Kungang Li
Decoupled Entity Representation Learning for Pinterest Ads Ranking
Sep 04, 2025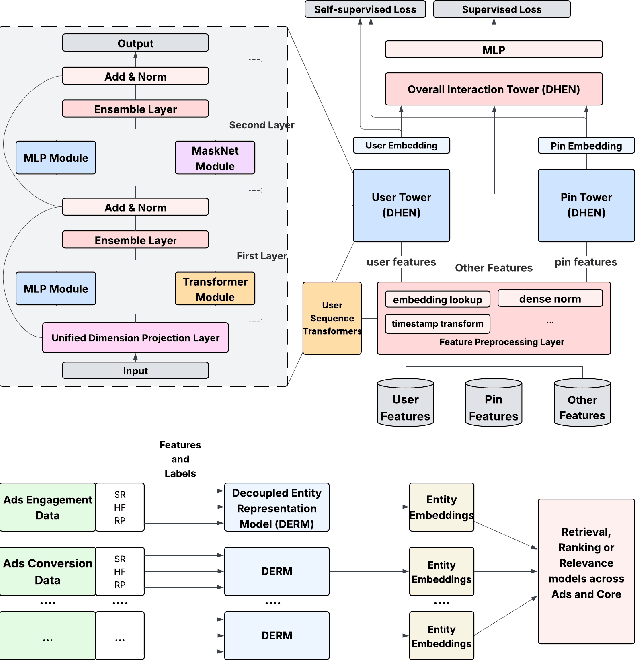



Abstract:In this paper, we introduce a novel framework following an upstream-downstream paradigm to construct user and item (Pin) embeddings from diverse data sources, which are essential for Pinterest to deliver personalized Pins and ads effectively. Our upstream models are trained on extensive data sources featuring varied signals, utilizing complex architectures to capture intricate relationships between users and Pins on Pinterest. To ensure scalability of the upstream models, entity embeddings are learned, and regularly refreshed, rather than real-time computation, allowing for asynchronous interaction between the upstream and downstream models. These embeddings are then integrated as input features in numerous downstream tasks, including ad retrieval and ranking models for CTR and CVR predictions. We demonstrate that our framework achieves notable performance improvements in both offline and online settings across various downstream tasks. This framework has been deployed in Pinterest's production ad ranking systems, resulting in significant gains in online metrics.
Privacy Preserving Conversion Modeling in Data Clean Room
May 20, 2025Abstract:In the realm of online advertising, accurately predicting the conversion rate (CVR) is crucial for enhancing advertising efficiency and user satisfaction. This paper addresses the challenge of CVR prediction while adhering to user privacy preferences and advertiser requirements. Traditional methods face obstacles such as the reluctance of advertisers to share sensitive conversion data and the limitations of model training in secure environments like data clean rooms. We propose a novel model training framework that enables collaborative model training without sharing sample-level gradients with the advertising platform. Our approach introduces several innovative components: (1) utilizing batch-level aggregated gradients instead of sample-level gradients to minimize privacy risks; (2) applying adapter-based parameter-efficient fine-tuning and gradient compression to reduce communication costs; and (3) employing de-biasing techniques to train the model under label differential privacy, thereby maintaining accuracy despite privacy-enhanced label perturbations. Our experimental results, conducted on industrial datasets, demonstrate that our method achieves competitive ROCAUC performance while significantly decreasing communication overhead and complying with both advertiser privacy requirements and user privacy choices. This framework establishes a new standard for privacy-preserving, high-performance CVR prediction in the digital advertising landscape.
The Evolution of Embedding Table Optimization and Multi-Epoch Training in Pinterest Ads Conversion
May 08, 2025Abstract:Deep learning for conversion prediction has found widespread applications in online advertising. These models have become more complex as they are trained to jointly predict multiple objectives such as click, add-to-cart, checkout and other conversion types. Additionally, the capacity and performance of these models can often be increased with the use of embedding tables that encode high cardinality categorical features such as advertiser, user, campaign, and product identifiers (IDs). These embedding tables can be pre-trained, but also learned end-to-end jointly with the model to directly optimize the model objectives. Training these large tables is challenging due to: gradient sparsity, the high cardinality of the categorical features, the non-uniform distribution of IDs and the very high label sparsity. These issues make training prone to both slow convergence and overfitting after the first epoch. Previous works addressed the multi-epoch overfitting issue by using: stronger feature hashing to reduce cardinality, filtering of low frequency IDs, regularization of the embedding tables, re-initialization of the embedding tables after each epoch, etc. Some of these techniques reduce overfitting at the expense of reduced model performance if used too aggressively. In this paper, we share key learnings from the development of embedding table optimization and multi-epoch training in Pinterest Ads Conversion models. We showcase how our Sparse Optimizer speeds up convergence, and how multi-epoch overfitting varies in severity between different objectives in a multi-task model depending on label sparsity. We propose a new approach to deal with multi-epoch overfitting: the use of a frequency-adaptive learning rate on the embedding tables and compare it to embedding re-initialization. We evaluate both methods offline using an industrial large-scale production dataset.
On the Practice of Deep Hierarchical Ensemble Network for Ad Conversion Rate Prediction
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:The predictions of click through rate (CTR) and conversion rate (CVR) play a crucial role in the success of ad-recommendation systems. A Deep Hierarchical Ensemble Network (DHEN) has been proposed to integrate multiple feature crossing modules and has achieved great success in CTR prediction. However, its performance for CVR prediction is unclear in the conversion ads setting, where an ad bids for the probability of a user's off-site actions on a third party website or app, including purchase, add to cart, sign up, etc. A few challenges in DHEN: 1) What feature-crossing modules (MLP, DCN, Transformer, to name a few) should be included in DHEN? 2) How deep and wide should DHEN be to achieve the best trade-off between efficiency and efficacy? 3) What hyper-parameters to choose in each feature-crossing module? Orthogonal to the model architecture, the input personalization features also significantly impact model performance with a high degree of freedom. In this paper, we attack this problem and present our contributions biased to the applied data science side, including: First, we propose a multitask learning framework with DHEN as the single backbone model architecture to predict all CVR tasks, with a detailed study on how to make DHEN work effectively in practice; Second, we build both on-site real-time user behavior sequences and off-site conversion event sequences for CVR prediction purposes, and conduct ablation study on its importance; Last but not least, we propose a self-supervised auxiliary loss to predict future actions in the input sequence, to help resolve the label sparseness issue in CVR prediction. Our method achieves state-of-the-art performance compared to previous single feature crossing modules with pre-trained user personalization features.
Detection and Attention: Diagnosing Pulmonary Lung Cancer from CT by Imitating Physicians
Dec 14, 2017
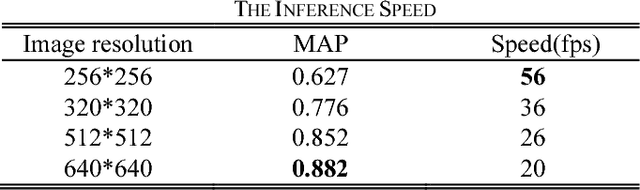
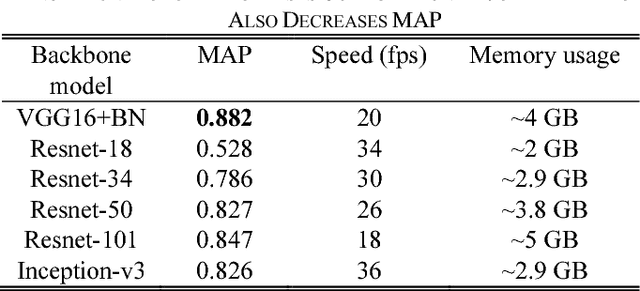
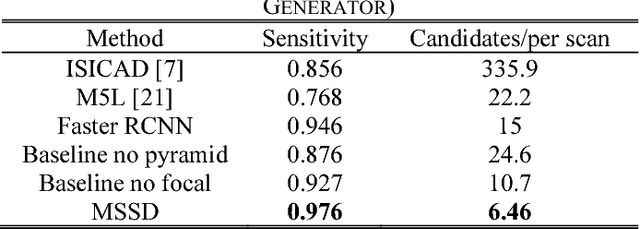
Abstract:This paper proposes a novel and efficient method to build a Computer-Aided Diagnoses (CAD) system for lung nodule detection based on Computed Tomography (CT). This task was treated as an Object Detection on Video (VID) problem by imitating how a radiologist reads CT scans. A lung nodule detector was trained to automatically learn nodule features from still images to detect lung nodule candidates with both high recall and accuracy. Unlike previous work which used 3-dimensional information around the nodule to reduce false positives, we propose two simple but efficient methods, Multi-slice propagation (MSP) and Motionless-guide suppression (MLGS), which analyze sequence information of CT scans to reduce false negatives and suppress false positives. We evaluated our method in open-source LUNA16 dataset which contains 888 CT scans, and obtained state-of-the-art result (Free-Response Receiver Operating Characteristic score of 0.892) with detection speed (end to end within 20 seconds per patient on a single NVidia GTX 1080) much higher than existing methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge