Alex Olenskyj
Simultaneously Predicting Multiple Plant Traits from Multiple Sensors via Deformable CNN Regression
Dec 06, 2021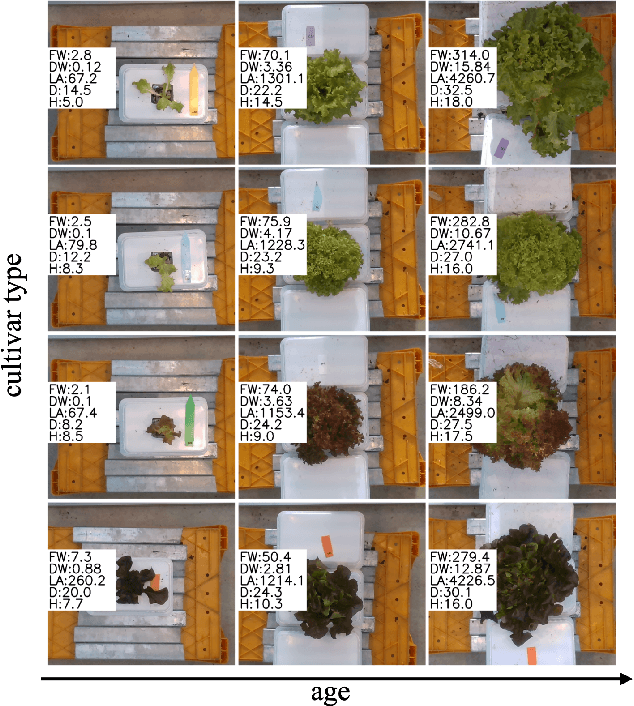
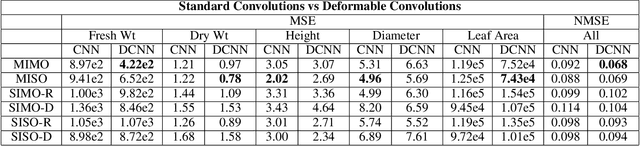
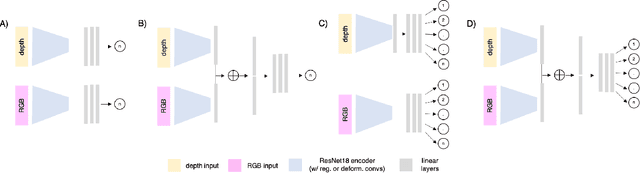
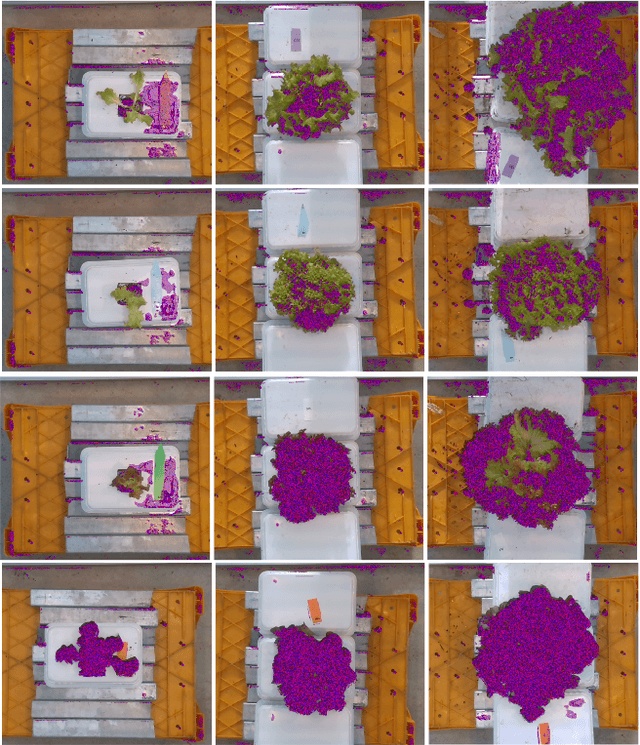
Abstract:Trait measurement is critical for the plant breeding and agricultural production pipeline. Typically, a suite of plant traits is measured using laborious manual measurements and then used to train and/or validate higher throughput trait estimation techniques. Here, we introduce a relatively simple convolutional neural network (CNN) model that accepts multiple sensor inputs and predicts multiple continuous trait outputs - i.e. a multi-input, multi-output CNN (MIMO-CNN). Further, we introduce deformable convolutional layers into this network architecture (MIMO-DCNN) to enable the model to adaptively adjust its receptive field, model complex variable geometric transformations in the data, and fine-tune the continuous trait outputs. We examine how the MIMO-CNN and MIMO-DCNN models perform on a multi-input (i.e. RGB and depth images), multi-trait output lettuce dataset from the 2021 Autonomous Greenhouse Challenge. Ablation studies were conducted to examine the effect of using single versus multiple inputs, and single versus multiple outputs. The MIMO-DCNN model resulted in a normalized mean squared error (NMSE) of 0.068 - a substantial improvement over the top 2021 leaderboard score of 0.081. Open-source code is provided.
Enlisting 3D Crop Models and GANs for More Data Efficient and Generalizable Fruit Detection
Aug 30, 2021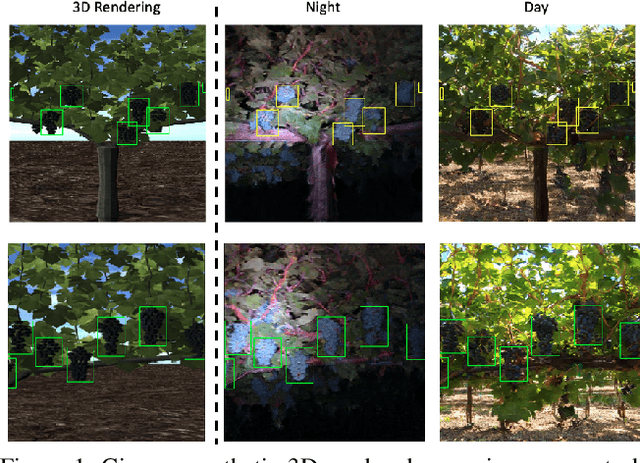
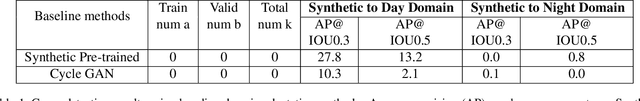

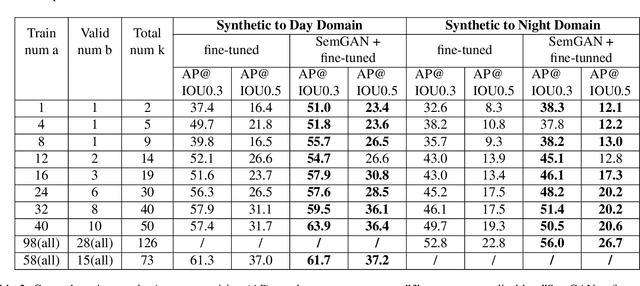
Abstract:Training real-world neural network models to achieve high performance and generalizability typically requires a substantial amount of labeled data, spanning a broad range of variation. This data-labeling process can be both labor and cost intensive. To achieve desirable predictive performance, a trained model is typically applied into a domain where the data distribution is similar to the training dataset. However, for many agricultural machine learning problems, training datasets are collected at a specific location, during a specific period in time of the growing season. Since agricultural systems exhibit substantial variability in terms of crop type, cultivar, management, seasonal growth dynamics, lighting condition, sensor type, etc, a model trained from one dataset often does not generalize well across domains. To enable more data efficient and generalizable neural network models in agriculture, we propose a method that generates photorealistic agricultural images from a synthetic 3D crop model domain into real world crop domains. The method uses a semantically constrained GAN (generative adversarial network) to preserve the fruit position and geometry. We observe that a baseline CycleGAN method generates visually realistic target domain images but does not preserve fruit position information while our method maintains fruit positions well. Image generation results in vineyard grape day and night images show the visual outputs of our network are much better compared to a baseline network. Incremental training experiments in vineyard grape detection tasks show that the images generated from our method can significantly speed the domain adaption process, increase performance for a given number of labeled images (i.e. data efficiency), and decrease labeling requirements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge