Jeroen de Bresser
for the Heart-Brain Connection Consortium
Prior-knowledge-informed deep learning for lacune detection and quantification using multi-site brain MRI
Jun 18, 2023

Abstract:Lacunes of presumed vascular origin, also referred to as lacunar infarcts, are important to assess cerebral small vessel disease and cognitive diseases such as dementia. However, visual rating of lacunes from imaging data is challenging, time-consuming, and rater-dependent, owing to their small size, sparsity, and mimics. Whereas recent developments in automatic algorithms have shown to make the detection of lacunes faster while preserving sensitivity, they also showed a large number of false positives, which makes them impractical for use in clinical practice or large-scale studies. Here, we develop a novel framework that, in addition to lacune detection, outputs a categorical burden score. This score could provide a more practical estimate of lacune presence that simplifies and effectively accelerates the imaging assessment of lacunes. We hypothesize that the combination of detection and the categorical score makes the procedure less sensitive to noisy labels.
Standardized Assessment of Automatic Segmentation of White Matter Hyperintensities and Results of the WMH Segmentation Challenge
Apr 01, 2019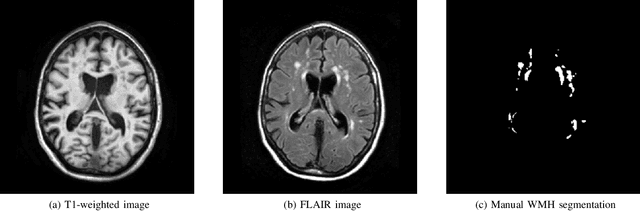
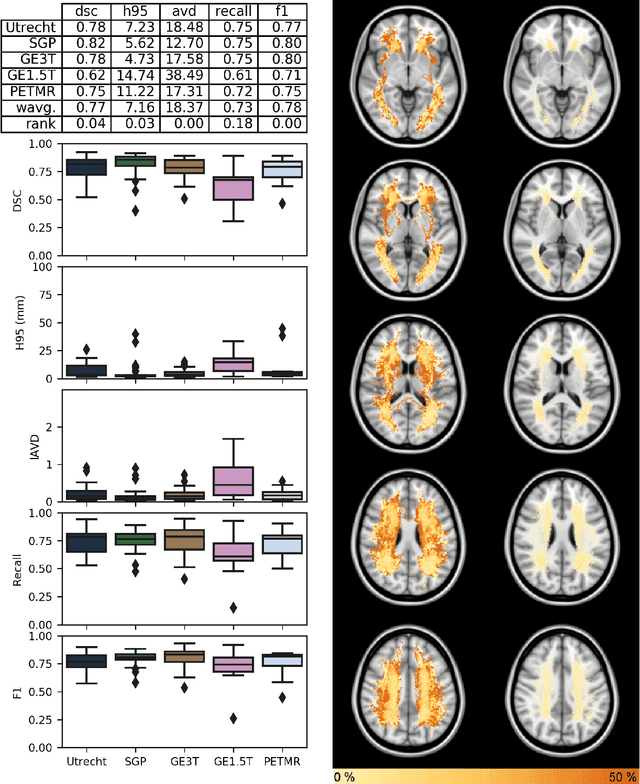
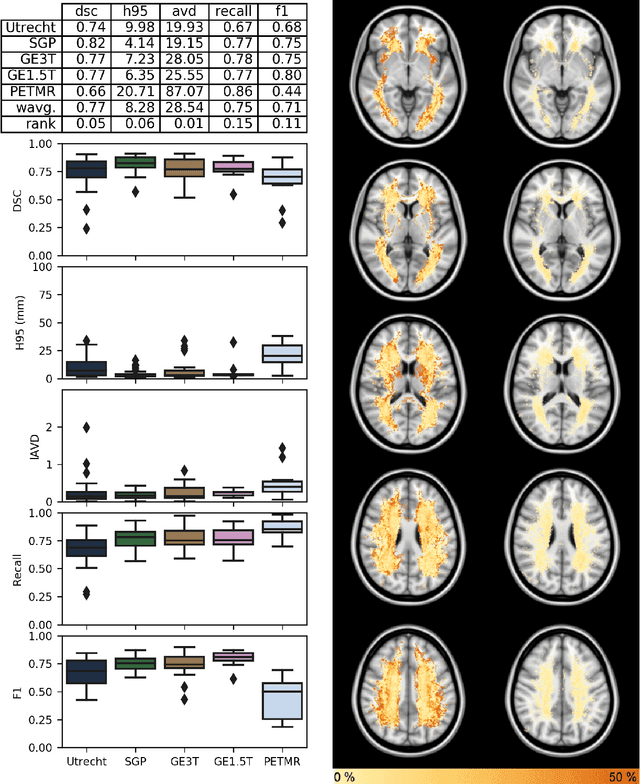
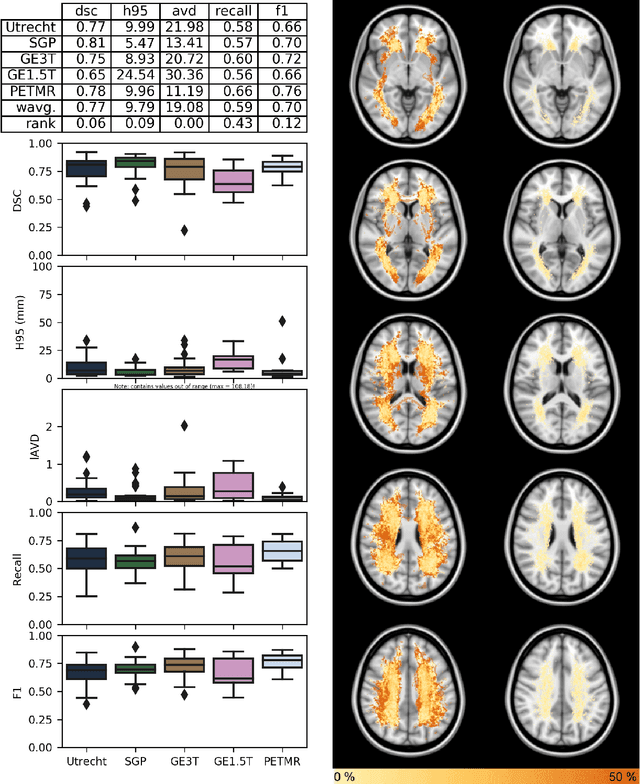
Abstract:Quantification of cerebral white matter hyperintensities (WMH) of presumed vascular origin is of key importance in many neurological research studies. Currently, measurements are often still obtained from manual segmentations on brain MR images, which is a laborious procedure. Automatic WMH segmentation methods exist, but a standardized comparison of the performance of such methods is lacking. We organized a scientific challenge, in which developers could evaluate their method on a standardized multi-center/-scanner image dataset, giving an objective comparison: the WMH Segmentation Challenge (https://wmh.isi.uu.nl/). Sixty T1+FLAIR images from three MR scanners were released with manual WMH segmentations for training. A test set of 110 images from five MR scanners was used for evaluation. Segmentation methods had to be containerized and submitted to the challenge organizers. Five evaluation metrics were used to rank the methods: (1) Dice similarity coefficient, (2) modified Hausdorff distance (95th percentile), (3) absolute log-transformed volume difference, (4) sensitivity for detecting individual lesions, and (5) F1-score for individual lesions. Additionally, methods were ranked on their inter-scanner robustness. Twenty participants submitted their method for evaluation. This paper provides a detailed analysis of the results. In brief, there is a cluster of four methods that rank significantly better than the other methods, with one clear winner. The inter-scanner robustness ranking shows that not all methods generalize to unseen scanners. The challenge remains open for future submissions and provides a public platform for method evaluation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge