Marion Smits
for the Alzheimers Disease Neuroimaging Initiative
Deep learning-based group-wise registration for longitudinal MRI analysis in glioma
Jun 18, 2023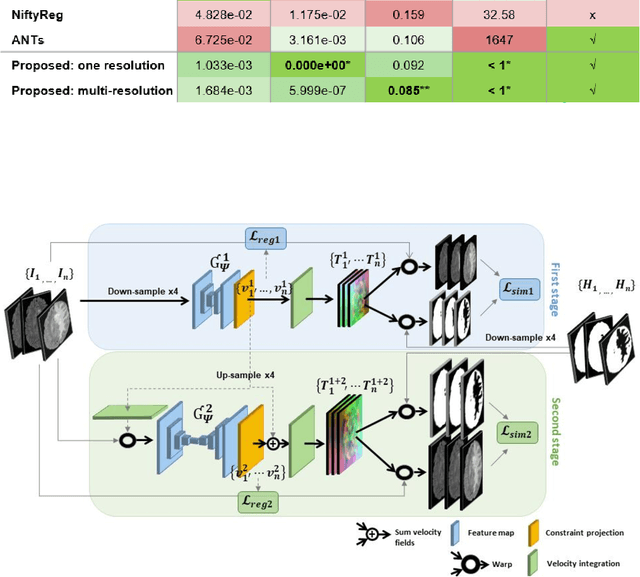
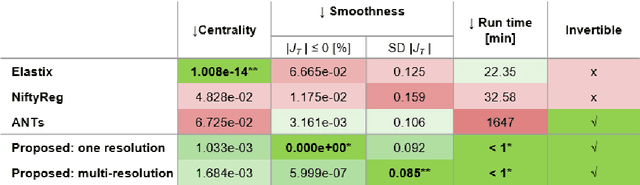
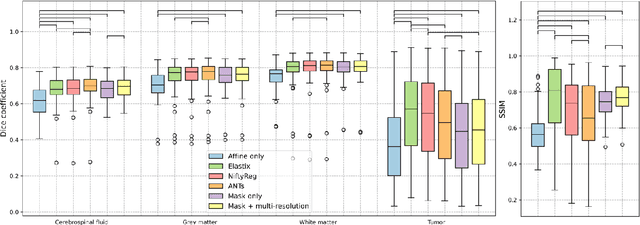
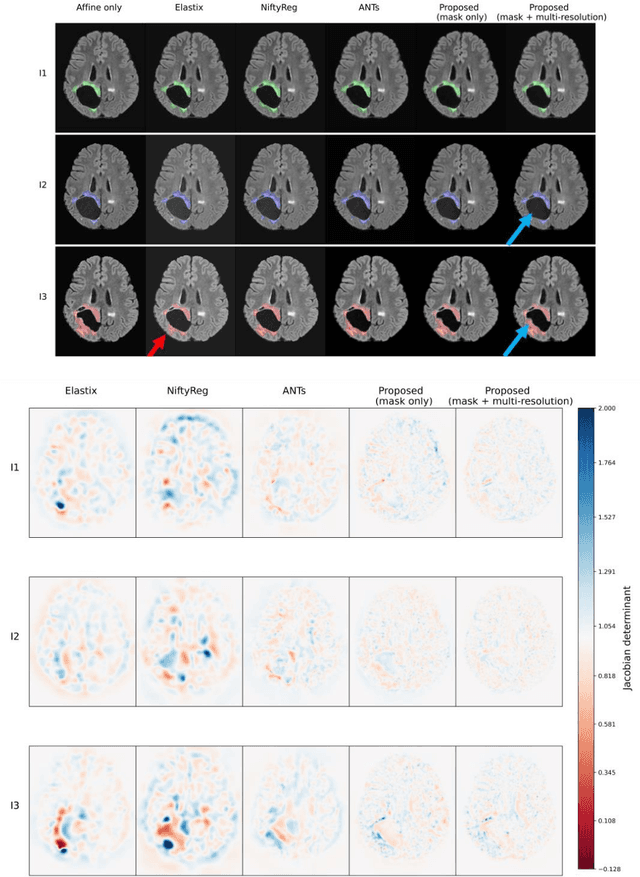
Abstract:Glioma growth may be quantified with longitudinal image registration. However, the large mass-effects and tissue changes across images pose an added challenge. Here, we propose a longitudinal, learning-based, and groupwise registration method for the accurate and unbiased registration of glioma MRI. We evaluate on a dataset from the Glioma Longitudinal AnalySiS consortium and compare it to classical registration methods. We achieve comparable Dice coefficients, with more detailed registrations, while significantly reducing the runtime to under a minute. The proposed methods may serve as an alternative to classical toolboxes, to provide further insight into glioma growth.
Computer-aided diagnosis and prediction in brain disorders
Jun 29, 2022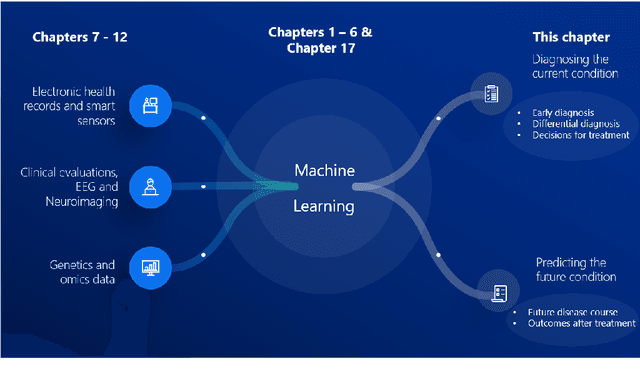
Abstract:Computer-aided methods have shown added value for diagnosing and predicting brain disorders and can thus support decision making in clinical care and treatment planning. This chapter will provide insight into the type of methods, their working, their input data - such as cognitive tests, imaging and genetic data - and the types of output they provide. We will focus on specific use cases for diagnosis, i.e. estimating the current 'condition' of the patient, such as early detection and diagnosis of dementia, differential diagnosis of brain tumours, and decision making in stroke. Regarding prediction, i.e. estimation of the future 'condition' of the patient, we will zoom in on use cases such as predicting the disease course in multiple sclerosis and predicting patient outcomes after treatment in brain cancer. Furthermore, based on these use cases, we will assess the current state-of-the-art methodology and highlight current efforts on benchmarking of these methods and the importance of open science therein. Finally, we assess the current clinical impact of computer-aided methods and discuss the required next steps to increase clinical impact.
Federated Learning Enables Big Data for Rare Cancer Boundary Detection
Apr 25, 2022Abstract:Although machine learning (ML) has shown promise in numerous domains, there are concerns about generalizability to out-of-sample data. This is currently addressed by centrally sharing ample, and importantly diverse, data from multiple sites. However, such centralization is challenging to scale (or even not feasible) due to various limitations. Federated ML (FL) provides an alternative to train accurate and generalizable ML models, by only sharing numerical model updates. Here we present findings from the largest FL study to-date, involving data from 71 healthcare institutions across 6 continents, to generate an automatic tumor boundary detector for the rare disease of glioblastoma, utilizing the largest dataset of such patients ever used in the literature (25,256 MRI scans from 6,314 patients). We demonstrate a 33% improvement over a publicly trained model to delineate the surgically targetable tumor, and 23% improvement over the tumor's entire extent. We anticipate our study to: 1) enable more studies in healthcare informed by large and diverse data, ensuring meaningful results for rare diseases and underrepresented populations, 2) facilitate further quantitative analyses for glioblastoma via performance optimization of our consensus model for eventual public release, and 3) demonstrate the effectiveness of FL at such scale and task complexity as a paradigm shift for multi-site collaborations, alleviating the need for data sharing.
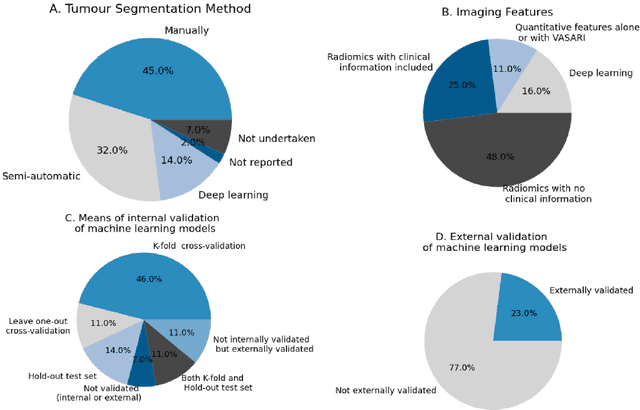
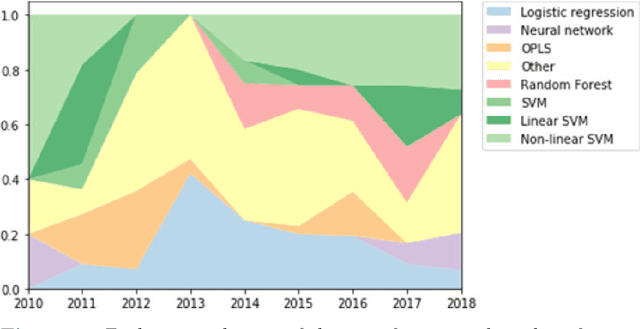
Reproducible radiomics through automated machine learning validated on twelve clinical applications
Aug 19, 2021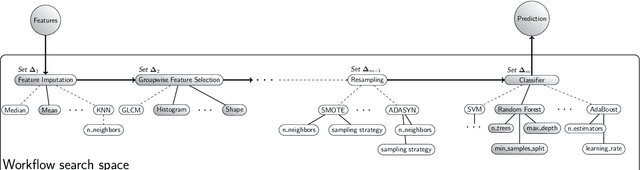
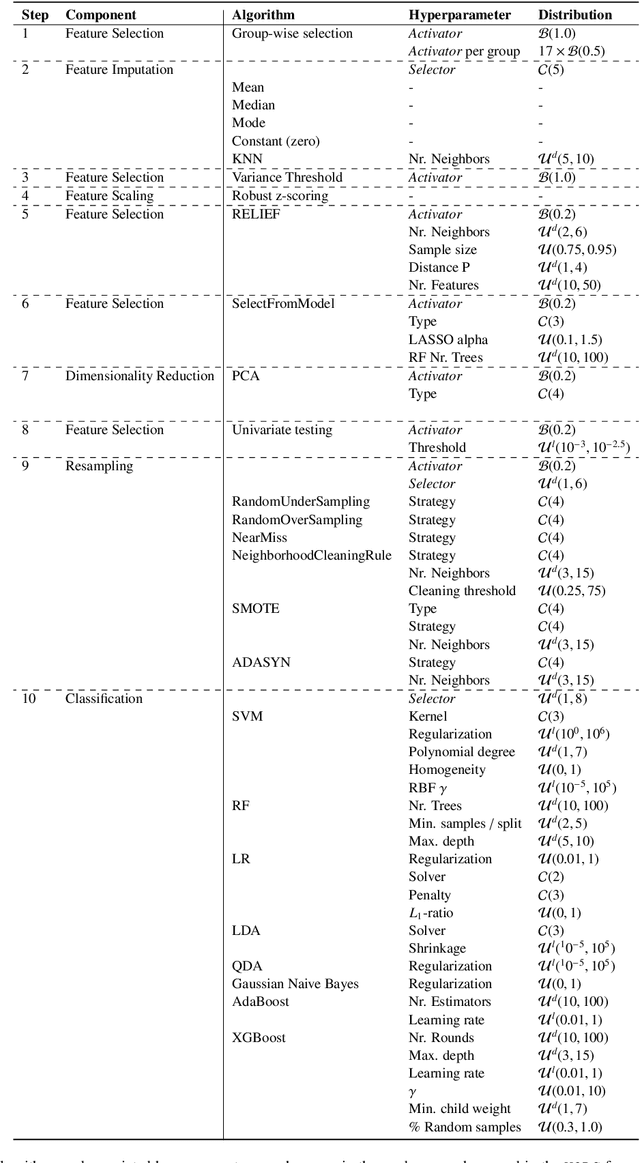
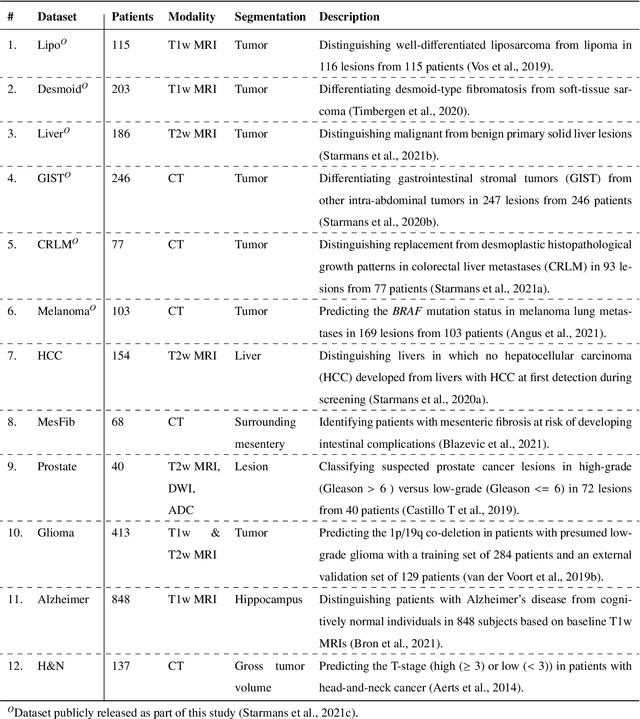
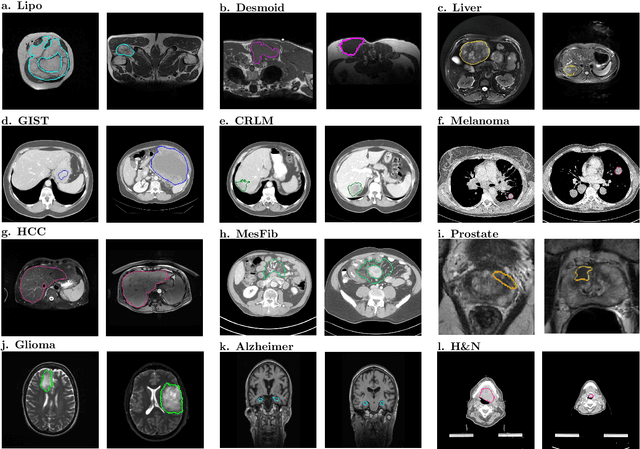
Abstract:Radiomics uses quantitative medical imaging features to predict clinical outcomes. While many radiomics methods have been described in the literature, these are generally designed for a single application. The aim of this study is to generalize radiomics across applications by proposing a framework to automatically construct and optimize the radiomics workflow per application. To this end, we formulate radiomics as a modular workflow, consisting of several components: image and segmentation preprocessing, feature extraction, feature and sample preprocessing, and machine learning. For each component, a collection of common algorithms is included. To optimize the workflow per application, we employ automated machine learning using a random search and ensembling. We evaluate our method in twelve different clinical applications, resulting in the following area under the curves: 1) liposarcoma (0.83); 2) desmoid-type fibromatosis (0.82); 3) primary liver tumors (0.81); 4) gastrointestinal stromal tumors (0.77); 5) colorectal liver metastases (0.68); 6) melanoma metastases (0.51); 7) hepatocellular carcinoma (0.75); 8) mesenteric fibrosis (0.81); 9) prostate cancer (0.72); 10) glioma (0.70); 11) Alzheimer's disease (0.87); and 12) head and neck cancer (0.84). Concluding, our method fully automatically constructs and optimizes the radiomics workflow, thereby streamlining the search for radiomics biomarkers in new applications. To facilitate reproducibility and future research, we publicly release six datasets, the software implementation of our framework (open-source), and the code to reproduce this study.
Evaluating glioma growth predictions as a forward ranking problem
Mar 22, 2021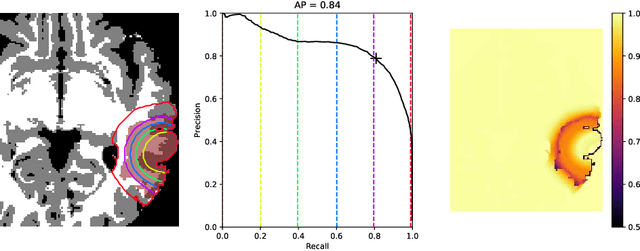
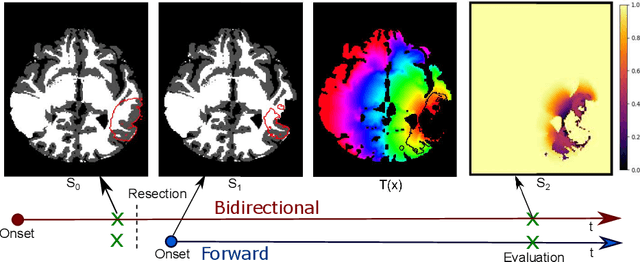
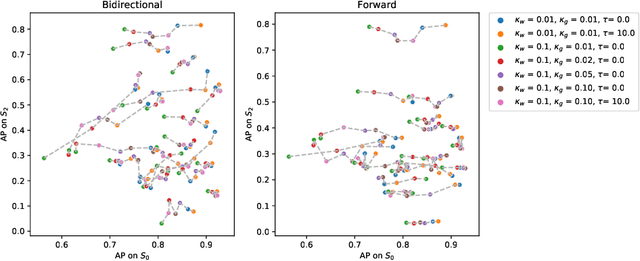
Abstract:The problem of tumor growth prediction is challenging, but promising results have been achieved with both model-driven and statistical methods. In this work, we present a framework for the evaluation of growth predictions that focuses on the spatial infiltration patterns, and specifically evaluating a prediction of future growth. We propose to frame the problem as a ranking problem rather than a segmentation problem. Using the average precision as a metric, we can evaluate the results with segmentations while using the full spatiotemporal prediction. Furthermore, by separating the model goodness-of-fit from future predictive performance, we show that in some cases, a better fit of model parameters does not guarantee a better the predictive power.
Cross-Cohort Generalizability of Deep and Conventional Machine Learning for MRI-based Diagnosis and Prediction of Alzheimer's Disease
Dec 16, 2020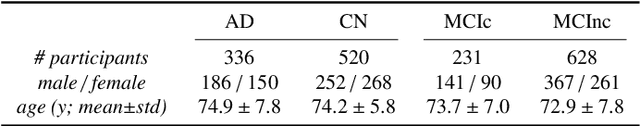
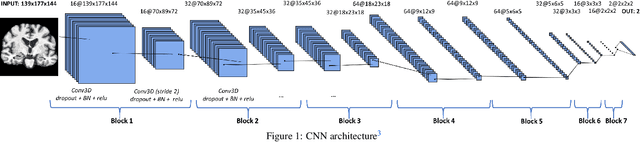
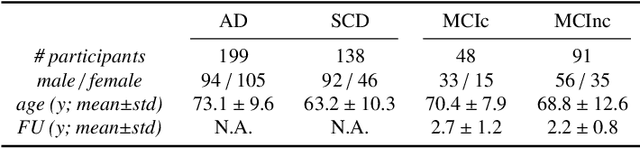
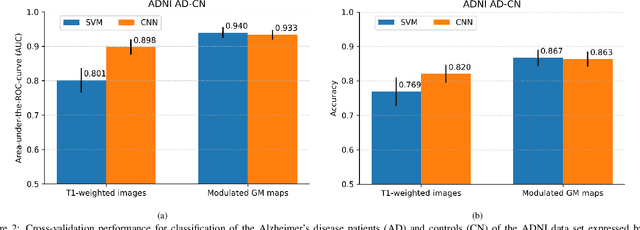
Abstract:This work validates the generalizability of MRI-based classification of Alzheimer's disease (AD) patients and controls (CN) to an external data set and to the task of prediction of conversion to AD in individuals with mild cognitive impairment (MCI). We used a conventional support vector machine (SVM) and a deep convolutional neural network (CNN) approach based on structural MRI scans that underwent either minimal pre-processing or more extensive pre-processing into modulated gray matter (GM) maps. Classifiers were optimized and evaluated using cross-validation in the ADNI (334 AD, 520 CN). Trained classifiers were subsequently applied to predict conversion to AD in ADNI MCI patients (231 converters, 628 non-converters) and in the independent Health-RI Parelsnoer data set. From this multi-center study representing a tertiary memory clinic population, we included 199 AD patients, 139 participants with subjective cognitive decline, 48 MCI patients converting to dementia, and 91 MCI patients who did not convert to dementia. AD-CN classification based on modulated GM maps resulted in a similar AUC for SVM (0.940) and CNN (0.933). Application to conversion prediction in MCI yielded significantly higher performance for SVM (0.756) than for CNN (0.742). In external validation, performance was slightly decreased. For AD-CN, it again gave similar AUCs for SVM (0.896) and CNN (0.876). For prediction in MCI, performances decreased for both SVM (0.665) and CNN (0.702). Both with SVM and CNN, classification based on modulated GM maps significantly outperformed classification based on minimally processed images. Deep and conventional classifiers performed equally well for AD classification and their performance decreased only slightly when applied to the external cohort. We expect that this work on external validation contributes towards translation of machine learning to clinical practice.
WHO 2016 subtyping and automated segmentation of glioma using multi-task deep learning
Oct 09, 2020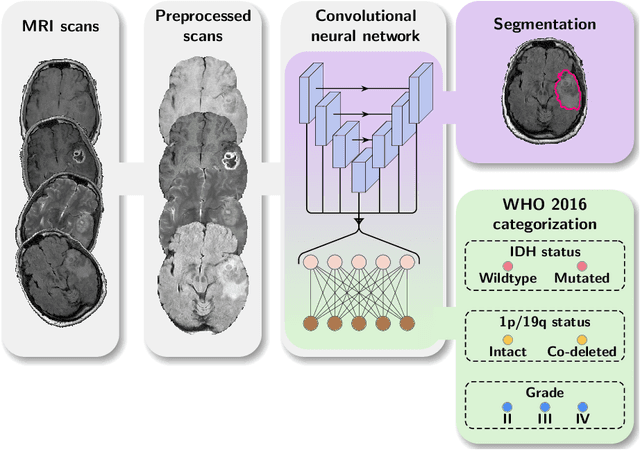
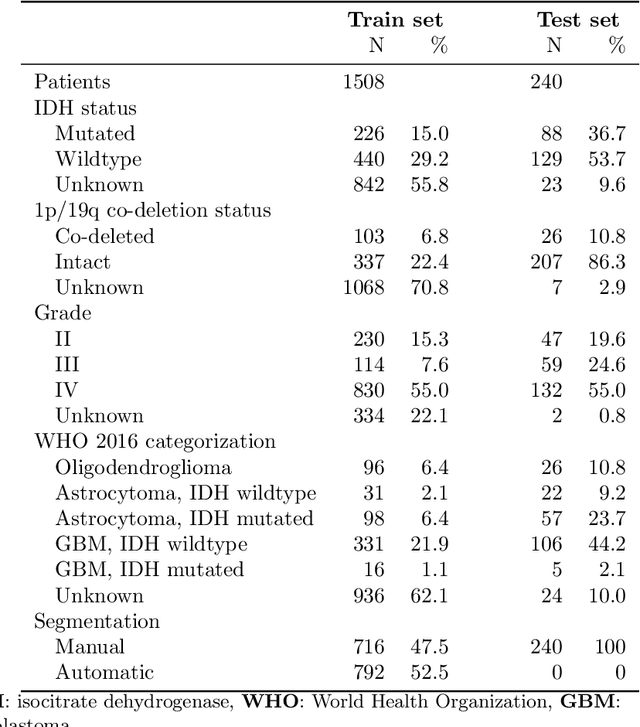
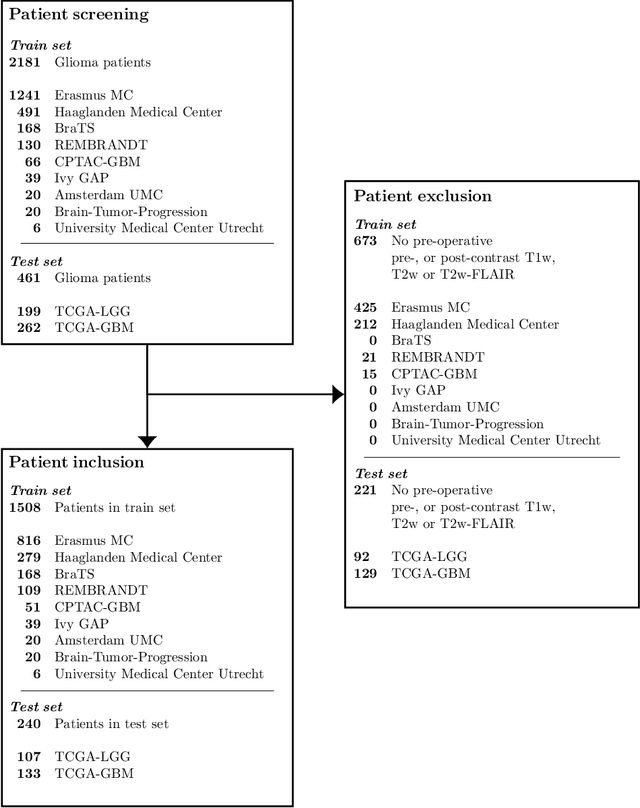
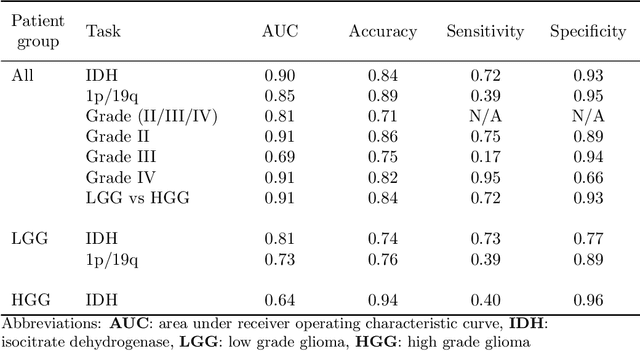
Abstract:Accurate characterization of glioma is crucial for clinical decision making. A delineation of the tumor is also desirable in the initial decision stages but is a time-consuming task. Leveraging the latest GPU capabilities, we developed a single multi-task convolutional neural network that uses the full 3D, structural, pre-operative MRI scans to can predict the IDH mutation status, the 1p/19q co-deletion status, and the grade of a tumor, while simultaneously segmenting the tumor. We trained our method using the largest, most diverse patient cohort to date containing 1508 glioma patients from 16 institutes. We tested our method on an independent dataset of 240 patients from 13 different institutes, and achieved an IDH-AUC of 0.90, 1p/19q-AUC of 0.85, grade-AUC of 0.81, and a mean whole tumor DICE score of 0.84. Thus, our method non-invasively predicts multiple, clinically relevant parameters and generalizes well to the broader clinical population.
Neuro4Neuro: A neural network approach for neural tract segmentation using large-scale population-based diffusion imaging
May 26, 2020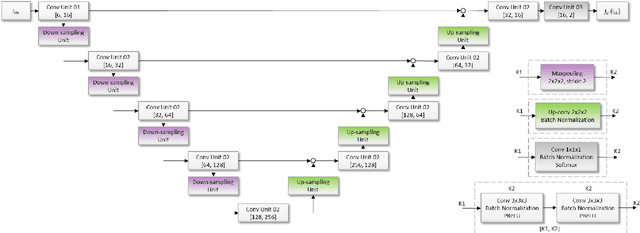
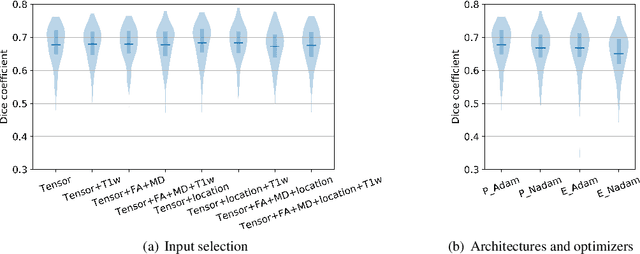
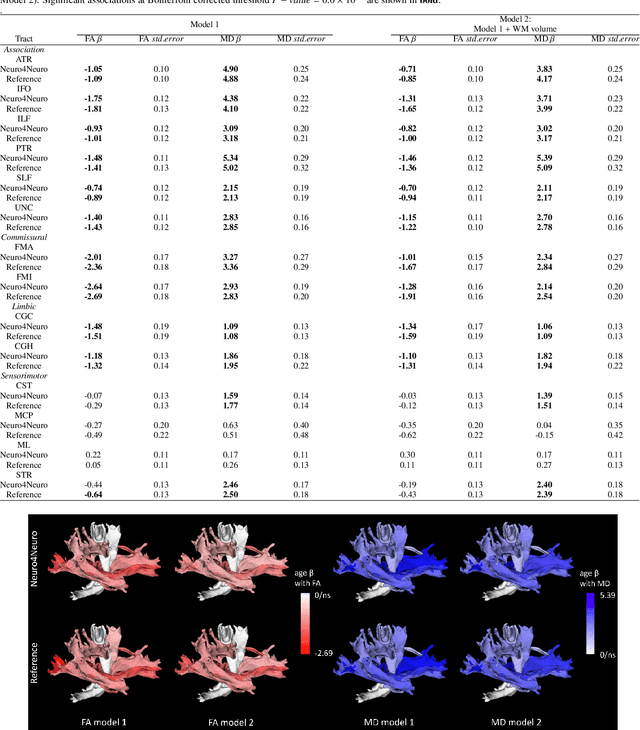
Abstract:Subtle changes in white matter (WM) microstructure have been associated with normal aging and neurodegeneration. To study these associations in more detail, it is highly important that the WM tracts can be accurately and reproducibly characterized from brain diffusion MRI. In addition, to enable analysis of WM tracts in large datasets and in clinical practice it is essential to have methodology that is fast and easy to apply. This work therefore presents a new approach for WM tract segmentation: Neuro4Neuro, that is capable of direct extraction of WM tracts from diffusion tensor images using convolutional neural network (CNN). This 3D end-to-end method is trained to segment 25 WM tracts in aging individuals from a large population-based study (N=9752, 1.5T MRI). The proposed method showed good segmentation performance and high reproducibility, i.e., a high spatial agreement (Cohen's kappa, k = 0.72 ~ 0.83) and a low scan-rescan error in tract-specific diffusion measures (e.g., fractional anisotropy: error = 1% ~ 5%). The reproducibility of the proposed method was higher than that of a tractography-based segmentation algorithm, while being orders of magnitude faster (0.5s to segment one tract). In addition, we showed that the method successfully generalizes to diffusion scans from an external dementia dataset (N=58, 3T MRI). In two proof-of-principle experiments, we associated WM microstructure obtained using the proposed method with age in a normal elderly population, and with disease subtypes in a dementia cohort. In concordance with the literature, results showed a widespread reduction of microstructural organization with aging and substantial group-wise microstructure differences between dementia subtypes. In conclusion, we presented a highly reproducible and fast method for WM tract segmentation that has the potential of being used in large-scale studies and clinical practice.
Towards continuous learning for glioma segmentation with elastic weight consolidation
Sep 25, 2019

Abstract:When finetuning a convolutional neural network (CNN) on data from a new domain, catastrophic forgetting will reduce performance on the original training data. Elastic Weight Consolidation (EWC) is a recent technique to prevent this, which we evaluated while training and re-training a CNN to segment glioma on two different datasets. The network was trained on the public BraTS dataset and finetuned on an in-house dataset with non-enhancing low-grade glioma. EWC was found to decrease catastrophic forgetting in this case, but was also found to restrict adaptation to the new domain.
Multi-modal segmentation with missing MR sequences using pre-trained fusion networks
Sep 25, 2019


Abstract:Missing data is a common problem in machine learning and in retrospective imaging research it is often encountered in the form of missing imaging modalities. We propose to take into account missing modalities in the design and training of neural networks, to ensure that they are capable of providing the best possible prediction even when multiple images are not available. The proposed network combines three modifications to the standard 3D UNet architecture: a training scheme with dropout of modalities, a multi-pathway architecture with fusion layer in the final stage, and the separate pre-training of these pathways. These modifications are evaluated incrementally in terms of performance on full and missing data, using the BraTS multi-modal segmentation challenge. The final model shows significant improvement with respect to the state of the art on missing data and requires less memory during training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge