Esther Bron
for the Heart-Brain Connection Consortium
GL-ICNN: An End-To-End Interpretable Convolutional Neural Network for the Diagnosis and Prediction of Alzheimer's Disease
Jan 20, 2025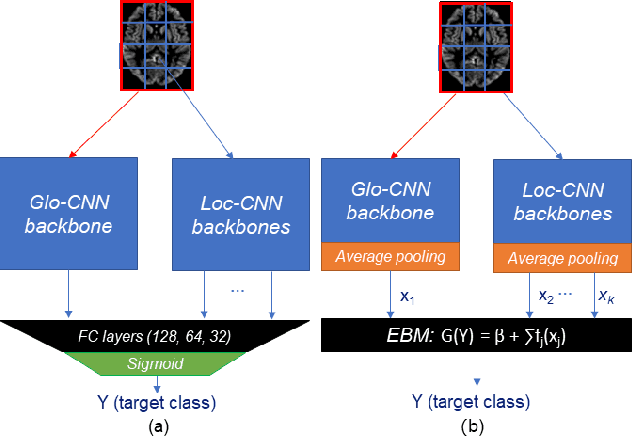
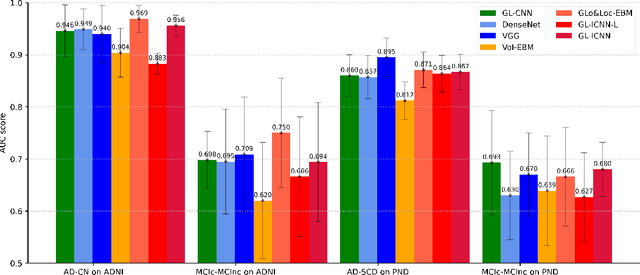
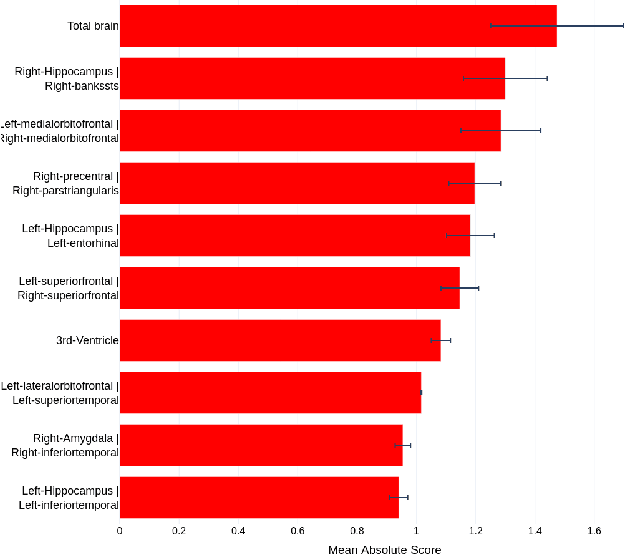
Abstract:Deep learning methods based on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) have shown great potential to improve early and accurate diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease (AD) dementia based on imaging data. However, these methods have yet to be widely adopted in clinical practice, possibly due to the limited interpretability of deep learning models. The Explainable Boosting Machine (EBM) is a glass-box model but cannot learn features directly from input imaging data. In this study, we propose a novel interpretable model that combines CNNs and EBMs for the diagnosis and prediction of AD. We develop an innovative training strategy that alternatingly trains the CNN component as a feature extractor and the EBM component as the output block to form an end-to-end model. The model takes imaging data as input and provides both predictions and interpretable feature importance measures. We validated the proposed model on the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) dataset and the Health-RI Parelsnoer Neurodegenerative Diseases Biobank (PND) as an external testing set. The proposed model achieved an area-under-the-curve (AUC) of 0.956 for AD and control classification, and 0.694 for the prediction of conversion of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) to AD on the ADNI cohort. The proposed model is a glass-box model that achieves a comparable performance with other state-of-the-art black-box models. Our code is publicly available at: https://anonymous.4open.science/r/GL-ICNN.
Deep learning-based group-wise registration for longitudinal MRI analysis in glioma
Jun 18, 2023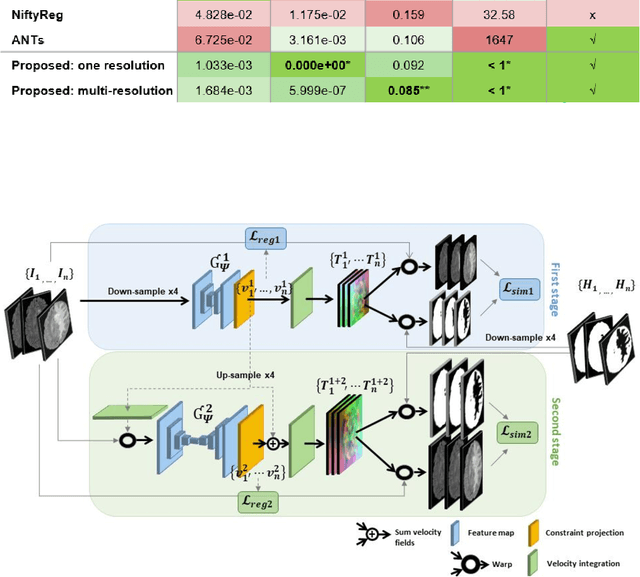
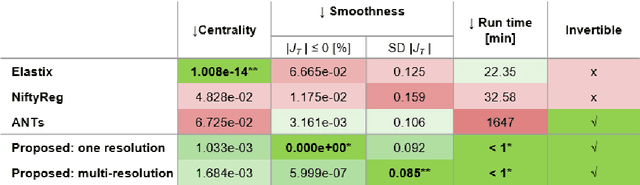
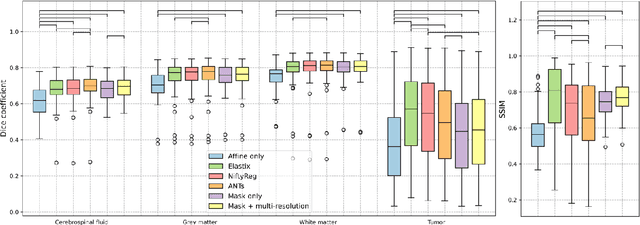
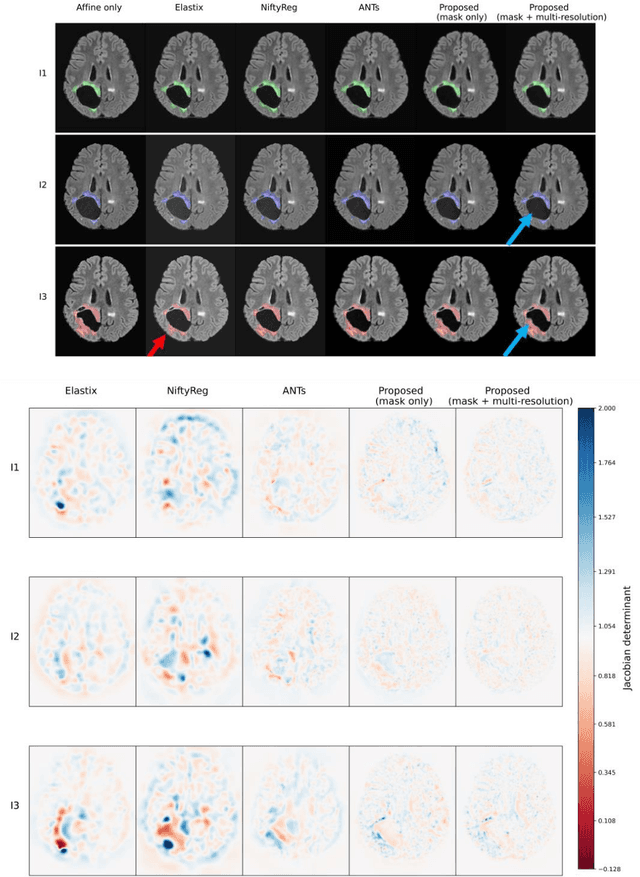
Abstract:Glioma growth may be quantified with longitudinal image registration. However, the large mass-effects and tissue changes across images pose an added challenge. Here, we propose a longitudinal, learning-based, and groupwise registration method for the accurate and unbiased registration of glioma MRI. We evaluate on a dataset from the Glioma Longitudinal AnalySiS consortium and compare it to classical registration methods. We achieve comparable Dice coefficients, with more detailed registrations, while significantly reducing the runtime to under a minute. The proposed methods may serve as an alternative to classical toolboxes, to provide further insight into glioma growth.
Prior-knowledge-informed deep learning for lacune detection and quantification using multi-site brain MRI
Jun 18, 2023

Abstract:Lacunes of presumed vascular origin, also referred to as lacunar infarcts, are important to assess cerebral small vessel disease and cognitive diseases such as dementia. However, visual rating of lacunes from imaging data is challenging, time-consuming, and rater-dependent, owing to their small size, sparsity, and mimics. Whereas recent developments in automatic algorithms have shown to make the detection of lacunes faster while preserving sensitivity, they also showed a large number of false positives, which makes them impractical for use in clinical practice or large-scale studies. Here, we develop a novel framework that, in addition to lacune detection, outputs a categorical burden score. This score could provide a more practical estimate of lacune presence that simplifies and effectively accelerates the imaging assessment of lacunes. We hypothesize that the combination of detection and the categorical score makes the procedure less sensitive to noisy labels.
Projection-wise Disentangling for Fair and Interpretable Representation Learning: Application to 3D Facial Shape Analysis
Jun 28, 2021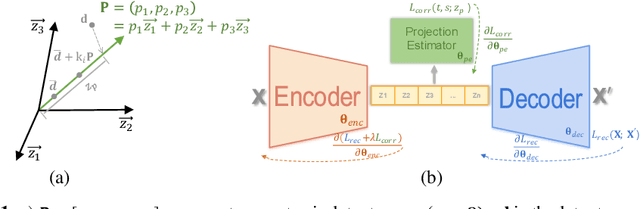
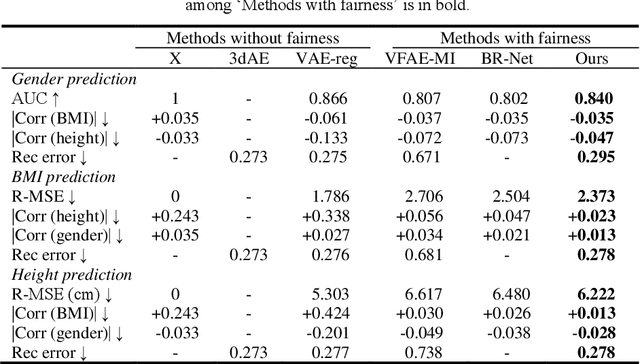
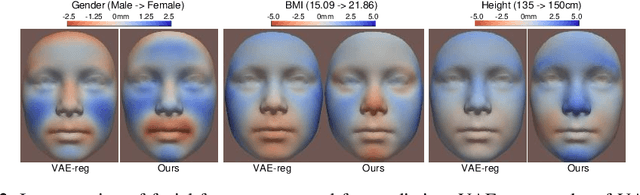
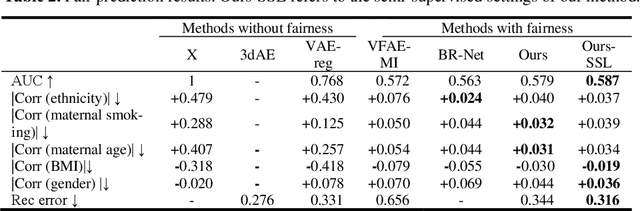
Abstract:Confounding bias is a crucial problem when applying machine learning to practice, especially in clinical practice. We consider the problem of learning representations independent to multiple biases. In literature, this is mostly solved by purging the bias information from learned representations. We however expect this strategy to harm the diversity of information in the representation, and thus limiting its prospective usage (e.g., interpretation). Therefore, we propose to mitigate the bias while keeping almost all information in the latent representations, which enables us to observe and interpret them as well. To achieve this, we project latent features onto a learned vector direction, and enforce the independence between biases and projected features rather than all learned features. To interpret the mapping between projected features and input data, we propose projection-wise disentangling: a sampling and reconstruction along the learned vector direction. The proposed method was evaluated on the analysis of 3D facial shape and patient characteristics (N=5011). Experiments showed that this conceptually simple method achieved state-of-the-art fair prediction performance and interpretability, showing its great potential for clinical applications.
Reproducible White Matter Tract Segmentation Using 3D U-Net on a Large-scale DTI Dataset
Aug 26, 2019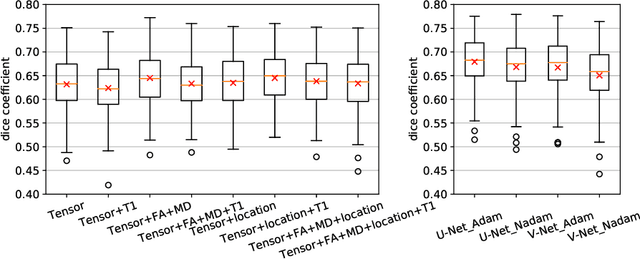
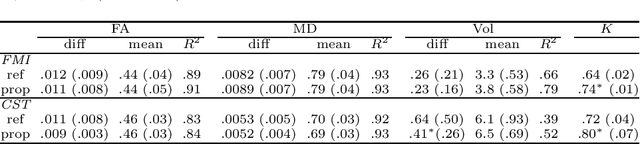
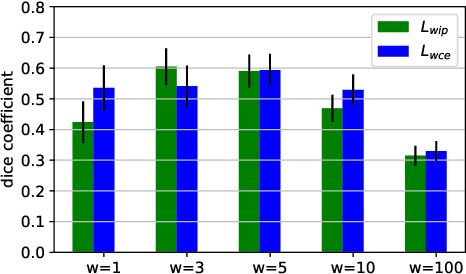
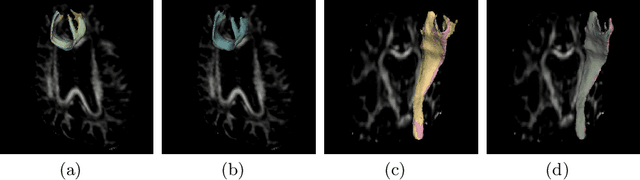
Abstract:Tract-specific diffusion measures, as derived from brain diffusion MRI, have been linked to white matter tract structural integrity and neurodegeneration. As a consequence, there is a large interest in the automatic segmentation of white matter tract in diffusion tensor MRI data. Methods based on the tractography are popular for white matter tract segmentation. However, because of the limited consistency and long processing time, such methods may not be suitable for clinical practice. We therefore developed a novel convolutional neural network based method to directly segment white matter tract trained on a low-resolution dataset of 9149 DTI images. The method is optimized on input, loss function and network architecture selections. We evaluated both segmentation accuracy and reproducibility, and reproducibility of determining tract-specific diffusion measures. The reproducibility of the method is higher than that of the reference standard and the determined diffusion measures are consistent. Therefore, we expect our method to be applicable in clinical practice and in longitudinal analysis of white matter microstructure.
A hybrid deep learning framework for integrated segmentation and registration: evaluation on longitudinal white matter tract changes
Aug 26, 2019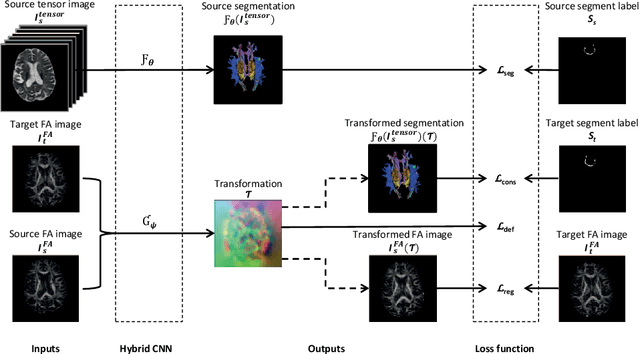
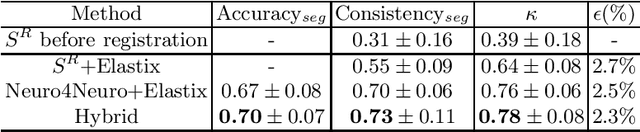
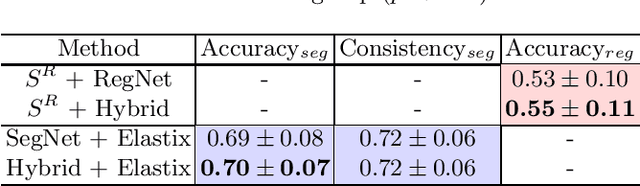
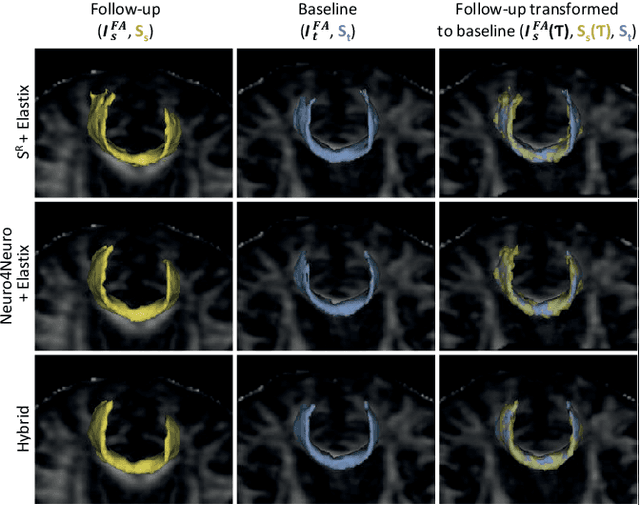
Abstract:To accurately analyze changes of anatomical structures in longitudinal imaging studies, consistent segmentation across multiple time-points is required. Existing solutions often involve independent registration and segmentation components. Registration between time-points is used either as a prior for segmentation in a subsequent time point or to perform segmentation in a common space. In this work, we propose a novel hybrid convolutional neural network (CNN) that integrates segmentation and registration into a single procedure. We hypothesize that the joint optimization leads to increased performance on both tasks. The hybrid CNN is trained by minimizing an integrated loss function composed of four different terms, measuring segmentation accuracy, similarity between registered images, deformation field smoothness, and segmentation consistency. We applied this method to the segmentation of white matter tracts, describing functionally grouped axonal fibers, using N=8045 longitudinal brain MRI data of 3249 individuals. The proposed method was compared with two multistage pipelines using two existing segmentation methods combined with a conventional deformable registration algorithm. In addition, we assessed the added value of the joint optimization for segmentation and registration separately. The hybrid CNN yielded significantly higher accuracy, consistency and reproducibility of segmentation than the multistage pipelines, and was orders of magnitude faster. Therefore, we expect it can serve as a novel tool to support clinical and epidemiological analyses on understanding microstructural brain changes over time.
A Discriminative Event Based Model for Alzheimer's Disease Progression Modeling
Feb 21, 2017
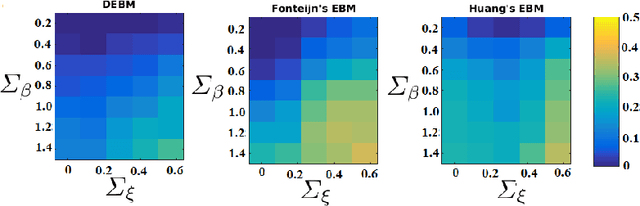
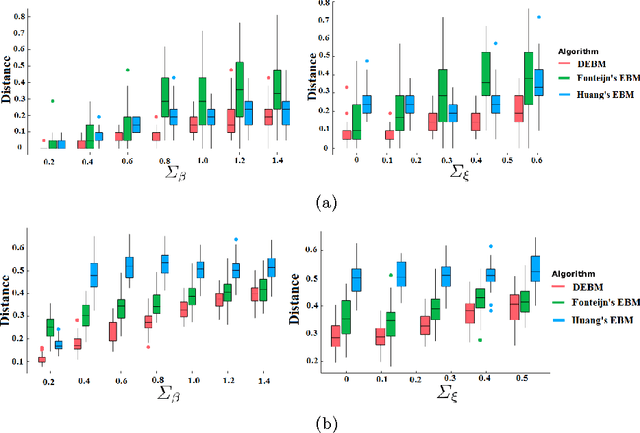
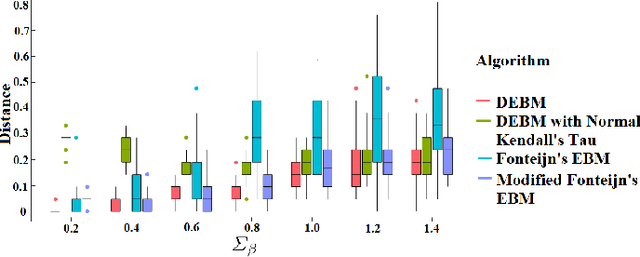
Abstract:The event-based model (EBM) for data-driven disease progression modeling estimates the sequence in which biomarkers for a disease become abnormal. This helps in understanding the dynamics of disease progression and facilitates early diagnosis by staging patients on a disease progression timeline. Existing EBM methods are all generative in nature. In this work we propose a novel discriminative approach to EBM, which is shown to be more accurate as well as computationally more efficient than existing state-of-the art EBM methods. The method first estimates for each subject an approximate ordering of events, by ranking the posterior probabilities of individual biomarkers being abnormal. Subsequently, the central ordering over all subjects is estimated by fitting a generalized Mallows model to these approximate subject-specific orderings based on a novel probabilistic Kendall's Tau distance. To evaluate the accuracy, we performed extensive experiments on synthetic data simulating the progression of Alzheimer's disease. Subsequently, the method was applied to the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) data to estimate the central event ordering in the dataset. The experiments benchmark the accuracy of the new model under various conditions and compare it with existing state-of-the-art EBM methods. The results indicate that discriminative EBM could be a simple and elegant approach to disease progression modeling.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge