Mason Earles
California Crop Yield Benchmark: Combining Satellite Image, Climate, Evapotranspiration, and Soil Data Layers for County-Level Yield Forecasting of Over 70 Crops
Jun 11, 2025



Abstract:California is a global leader in agricultural production, contributing 12.5% of the United States total output and ranking as the fifth-largest food and cotton supplier in the world. Despite the availability of extensive historical yield data from the USDA National Agricultural Statistics Service, accurate and timely crop yield forecasting remains a challenge due to the complex interplay of environmental, climatic, and soil-related factors. In this study, we introduce a comprehensive crop yield benchmark dataset covering over 70 crops across all California counties from 2008 to 2022. The benchmark integrates diverse data sources, including Landsat satellite imagery, daily climate records, monthly evapotranspiration, and high-resolution soil properties. To effectively learn from these heterogeneous inputs, we develop a multi-modal deep learning model tailored for county-level, crop-specific yield forecasting. The model employs stratified feature extraction and a timeseries encoder to capture spatial and temporal dynamics during the growing season. Static inputs such as soil characteristics and crop identity inform long-term variability. Our approach achieves an overall R2 score of 0.76 across all crops of unseen test dataset, highlighting strong predictive performance across California diverse agricultural regions. This benchmark and modeling framework offer a valuable foundation for advancing agricultural forecasting, climate adaptation, and precision farming. The full dataset and codebase are publicly available at our GitHub repository.
AgRowStitch: A High-fidelity Image Stitching Pipeline for Ground-based Agricultural Images
Mar 27, 2025Abstract:Agricultural imaging often requires individual images to be stitched together into a final mosaic for analysis. However, agricultural images can be particularly challenging to stitch because feature matching across images is difficult due to repeated textures, plants are non-planar, and mosaics built from many images can accumulate errors that cause drift. Although these issues can be mitigated by using georeferenced images or taking images at high altitude, there is no general solution for images taken close to the crop. To address this, we created a user-friendly and open source pipeline for stitching ground-based images of a linear row of crops that does not rely on additional data. First, we use SuperPoint and LightGlue to extract and match features within small batches of images. Then we stitch the images in each batch in series while imposing constraints on the camera movement. After straightening and rescaling each batch mosaic, all batch mosaics are stitched together in series and then straightened into a final mosaic. We tested the pipeline on images collected along 72 m long rows of crops using two different agricultural robots and a camera manually carried over the row. In all three cases, the pipeline produced high-quality mosaics that could be used to georeference real world positions with a mean absolute error of 20 cm. This approach provides accessible leaf-scale stitching to users who need to coarsely georeference positions within a row, but do not have access to accurate positional data or sophisticated imaging systems.
iNatAg: Multi-Class Classification Models Enabled by a Large-Scale Benchmark Dataset with 4.7M Images of 2,959 Crop and Weed Species
Mar 25, 2025Abstract:Accurate identification of crop and weed species is critical for precision agriculture and sustainable farming. However, it remains a challenging task due to a variety of factors -- a high degree of visual similarity among species, environmental variability, and a continued lack of large, agriculture-specific image data. We introduce iNatAg, a large-scale image dataset which contains over 4.7 million images of 2,959 distinct crop and weed species, with precise annotations along the taxonomic hierarchy from binary crop/weed labels to specific species labels. Curated from the broader iNaturalist database, iNatAg contains data from every continent and accurately reflects the variability of natural image captures and environments. Enabled by this data, we train benchmark models built upon the Swin Transformer architecture and evaluate the impact of various modifications such as the incorporation of geospatial data and LoRA finetuning. Our best models achieve state-of-the-art performance across all taxonomic classification tasks, achieving 92.38\% on crop and weed classification. Furthermore, the scale of our dataset enables us to explore incorrect misclassifications and unlock new analytic possiblities for plant species. By combining large-scale species coverage, multi-task labels, and geographic diversity, iNatAg provides a new foundation for building robust, geolocation-aware agricultural classification systems. We release the iNatAg dataset publicly through AgML (https://github.com/Project-AgML/AgML), enabling direct access and integration into agricultural machine learning workflows.
Enhancing AI microscopy for foodborne bacterial classification via adversarial domain adaptation across optical and biological variability
Nov 29, 2024Abstract:Rapid detection of foodborne bacteria is critical for food safety and quality, yet traditional culture-based methods require extended incubation and specialized sample preparation. This study addresses these challenges by i) enhancing the generalizability of AI-enabled microscopy for bacterial classification using adversarial domain adaptation and ii) comparing the performance of single-target and multi-domain adaptation. Three Gram-positive (Bacillus coagulans, Bacillus subtilis, Listeria innocua) and three Gram-negative (E. coli, Salmonella Enteritidis, Salmonella Typhimurium) strains were classified. EfficientNetV2 served as the backbone architecture, leveraging fine-grained feature extraction for small targets. Few-shot learning enabled scalability, with domain-adversarial neural networks (DANNs) addressing single domains and multi-DANNs (MDANNs) generalizing across all target domains. The model was trained on source domain data collected under controlled conditions (phase contrast microscopy, 60x magnification, 3-h bacterial incubation) and evaluated on target domains with variations in microscopy modality (brightfield, BF), magnification (20x), and extended incubation to compensate for lower resolution (20x-5h). DANNs improved target domain classification accuracy by up to 54.45% (20x), 43.44% (20x-5h), and 31.67% (BF), with minimal source domain degradation (<4.44%). MDANNs achieved superior performance in the BF domain and substantial gains in the 20x domain. Grad-CAM and t-SNE visualizations validated the model's ability to learn domain-invariant features across diverse conditions. This study presents a scalable and adaptable framework for bacterial classification, reducing reliance on extensive sample preparation and enabling application in decentralized and resource-limited environments.
DAVIS-Ag: A Synthetic Plant Dataset for Developing Domain-Inspired Active Vision in Agricultural Robots
Mar 10, 2023



Abstract:In agricultural environments, viewpoint planning can be a critical functionality for a robot with visual sensors to obtain informative observations of objects of interest (e.g., fruits) from complex structures of plant with random occlusions. Although recent studies on active vision have shown some potential for agricultural tasks, each model has been designed and validated on a unique environment that would not easily be replicated for benchmarking novel methods being developed later. In this paper, hence, we introduce a dataset for more extensive research on Domain-inspired Active VISion in Agriculture (DAVIS-Ag). To be specific, we utilized our open-source "AgML" framework and the 3D plant simulator of "Helios" to produce 502K RGB images from 30K dense spatial locations in 632 realistically synthesized orchards of strawberries, tomatoes, and grapes. In addition, useful labels are provided for each image, including (1) bounding boxes and (2) pixel-wise instance segmentations for all identifiable fruits, and also (3) pointers to other images that are reachable by an execution of action so as to simulate the active selection of viewpoint at each time step. Using DAVIS-Ag, we show the motivating examples in which performance of fruit detection for the same plant can significantly vary depending on the position and orientation of camera view primarily due to occlusions by other components such as leaves. Furthermore, we develop several baseline models to showcase the "usage" of data with one of agricultural active vision tasks--fruit search optimization--providing evaluation results against which future studies could benchmark their methodologies. For encouraging relevant research, our dataset is released online to be freely available at: https://github.com/ctyeong/DAVIS-Ag
Standardizing and Centralizing Datasets to Enable Efficient Training of Agricultural Deep Learning Models
Aug 04, 2022
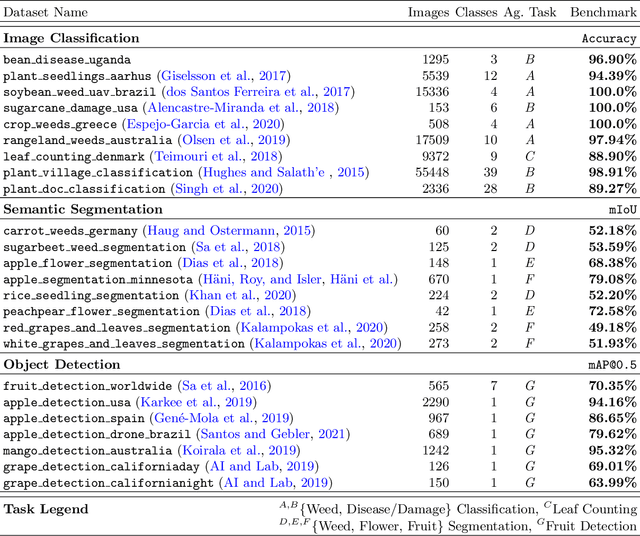
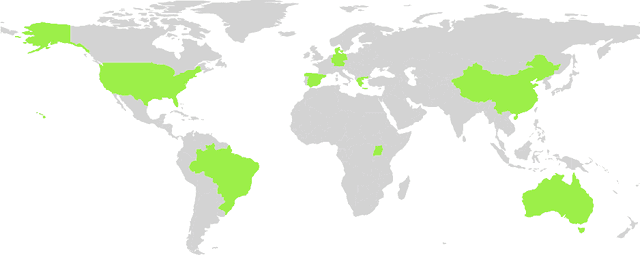
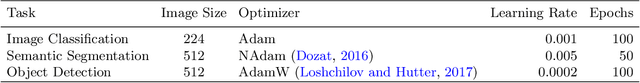
Abstract:In recent years, deep learning models have become the standard for agricultural computer vision. Such models are typically fine-tuned to agricultural tasks using model weights that were originally fit to more general, non-agricultural datasets. This lack of agriculture-specific fine-tuning potentially increases training time and resource use, and decreases model performance, leading an overall decrease in data efficiency. To overcome this limitation, we collect a wide range of existing public datasets for three distinct tasks, standardize them, and construct standard training and evaluation pipelines, providing us with a set of benchmarks and pretrained models. We then conduct a number of experiments using methods which are commonly used in deep learning tasks, but unexplored in their domain-specific applications for agriculture. Our experiments guide us in developing a number of approaches to improve data efficiency when training agricultural deep learning models, without large-scale modifications to existing pipelines. Our results demonstrate that even slight training modifications, such as using agricultural pretrained model weights, or adopting specific spatial augmentations into data processing pipelines, can significantly boost model performance and result in shorter convergence time, saving training resources. Furthermore, we find that even models trained on low-quality annotations can produce comparable levels of performance to their high-quality equivalents, suggesting that datasets with poor annotations can still be used for training, expanding the pool of currently available datasets. Our methods are broadly applicable throughout agricultural deep learning, and present high potential for significant data efficiency improvements.
Simultaneously Predicting Multiple Plant Traits from Multiple Sensors via Deformable CNN Regression
Dec 06, 2021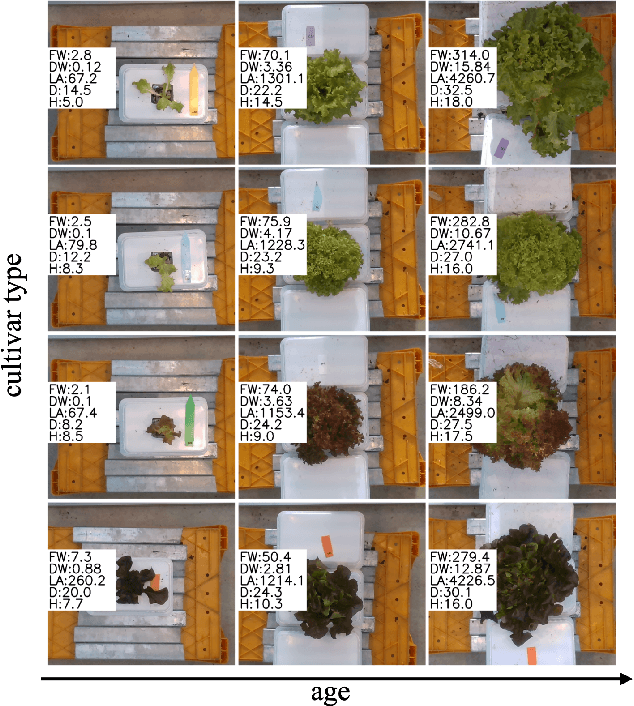
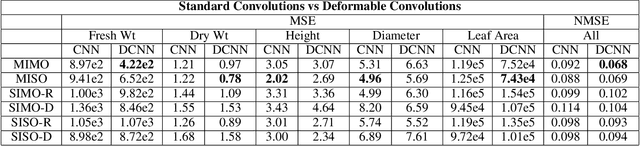
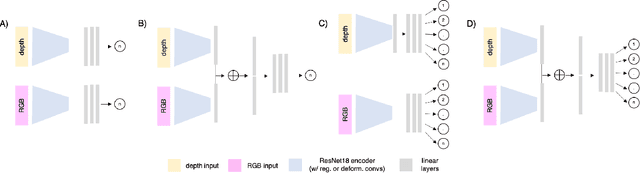
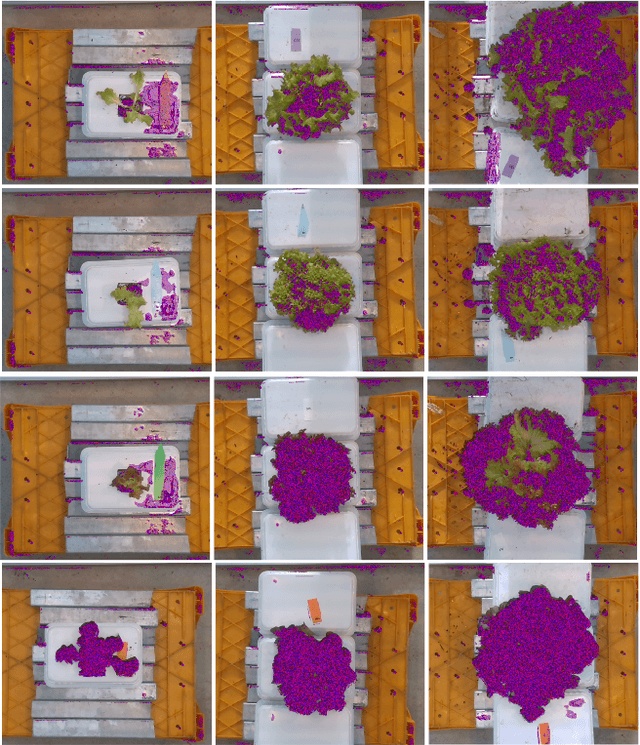
Abstract:Trait measurement is critical for the plant breeding and agricultural production pipeline. Typically, a suite of plant traits is measured using laborious manual measurements and then used to train and/or validate higher throughput trait estimation techniques. Here, we introduce a relatively simple convolutional neural network (CNN) model that accepts multiple sensor inputs and predicts multiple continuous trait outputs - i.e. a multi-input, multi-output CNN (MIMO-CNN). Further, we introduce deformable convolutional layers into this network architecture (MIMO-DCNN) to enable the model to adaptively adjust its receptive field, model complex variable geometric transformations in the data, and fine-tune the continuous trait outputs. We examine how the MIMO-CNN and MIMO-DCNN models perform on a multi-input (i.e. RGB and depth images), multi-trait output lettuce dataset from the 2021 Autonomous Greenhouse Challenge. Ablation studies were conducted to examine the effect of using single versus multiple inputs, and single versus multiple outputs. The MIMO-DCNN model resulted in a normalized mean squared error (NMSE) of 0.068 - a substantial improvement over the top 2021 leaderboard score of 0.081. Open-source code is provided.
Enlisting 3D Crop Models and GANs for More Data Efficient and Generalizable Fruit Detection
Aug 30, 2021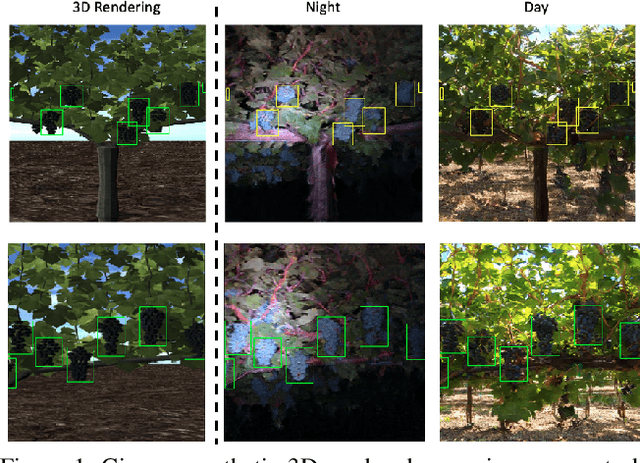
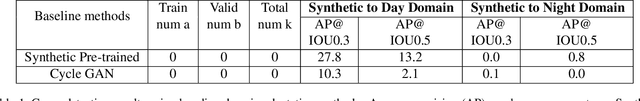

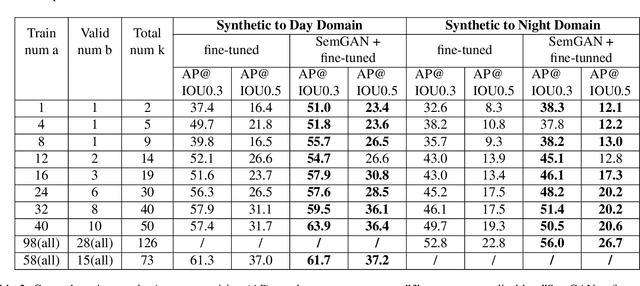
Abstract:Training real-world neural network models to achieve high performance and generalizability typically requires a substantial amount of labeled data, spanning a broad range of variation. This data-labeling process can be both labor and cost intensive. To achieve desirable predictive performance, a trained model is typically applied into a domain where the data distribution is similar to the training dataset. However, for many agricultural machine learning problems, training datasets are collected at a specific location, during a specific period in time of the growing season. Since agricultural systems exhibit substantial variability in terms of crop type, cultivar, management, seasonal growth dynamics, lighting condition, sensor type, etc, a model trained from one dataset often does not generalize well across domains. To enable more data efficient and generalizable neural network models in agriculture, we propose a method that generates photorealistic agricultural images from a synthetic 3D crop model domain into real world crop domains. The method uses a semantically constrained GAN (generative adversarial network) to preserve the fruit position and geometry. We observe that a baseline CycleGAN method generates visually realistic target domain images but does not preserve fruit position information while our method maintains fruit positions well. Image generation results in vineyard grape day and night images show the visual outputs of our network are much better compared to a baseline network. Incremental training experiments in vineyard grape detection tasks show that the images generated from our method can significantly speed the domain adaption process, increase performance for a given number of labeled images (i.e. data efficiency), and decrease labeling requirements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge