: Learning Interpretable Moral Contexts from Human Data with Probabilistic Clustering and Large Language Models
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:Moral actions are judged not only by their outcomes but by the context in which they occur. We present COMETH (Contextual Organization of Moral Evaluation from Textual Human inputs), a framework that integrates a probabilistic context learner with LLM-based semantic abstraction and human moral evaluations to model how context shapes the acceptability of ambiguous actions. We curate an empirically grounded dataset of 300 scenarios across six core actions (violating Do not kill, Do not deceive, and Do not break the law) and collect ternary judgments (Blame/Neutral/Support) from N=101 participants. A preprocessing pipeline standardizes actions via an LLM filter and MiniLM embeddings with K-means, producing robust, reproducible core-action clusters. COMETH then learns action-specific moral contexts by clustering scenarios online from human judgment distributions using principled divergence criteria. To generalize and explain predictions, a Generalization module extracts concise, non-evaluative binary contextual features and learns feature weights in a transparent likelihood-based model. Empirically, COMETH roughly doubles alignment with majority human judgments relative to end-to-end LLM prompting (approx. 60% vs. approx. 30% on average), while revealing which contextual features drive its predictions. The contributions are: (i) an empirically grounded moral-context dataset, (ii) a reproducible pipeline combining human judgments with model-based context learning and LLM semantics, and (iii) an interpretable alternative to end-to-end LLMs for context-sensitive moral prediction and explanation.
Semantic Deception: When Reasoning Models Can't Compute an Addition
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used in situations where human values are at stake, such as decision-making tasks that involve reasoning when performed by humans. We investigate the so-called reasoning capabilities of LLMs over novel symbolic representations by introducing an experimental framework that tests their ability to process and manipulate unfamiliar symbols. We introduce semantic deceptions: situations in which symbols carry misleading semantic associations due to their form, such as being embedded in specific contexts, designed to probe whether LLMs can maintain symbolic abstraction or whether they default to exploiting learned semantic associations. We redefine standard digits and mathematical operators using novel symbols, and task LLMs with solving simple calculations expressed in this altered notation. The objective is: (1) to assess LLMs' capacity for abstraction and manipulation of arbitrary symbol systems; (2) to evaluate their ability to resist misleading semantic cues that conflict with the task's symbolic logic. Through experiments with four LLMs we show that semantic cues can significantly deteriorate reasoning models' performance on very simple tasks. They reveal limitations in current LLMs' ability for symbolic manipulations and highlight a tendency to over-rely on surface-level semantics, suggesting that chain-of-thoughts may amplify reliance on statistical correlations. Even in situations where LLMs seem to correctly follow instructions, semantic cues still impact basic capabilities. These limitations raise ethical and societal concerns, undermining the widespread and pernicious tendency to attribute reasoning abilities to LLMs and suggesting how LLMs might fail, in particular in decision-making contexts where robust symbolic reasoning is essential and should not be compromised by residual semantic associations inherited from the model's training.
Strong and weak alignment of large language models with human values
Aug 05, 2024Abstract:Minimizing negative impacts of Artificial Intelligent (AI) systems on human societies without human supervision requires them to be able to align with human values. However, most current work only addresses this issue from a technical point of view, e.g., improving current methods relying on reinforcement learning from human feedback, neglecting what it means and is required for alignment to occur. Here, we propose to distinguish strong and weak value alignment. Strong alignment requires cognitive abilities (either human-like or different from humans) such as understanding and reasoning about agents' intentions and their ability to causally produce desired effects. We argue that this is required for AI systems like large language models (LLMs) to be able to recognize situations presenting a risk that human values may be flouted. To illustrate this distinction, we present a series of prompts showing ChatGPT's, Gemini's and Copilot's failures to recognize some of these situations. We moreover analyze word embeddings to show that the nearest neighbors of some human values in LLMs differ from humans' semantic representations. We then propose a new thought experiment that we call "the Chinese room with a word transition dictionary", in extension of John Searle's famous proposal. We finally mention current promising research directions towards a weak alignment, which could produce statistically satisfying answers in a number of common situations, however so far without ensuring any truth value.
Purpose for Open-Ended Learning Robots: A Computational Taxonomy, Definition, and Operationalisation
Mar 04, 2024Abstract:Autonomous open-ended learning (OEL) robots are able to cumulatively acquire new skills and knowledge through direct interaction with the environment, for example relying on the guidance of intrinsic motivations and self-generated goals. OEL robots have a high relevance for applications as they can use the autonomously acquired knowledge to accomplish tasks relevant for their human users. OEL robots, however, encounter an important limitation: this may lead to the acquisition of knowledge that is not so much relevant to accomplish the users' tasks. This work analyses a possible solution to this problem that pivots on the novel concept of `purpose'. Purposes indicate what the designers and/or users want from the robot. The robot should use internal representations of purposes, called here `desires', to focus its open-ended exploration towards the acquisition of knowledge relevant to accomplish them. This work contributes to develop a computational framework on purpose in two ways. First, it formalises a framework on purpose based on a three-level motivational hierarchy involving: (a) the purposes; (b) the desires, which are domain independent; (c) specific domain dependent state-goals. Second, the work highlights key challenges highlighted by the framework such as: the `purpose-desire alignment problem', the `purpose-goal grounding problem', and the `arbitration between desires'. Overall, the approach enables OEL robots to learn in an autonomous way but also to focus on acquiring goals and skills that meet the purposes of the designers and users.
DREAM Architecture: a Developmental Approach to Open-Ended Learning in Robotics
May 13, 2020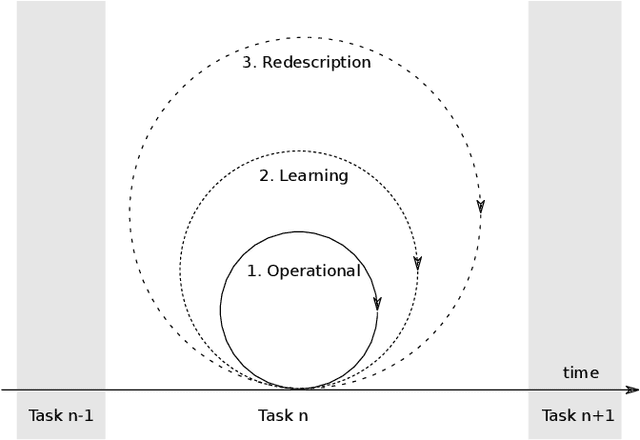


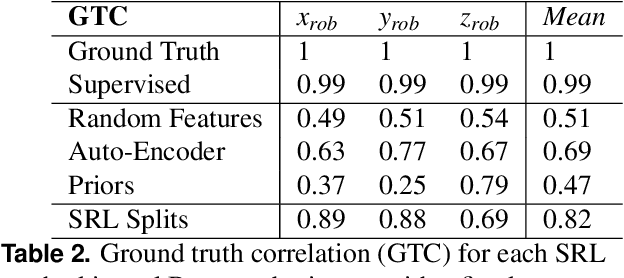
Abstract:Robots are still limited to controlled conditions, that the robot designer knows with enough details to endow the robot with the appropriate models or behaviors. Learning algorithms add some flexibility with the ability to discover the appropriate behavior given either some demonstrations or a reward to guide its exploration with a reinforcement learning algorithm. Reinforcement learning algorithms rely on the definition of state and action spaces that define reachable behaviors. Their adaptation capability critically depends on the representations of these spaces: small and discrete spaces result in fast learning while large and continuous spaces are challenging and either require a long training period or prevent the robot from converging to an appropriate behavior. Beside the operational cycle of policy execution and the learning cycle, which works at a slower time scale to acquire new policies, we introduce the redescription cycle, a third cycle working at an even slower time scale to generate or adapt the required representations to the robot, its environment and the task. We introduce the challenges raised by this cycle and we present DREAM (Deferred Restructuring of Experience in Autonomous Machines), a developmental cognitive architecture to bootstrap this redescription process stage by stage, build new state representations with appropriate motivations, and transfer the acquired knowledge across domains or tasks or even across robots. We describe results obtained so far with this approach and end up with a discussion of the questions it raises in Neuroscience.
Coping with the variability in humans reward during simulated human-robot interactions through the coordination of multiple learning strategies
May 06, 2020
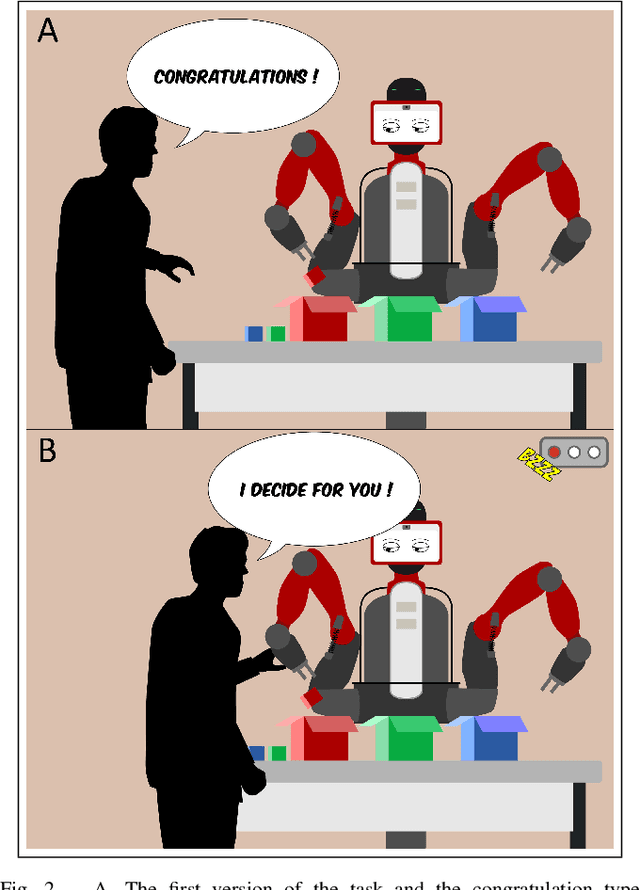


Abstract:An important current challenge in Human-Robot Interaction (HRI) is to enable robots to learn on-the-fly from human feedback. However, humans show a great variability in the way they reward robots. We propose to address this issue by enabling the robot to combine different learning strategies, namely model-based (MB) and model-free (MF) reinforcement learning. We simulate two HRI scenarios: a simple task where the human congratulates the robot for putting the right cubes in the right boxes, and a more complicated version of this task where cubes have to be placed in a specific order. We show that our existing MB-MF coordination algorithm previously tested in robot navigation works well here without retuning parameters. It leads to the maximal performance while producing the same minimal computational cost as MF alone. Moreover, the algorithm gives a robust performance no matter the variability of the simulated human feedback, while each strategy alone is impacted by this variability. Overall, the results suggest a promising way to promote robot learning flexibility when facing variable human feedback.
How to reduce computation time while sparing performance during robot navigation? A neuro-inspired architecture for autonomous shifting between model-based and model-free learning
Apr 30, 2020


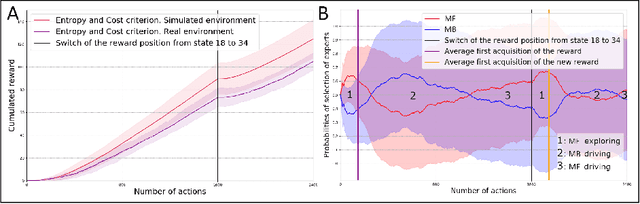
Abstract:Taking inspiration from how the brain coordinates multiple learning systems is an appealing strategy to endow robots with more flexibility. One of the expected advantages would be for robots to autonomously switch to the least costly system when its performance is satisfying. However, to our knowledge no study on a real robot has yet shown that the measured computational cost is reduced while performance is maintained with such brain-inspired algorithms. We present navigation experiments involving paths of different lengths to the goal, dead-end, and non-stationarity (i.e., change in goal location and apparition of obstacles). We present a novel arbitration mechanism between learning systems that explicitly measures performance and cost. We find that the robot can adapt to environment changes by switching between learning systems so as to maintain a high performance. Moreover, when the task is stable, the robot also autonomously shifts to the least costly system, which leads to a drastic reduction in computation cost while keeping a high performance. Overall, these results illustrates the interest of using multiple learning systems.
A Deep Learning Approach for Multi-View Engagement Estimation of Children in a Child-Robot Joint Attention task
Dec 01, 2018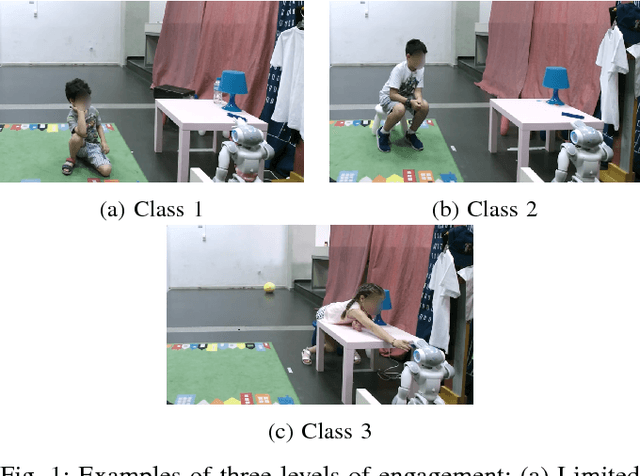



Abstract:In this work we tackle the problem of child engagement estimation while children freely interact with a robot in their room. We propose a deep-based multi-view solution that takes advantage of recent developments in human pose detection. We extract the child's pose from different RGB-D cameras placed elegantly in the room, fuse the results and feed them to a deep neural network trained for classifying engagement levels. The deep network contains a recurrent layer, in order to exploit the rich temporal information contained in the pose data. The resulting method outperforms a number of baseline classifiers, and provides a promising tool for better automatic understanding of a child's attitude, interest and attention while cooperating with a robot. The goal is to integrate this model in next generation social robots as an attention monitoring tool during various CRI tasks both for Typically Developed (TD) children and children affected by autism (ASD).
Prioritized Sweeping Neural DynaQ with Multiple Predecessors, and Hippocampal Replays
Aug 13, 2018



Abstract:During sleep and awake rest, the hippocampus replays sequences of place cells that have been activated during prior experiences. These have been interpreted as a memory consolidation process, but recent results suggest a possible interpretation in terms of reinforcement learning. The Dyna reinforcement learning algorithms use off-line replays to improve learning. Under limited replay budget, a prioritized sweeping approach, which requires a model of the transitions to the predecessors, can be used to improve performance. We investigate whether such algorithms can explain the experimentally observed replays. We propose a neural network version of prioritized sweeping Q-learning, for which we developed a growing multiple expert algorithm, able to cope with multiple predecessors. The resulting architecture is able to improve the learning of simulated agents confronted to a navigation task. We predict that, in animals, learning the world model should occur during rest periods, and that the corresponding replays should be shuffled.
Adaptive coordination of working-memory and reinforcement learning in non-human primates performing a trial-and-error problem solving task
Nov 02, 2017
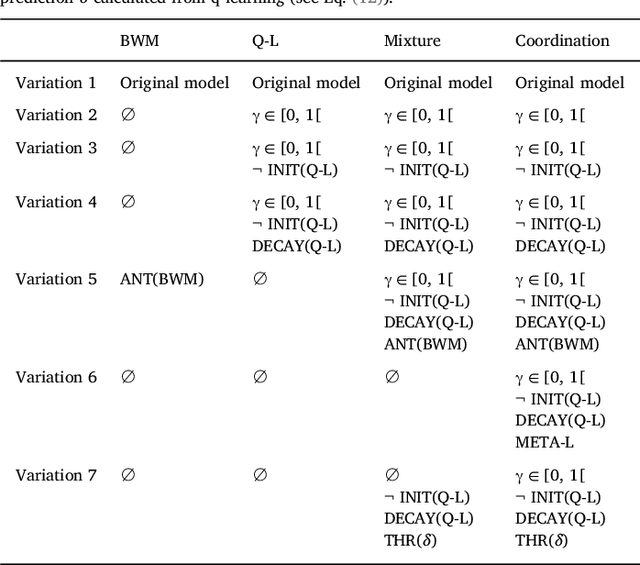


Abstract:Accumulating evidence suggest that human behavior in trial-and-error learning tasks based on decisions between discrete actions may involve a combination of reinforcement learning (RL) and working-memory (WM). While the understanding of brain activity at stake in this type of tasks often involve the comparison with non-human primate neurophysiological results, it is not clear whether monkeys use similar combined RL and WM processes to solve these tasks. Here we analyzed the behavior of five monkeys with computational models combining RL and WM. Our model-based analysis approach enables to not only fit trial-by-trial choices but also transient slowdowns in reaction times, indicative of WM use. We found that the behavior of the five monkeys was better explained in terms of a combination of RL and WM despite inter-individual differences. The same coordination dynamics we used in a previous study in humans best explained the behavior of some monkeys while the behavior of others showed the opposite pattern, revealing a possible different dynamics of WM process. We further analyzed different variants of the tested models to open a discussion on how the long pretraining in these tasks may have favored particular coordination dynamics between RL and WM. This points towards either inter-species differences or protocol differences which could be further tested in humans.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge