Luyao Ma
Is Your World Simulator a Good Story Presenter? A Consecutive Events-Based Benchmark for Future Long Video Generation
Dec 17, 2024
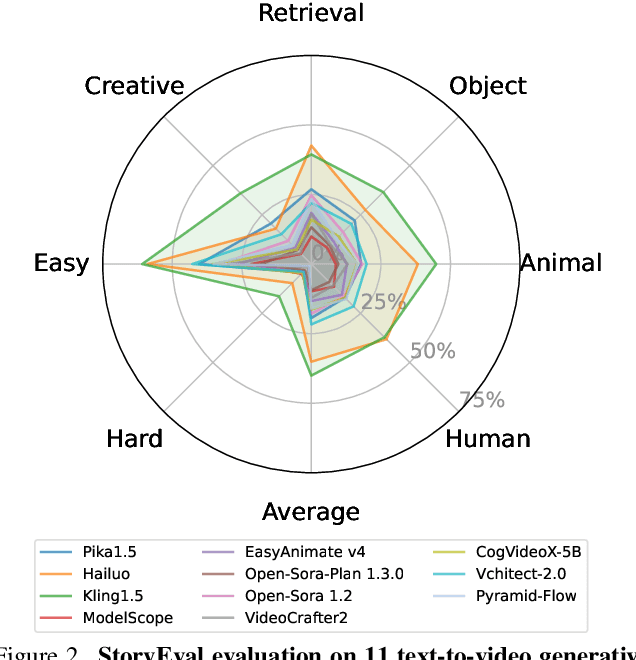


Abstract:The current state-of-the-art video generative models can produce commercial-grade videos with highly realistic details. However, they still struggle to coherently present multiple sequential events in the stories specified by the prompts, which is foreseeable an essential capability for future long video generation scenarios. For example, top T2V generative models still fail to generate a video of the short simple story 'how to put an elephant into a refrigerator.' While existing detail-oriented benchmarks primarily focus on fine-grained metrics like aesthetic quality and spatial-temporal consistency, they fall short of evaluating models' abilities to handle event-level story presentation. To address this gap, we introduce StoryEval, a story-oriented benchmark specifically designed to assess text-to-video (T2V) models' story-completion capabilities. StoryEval features 423 prompts spanning 7 classes, each representing short stories composed of 2-4 consecutive events. We employ advanced vision-language models, such as GPT-4V and LLaVA-OV-Chat-72B, to verify the completion of each event in the generated videos, applying a unanimous voting method to enhance reliability. Our methods ensure high alignment with human evaluations, and the evaluation of 11 models reveals its challenge, with none exceeding an average story-completion rate of 50%. StoryEval provides a new benchmark for advancing T2V models and highlights the challenges and opportunities in developing next-generation solutions for coherent story-driven video generation.
Enhancing AI microscopy for foodborne bacterial classification via adversarial domain adaptation across optical and biological variability
Nov 29, 2024Abstract:Rapid detection of foodborne bacteria is critical for food safety and quality, yet traditional culture-based methods require extended incubation and specialized sample preparation. This study addresses these challenges by i) enhancing the generalizability of AI-enabled microscopy for bacterial classification using adversarial domain adaptation and ii) comparing the performance of single-target and multi-domain adaptation. Three Gram-positive (Bacillus coagulans, Bacillus subtilis, Listeria innocua) and three Gram-negative (E. coli, Salmonella Enteritidis, Salmonella Typhimurium) strains were classified. EfficientNetV2 served as the backbone architecture, leveraging fine-grained feature extraction for small targets. Few-shot learning enabled scalability, with domain-adversarial neural networks (DANNs) addressing single domains and multi-DANNs (MDANNs) generalizing across all target domains. The model was trained on source domain data collected under controlled conditions (phase contrast microscopy, 60x magnification, 3-h bacterial incubation) and evaluated on target domains with variations in microscopy modality (brightfield, BF), magnification (20x), and extended incubation to compensate for lower resolution (20x-5h). DANNs improved target domain classification accuracy by up to 54.45% (20x), 43.44% (20x-5h), and 31.67% (BF), with minimal source domain degradation (<4.44%). MDANNs achieved superior performance in the BF domain and substantial gains in the 20x domain. Grad-CAM and t-SNE visualizations validated the model's ability to learn domain-invariant features across diverse conditions. This study presents a scalable and adaptable framework for bacterial classification, reducing reliance on extensive sample preparation and enabling application in decentralized and resource-limited environments.
Baichuan 2: Open Large-scale Language Models
Sep 20, 2023Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable performance on a variety of natural language tasks based on just a few examples of natural language instructions, reducing the need for extensive feature engineering. However, most powerful LLMs are closed-source or limited in their capability for languages other than English. In this technical report, we present Baichuan 2, a series of large-scale multilingual language models containing 7 billion and 13 billion parameters, trained from scratch, on 2.6 trillion tokens. Baichuan 2 matches or outperforms other open-source models of similar size on public benchmarks like MMLU, CMMLU, GSM8K, and HumanEval. Furthermore, Baichuan 2 excels in vertical domains such as medicine and law. We will release all pre-training model checkpoints to benefit the research community in better understanding the training dynamics of Baichuan 2.
Legal Judgment Prediction with Multi-Stage CaseRepresentation Learning in the Real Court Setting
Jul 12, 2021



Abstract:Legal judgment prediction(LJP) is an essential task for legal AI. While prior methods studied on this topic in a pseudo setting by employing the judge-summarized case narrative as the input to predict the judgment, neglecting critical case life-cycle information in real court setting could threaten the case logic representation quality and prediction correctness. In this paper, we introduce a novel challenging dataset from real courtrooms to predict the legal judgment in a reasonably encyclopedic manner by leveraging the genuine input of the case -- plaintiff's claims and court debate data, from which the case's facts are automatically recognized by comprehensively understanding the multi-role dialogues of the court debate, and then learnt to discriminate the claims so as to reach the final judgment through multi-task learning. An extensive set of experiments with a large civil trial data set shows that the proposed model can more accurately characterize the interactions among claims, fact and debate for legal judgment prediction, achieving significant improvements over strong state-of-the-art baselines. Moreover, the user study conducted with real judges and law school students shows the neural predictions can also be interpretable and easily observed, and thus enhancing the trial efficiency and judgment quality.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge