Lihua Qian
Diffusion Language Models Can Perform Many Tasks with Scaling and Instruction-Finetuning
Aug 25, 2023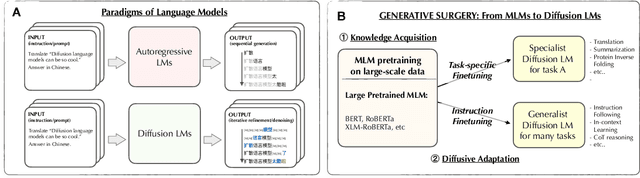
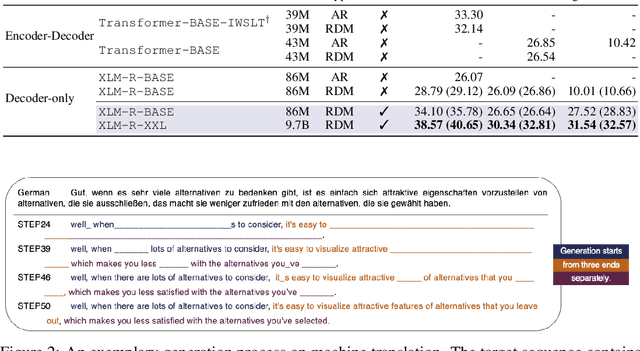

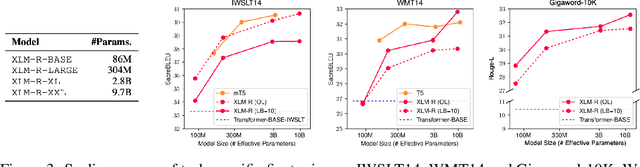
Abstract:The recent surge of generative AI has been fueled by the generative power of diffusion probabilistic models and the scalable capabilities of large language models. Despite their potential, it remains elusive whether diffusion language models can solve general language tasks comparable to their autoregressive counterparts. This paper demonstrates that scaling diffusion models w.r.t. data, sizes, and tasks can effectively make them strong language learners. We build competent diffusion language models at scale by first acquiring knowledge from massive data via masked language modeling pretraining thanks to their intrinsic connections. We then reprogram pretrained masked language models into diffusion language models via diffusive adaptation, wherein task-specific finetuning and instruction finetuning are explored to unlock their versatility in solving general language tasks. Experiments show that scaling diffusion language models consistently improves performance across downstream language tasks. We further discover that instruction finetuning can elicit zero-shot and few-shot in-context learning abilities that help tackle many unseen tasks by following natural language instructions, and show promise in advanced and challenging abilities such as reasoning.
DINOISER: Diffused Conditional Sequence Learning by Manipulating Noises
Feb 20, 2023



Abstract:While diffusion models have achieved great success in generating continuous signals such as images and audio, it remains elusive for diffusion models in learning discrete sequence data like natural languages. Although recent advances circumvent this challenge of discreteness by embedding discrete tokens as continuous surrogates, they still fall short of satisfactory generation quality. To understand this, we first dive deep into the denoised training protocol of diffusion-based sequence generative models and determine their three severe problems, i.e., 1) failing to learn, 2) lack of scalability, and 3) neglecting source conditions. We argue that these problems can be boiled down to the pitfall of the not completely eliminated discreteness in the embedding space, and the scale of noises is decisive herein. In this paper, we introduce DINOISER to facilitate diffusion models for sequence generation by manipulating noises. We propose to adaptively determine the range of sampled noise scales for counter-discreteness training; and encourage the proposed diffused sequence learner to leverage source conditions with amplified noise scales during inference. Experiments show that DINOISER enables consistent improvement over the baselines of previous diffusion-based sequence generative models on several conditional sequence modeling benchmarks thanks to both effective training and inference strategies. Analyses further verify that DINOISER can make better use of source conditions to govern its generative process.
Diff-Glat: Diffusion Glancing Transformer for Parallel Sequence to Sequence Learning
Dec 20, 2022



Abstract:For sequence generation, both autoregressive models and non-autoregressive models have been developed in recent years. Autoregressive models can achieve high generation quality, but the sequential decoding scheme causes slow decoding speed. Non-autoregressive models accelerate the inference speed with parallel decoding, while their generation quality still needs to be improved due to the difficulty of modeling multi-modalities in data. To address the multi-modality issue, we propose Diff-Glat, a non-autoregressive model featured with a modality diffusion process and residual glancing training. The modality diffusion process decomposes the modalities and reduces the modalities to learn for each transition. And the residual glancing sampling further smooths the modality learning procedures. Experiments demonstrate that, without using knowledge distillation data, Diff-Glat can achieve superior performance in both decoding efficiency and accuracy compared with the autoregressive Transformer.
$\textit{latent}$-GLAT: Glancing at Latent Variables for Parallel Text Generation
Apr 05, 2022



Abstract:Recently, parallel text generation has received widespread attention due to its success in generation efficiency. Although many advanced techniques are proposed to improve its generation quality, they still need the help of an autoregressive model for training to overcome the one-to-many multi-modal phenomenon in the dataset, limiting their applications. In this paper, we propose $\textit{latent}$-GLAT, which employs the discrete latent variables to capture word categorical information and invoke an advanced curriculum learning technique, alleviating the multi-modality problem. Experiment results show that our method outperforms strong baselines without the help of an autoregressive model, which further broadens the application scenarios of the parallel decoding paradigm.
The Volctrans GLAT System: Non-autoregressive Translation Meets WMT21
Sep 24, 2021



Abstract:This paper describes the Volctrans' submission to the WMT21 news translation shared task for German->English translation. We build a parallel (i.e., non-autoregressive) translation system using the Glancing Transformer, which enables fast and accurate parallel decoding in contrast to the currently prevailing autoregressive models. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first parallel translation system that can be scaled to such a practical scenario like WMT competition. More importantly, our parallel translation system achieves the best BLEU score (35.0) on German->English translation task, outperforming all strong autoregressive counterparts.
Glancing Transformer for Non-Autoregressive Neural Machine Translation
Aug 18, 2020



Abstract:Non-autoregressive neural machine translation achieves remarkable inference acceleration compared to autoregressive models. However, current non-autoregressive models still fall behind their autoregressive counterparts in prediction accuracy. We attribute the accuracy gaps to two disadvantages of non-autoregressive models: a) learning simultaneous generation under the overly strong conditional independence assumption; b) lacking explicit target language modeling. In this paper, we propose Glancing Transformer (GLAT) to address the above disadvantages, which reduces the difficulty of learning simultaneous generation and introduces explicit target language modeling in the non-autoregressive setting at the same time. Experiments on several benchmarks demonstrate that our approach significantly improves the accuracy of non-autoregressive models without sacrificing any inference efficiency. In particular, GLAT achieves 30.91 BLEU on WMT 2014 German-English, which narrows the gap between autoregressive models and non-autoregressive models to less than 0.5 BLEU score.
QA4IE: A Question Answering based Framework for Information Extraction
Apr 10, 2018



Abstract:Information Extraction (IE) refers to automatically extracting structured relation tuples from unstructured texts. Common IE solutions, including Relation Extraction (RE) and open IE systems, can hardly handle cross-sentence tuples, and are severely restricted by limited relation types as well as informal relation specifications (e.g., free-text based relation tuples). In order to overcome these weaknesses, we propose a novel IE framework named QA4IE, which leverages the flexible question answering (QA) approaches to produce high quality relation triples across sentences. Based on the framework, we develop a large IE benchmark with high quality human evaluation. This benchmark contains 293K documents, 2M golden relation triples, and 636 relation types. We compare our system with some IE baselines on our benchmark and the results show that our system achieves great improvements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge